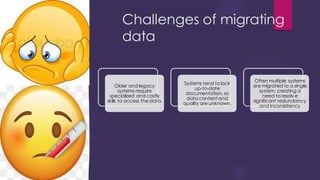
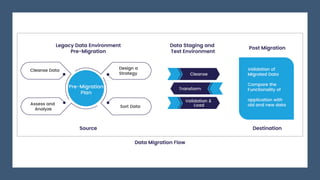
The document discusses data migration, which is defined as transferring data between different file formats, databases, or storage systems. It outlines requirements for data migration like ensuring data quality and type consistency. The types of data migration include application migration, cloud migration, and storage migration. The process involves pre-migration planning and assessment, data collection and cleansing, validation, and migration. Benefits are improved consistency and responsiveness, while challenges include dealing with legacy systems and resolving data redundancy across multiple sources. Careful planning is needed to avoid issues from unplanned migration.