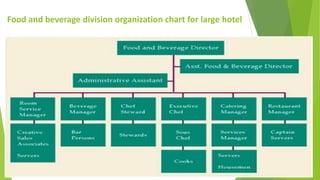
The document discusses various departments in hotel operations including security, guest services, food and beverage, housekeeping, catering, and more. It describes the roles and responsibilities of different positions like the director of food and beverage who oversees budgets, staffing, and profitability. It also outlines the types of restaurants a hotel may have and different food and beverage roles such as chefs, bar managers, and stewards who maintain cleanliness.