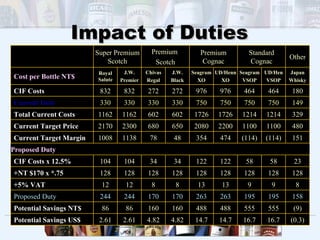
The document provides an analysis of Pernod Ricard's spirits portfolio and marketing strategy in Taiwan. It outlines key brands such as Chivas Regal, Martell cognac, and Royal Salute scotch. It then analyzes the Taiwanese market, noting opportunities and threats. Alternative strategies are evaluated, including distribution channels, pricing with duty changes, and promotional schemes. The marketing strategies section outlines plans for distribution, pricing, and promotional campaigns to introduce a new standard scotch product and target various consumer groups.