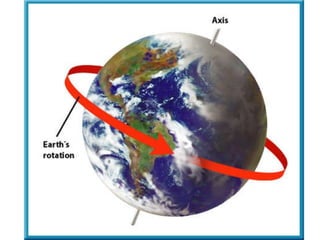
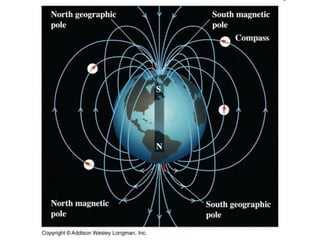
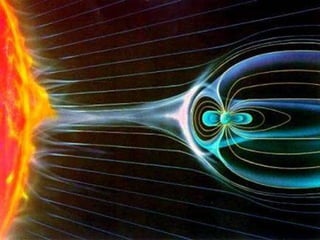
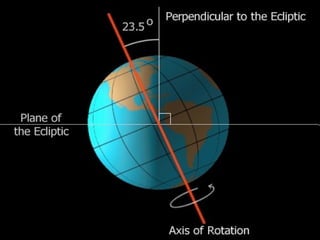
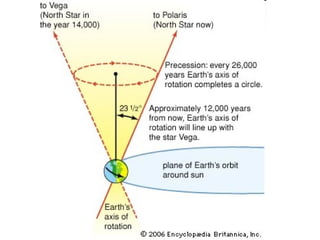
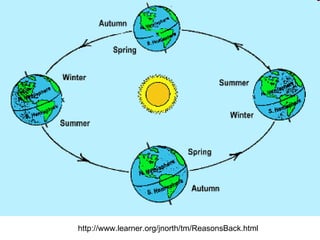
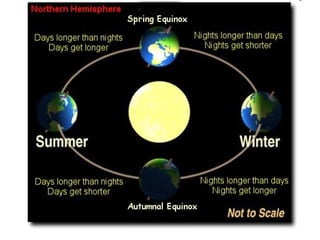
The document summarizes key concepts about the Earth's relationship to the sun and moon from a 6th grade science textbook. It discusses how ancient Greeks like Aristotle were able to determine the Earth was spherical by observing shadows on the moon. It also explains the Earth's axis of rotation, its tilted axis causing seasons, and defines solstices and equinoxes as the days when the sun is furthest or directly overhead at the equator.