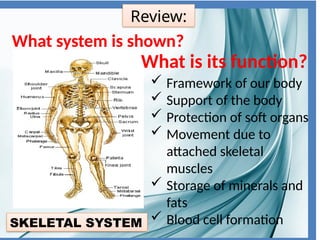
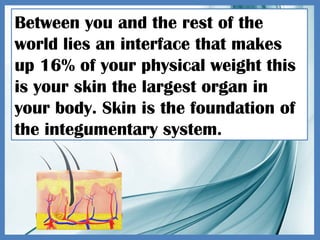
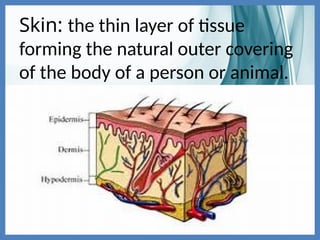
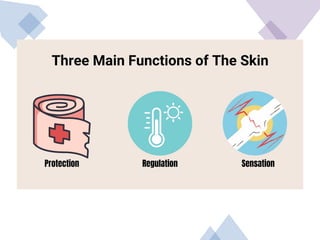
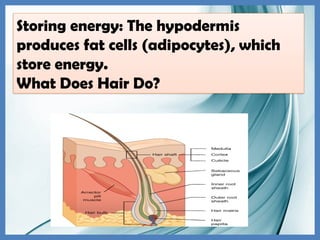
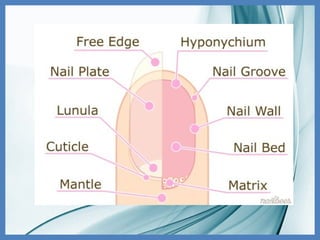
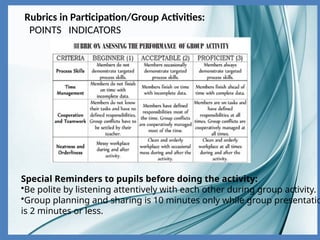
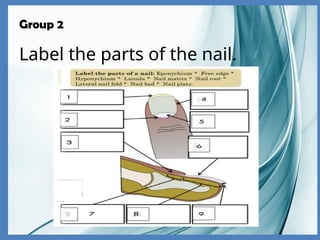
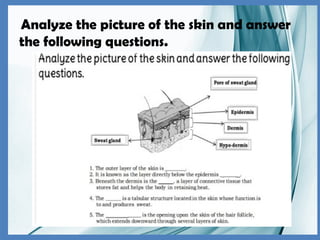
The integumentary system consists of the skin, hair, and nails, serving critical functions such as protecting internal organs, regulating temperature, and sensing environmental changes. The skin, the body's largest organ, is composed of multiple layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis, each playing vital roles in protection, moisture retention, and energy storage. Functions of the integumentary system include providing a barrier against pathogens, preventing dehydration, and facilitating temperature regulation.