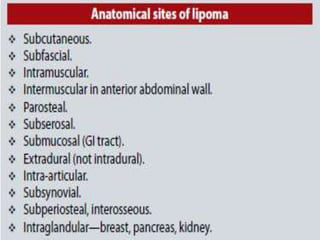
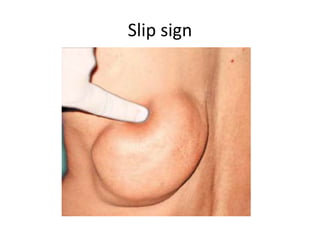
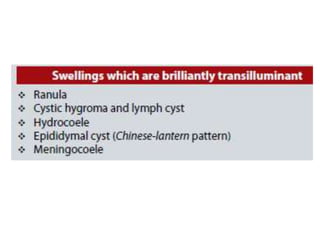
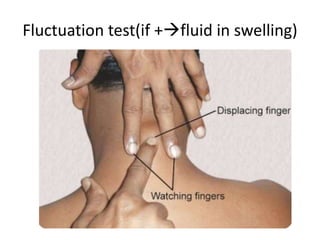
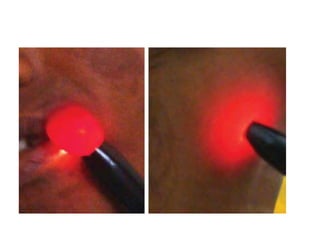
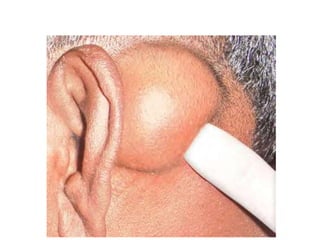
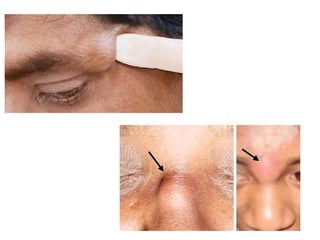
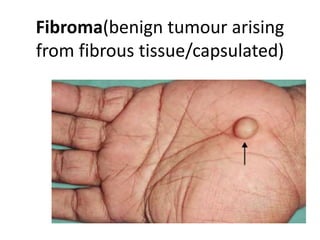
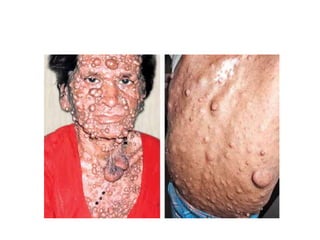
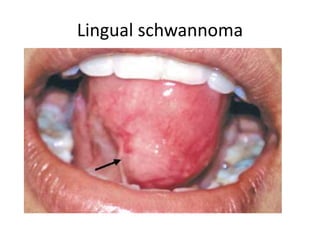
- Lipomas are the most common benign soft tissue tumors, occurring as localized or diffuse masses of fatty tissue that can develop anywhere on the body except the brain. Clinical features include a soft, lobular, movable mass that is non-tender and often fluctuant.
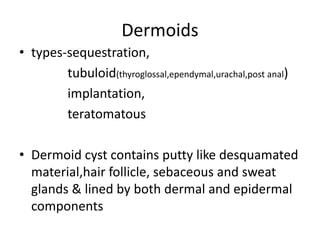
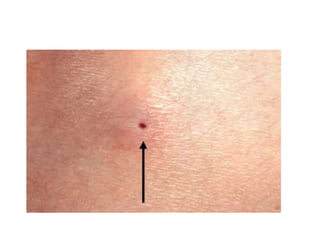
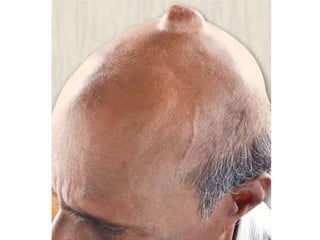
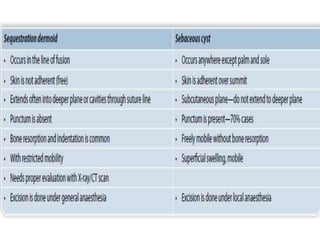
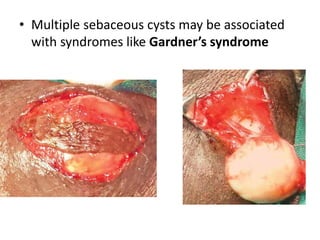
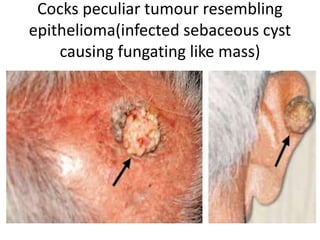
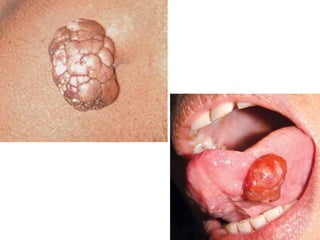
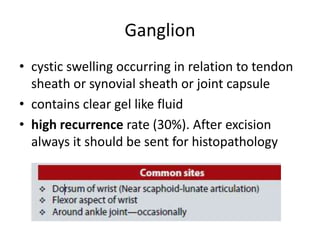
- Dermoid cysts contain tissues such as hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. Sebaceous cysts form due to blockage of sebaceous glands, containing a cheesy material within a cyst wall. Ganglions occur near tendons or joints and contain clear fluid. Proper diagnosis of soft tissue swellings requires determining their origin and type.