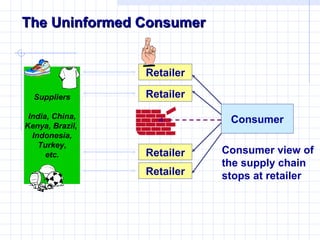
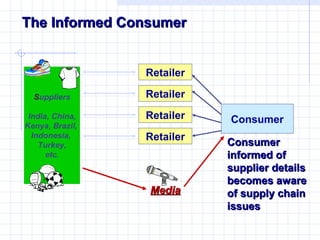
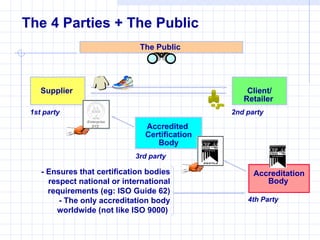
SA 8000 is a social accountability standard that was developed to allow companies to certify that they operate in accordance with international human rights and labor standards. It aims to ensure ethical sourcing and production through independent third-party audits and continuous improvement efforts. SA 8000 certification can benefit companies by improving their brand image, reducing risks, and increasing customer loyalty and access to international markets.