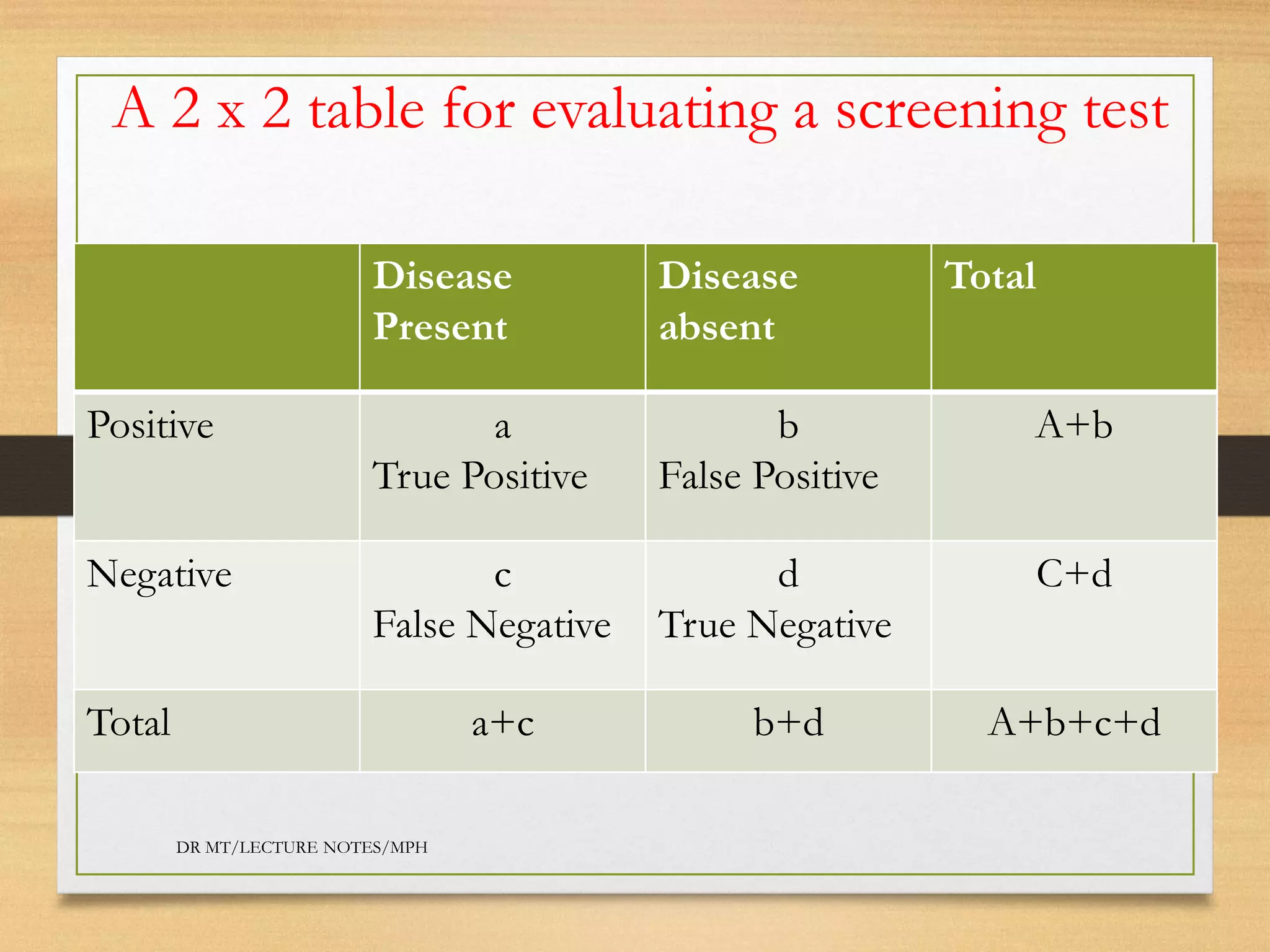
Screening tests are performed to identify diseases in asymptomatic individuals to improve outcomes. An ideal screening test is cheap, easy to use, reliable, and valid. Screening test accuracy is evaluated using a 2x2 table to calculate sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value. An example evaluates a diabetic retinopathy screening test and finds it has high sensitivity (96%) and specificity (95%) but low positive predictive value (70%), indicating many false positives.