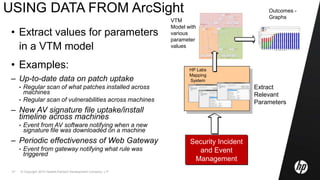
The document details research and development activities at HP Labs focused on cloud and security, specifically in the realms of security analytics and intelligence as a service. It examines challenges in security management, the integration of scientific knowledge into security analytics, and various models for vulnerability and threat management. Additionally, it discusses the implications of these findings for improving security risk assessments and management processes within organizations.