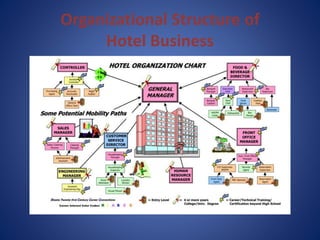
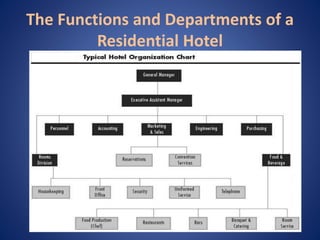
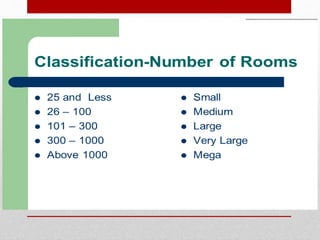
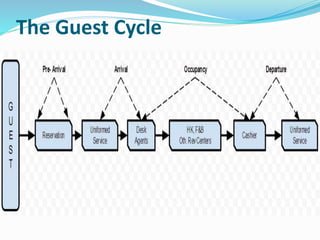
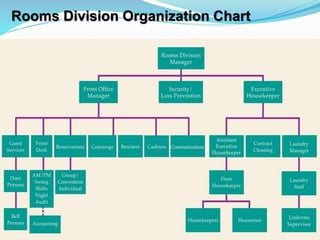
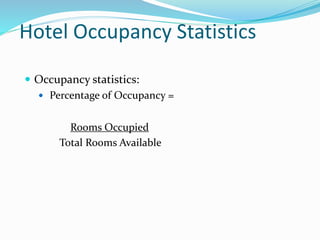
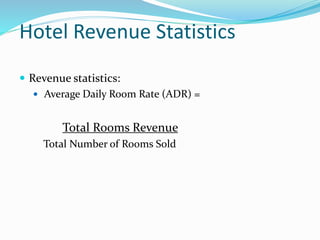
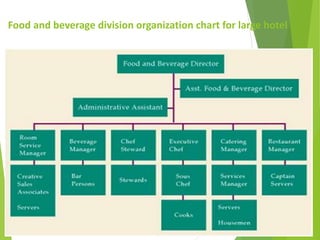
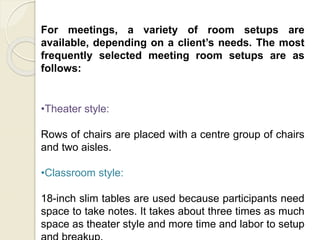
The document provides an overview of the history and evolution of hotels. It begins with the origins of hotels in ancient Roman bath houses and medieval inns. Over time, hotels grew in size and amenities, with 19th century hotels becoming more luxurious. The document then discusses future hotel trends like larger bathrooms, smartphone-controlled rooms, and a focus on locally-sourced food. It also outlines the organizational structure and key departments of hotel operations, including rooms, food and beverage, sales and marketing, and engineering.