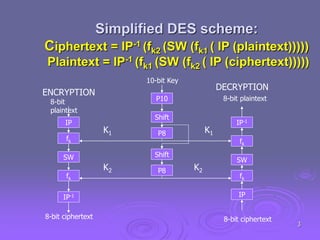
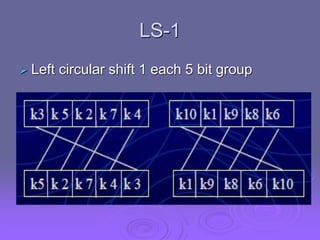
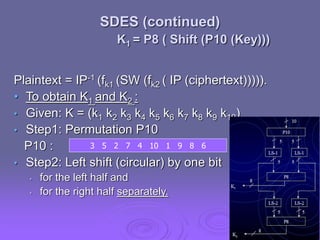
This document summarizes simplified DES (SDES), a simplified version of the Data Encryption Standard (DES) designed for educational purposes. SDES uses an 8-bit plaintext, 10-bit key, and 8-bit ciphertext. It has two rounds that each apply an initial permutation, complex 2-input function fk using a key, bit-switching, and inverse permutation. The function fk applies expansion/permutation, XOR with a key to generate left and right halves, S-box lookups, permutation, XOR, and switching input bits for the next round. Key generation applies permutations and shifts to the input key to derive two 8-bit subkeys for each round.