Scope of Software Engineering
Software engineering is concerned with the systematic development, operation, and maintenance of software systems. Its scope covers:
Requirement Analysis & Specification: Identifying user needs and defining system requirements clearly.
Software Design: Converting requirements into well-structured architectural and detailed design.
Implementation & Coding: Writing programs in suitable programming languages with coding standards.
Testing & Validation: Ensuring the software works correctly and meets requirements.
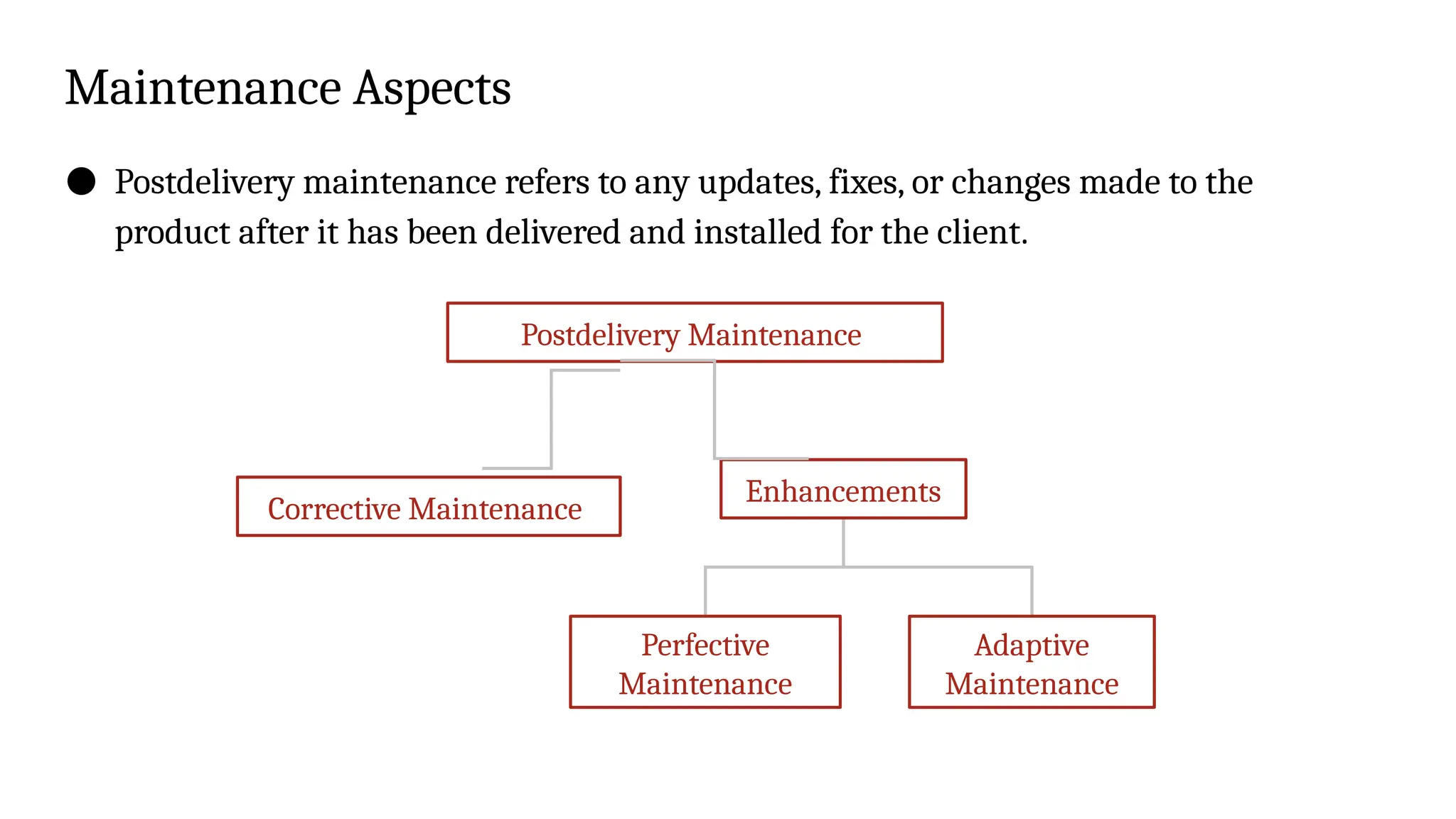
Deployment & Maintenance: Installing the software, providing updates, and fixing errors.
Project Management: Planning, scheduling, cost estimation, risk management, and quality assurance.
Process Models & Methodologies: Applying models like Waterfall, Agile, Spiral for development.
Software Tools & CASE, Using tools to automate design, coding, testing, and version control.
In summary, the scope of software engineering extends throughout the entire software life cycle, ensuring software is reliable, efficient, cost-effective, and user-friendly.