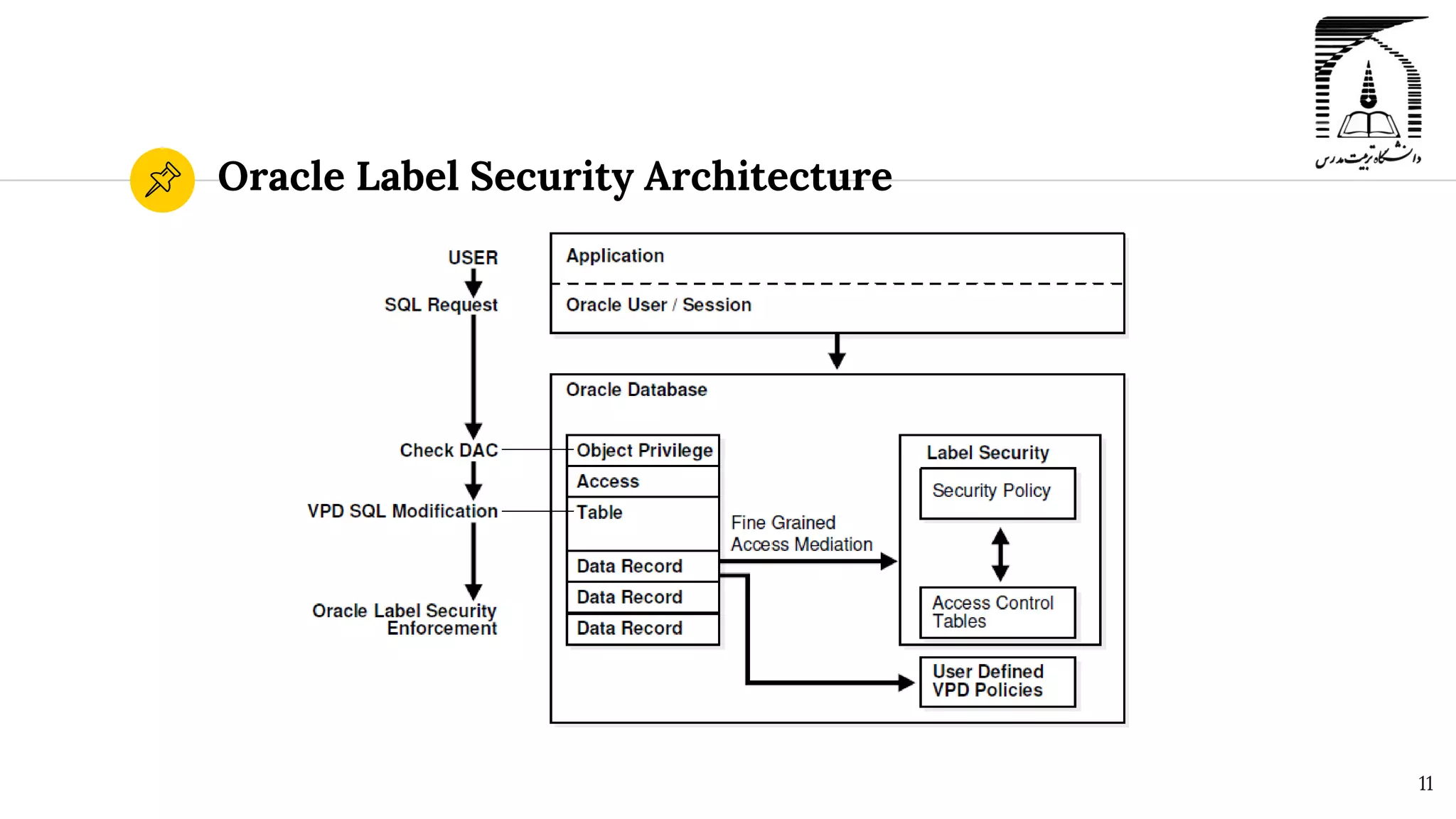
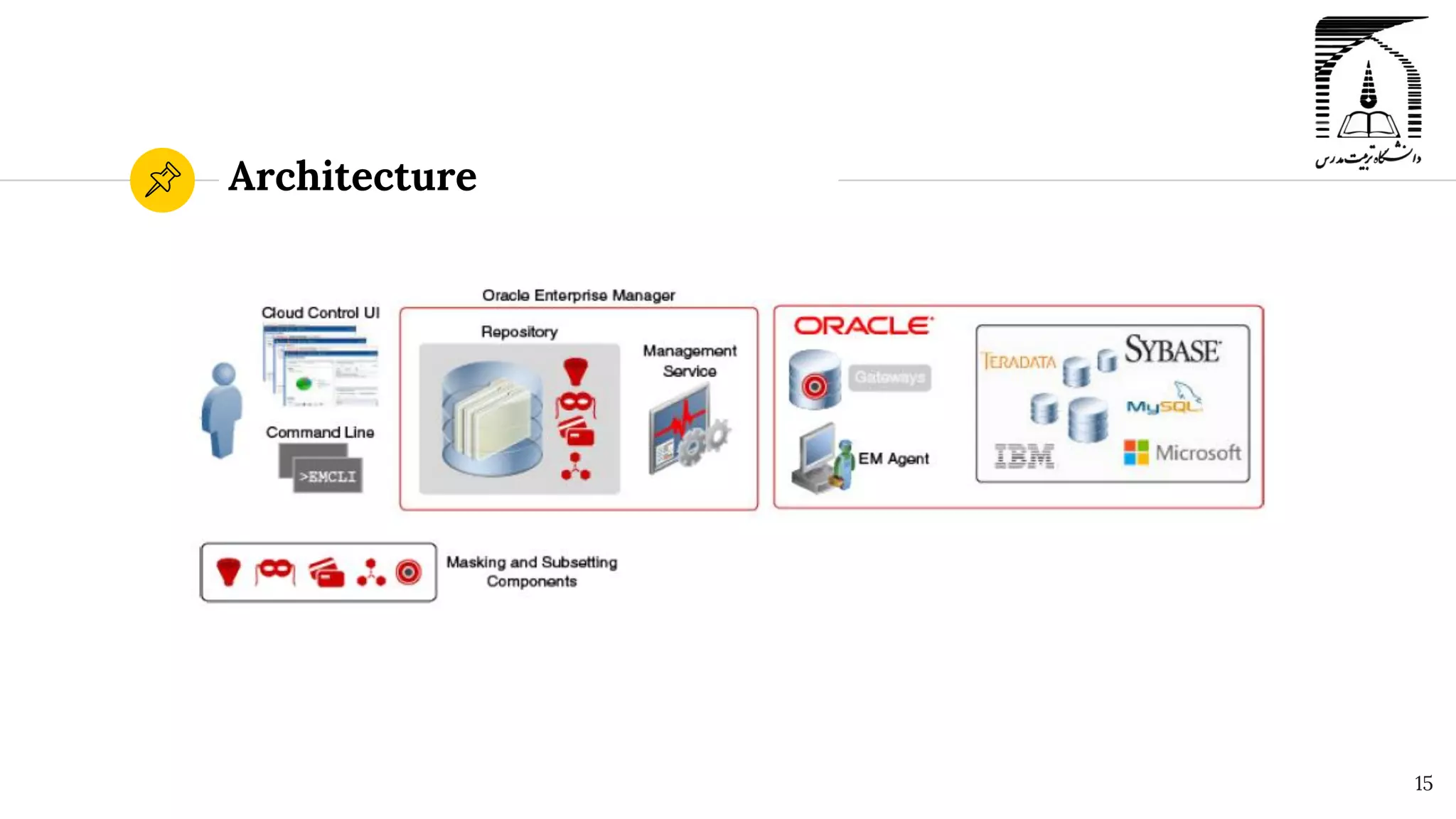
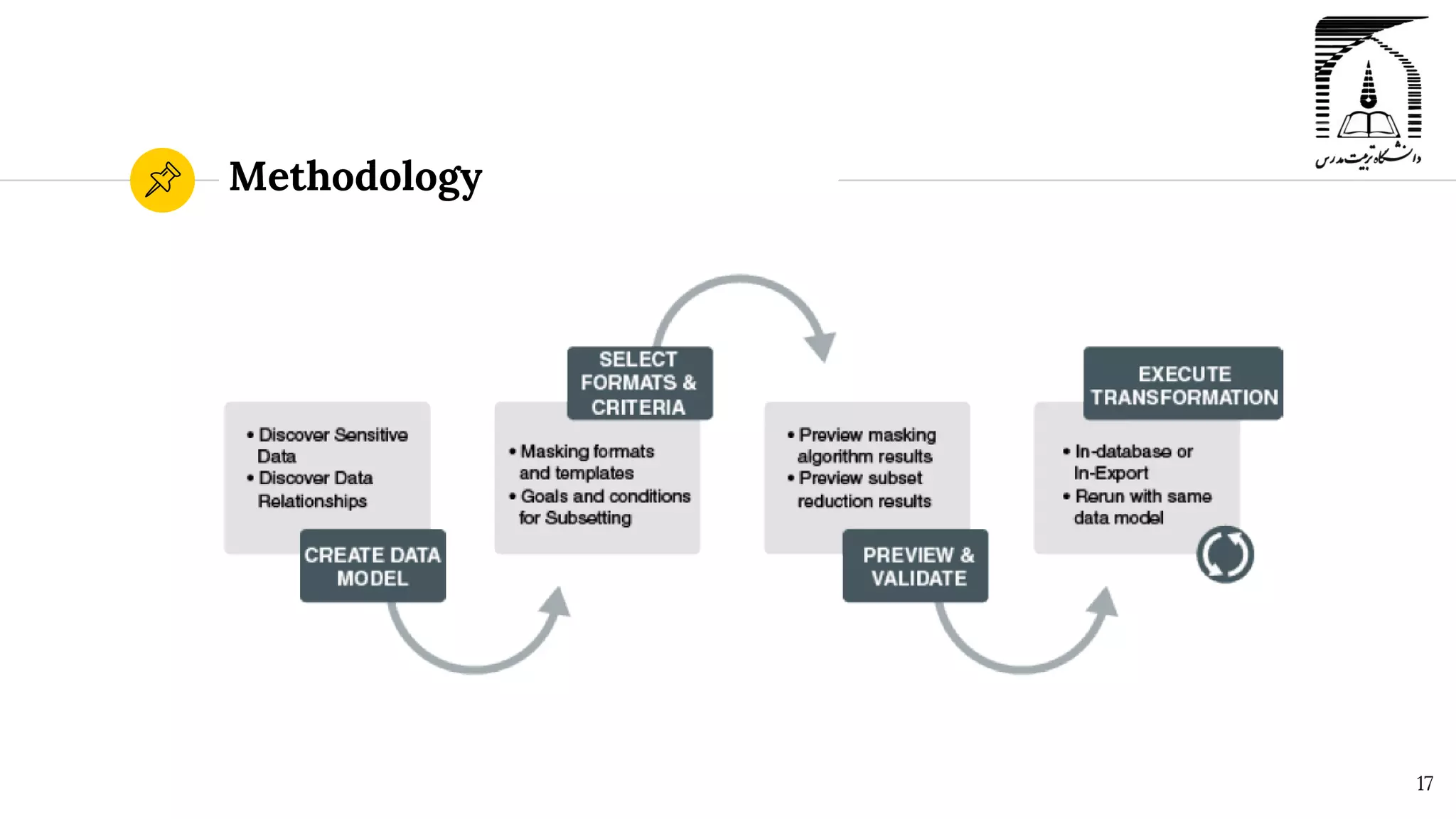
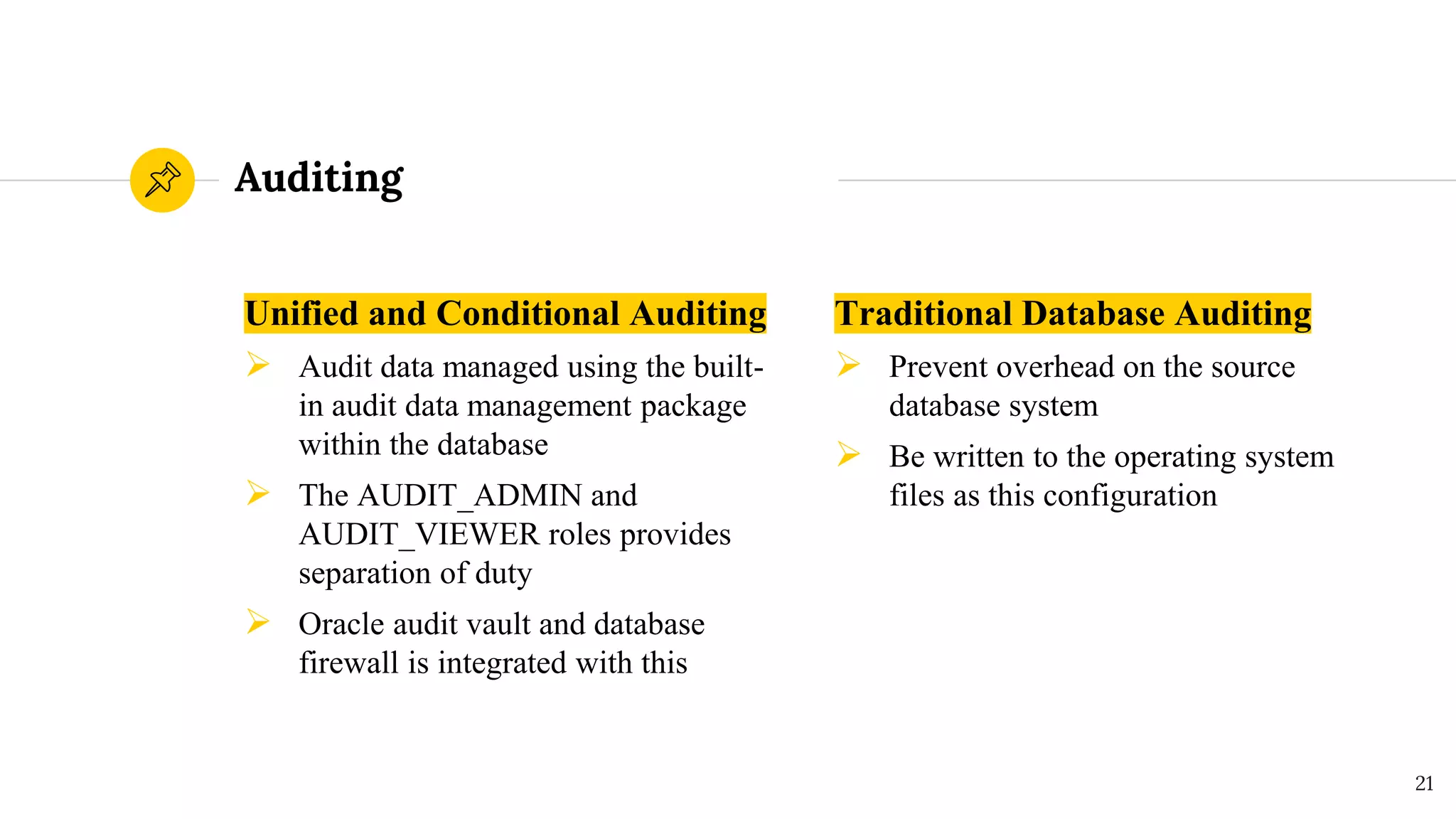
The document discusses security in Oracle databases. It covers several topics: Oracle Label Security which allows row-level access control based on user privileges; data masking and subsetting tools for replacing sensitive data; and auditing of database activities for accountability, investigation, and problem detection. Oracle provides various security components like encryption, redaction, key vaults, and firewalls to control access and monitor use of sensitive information in the database.