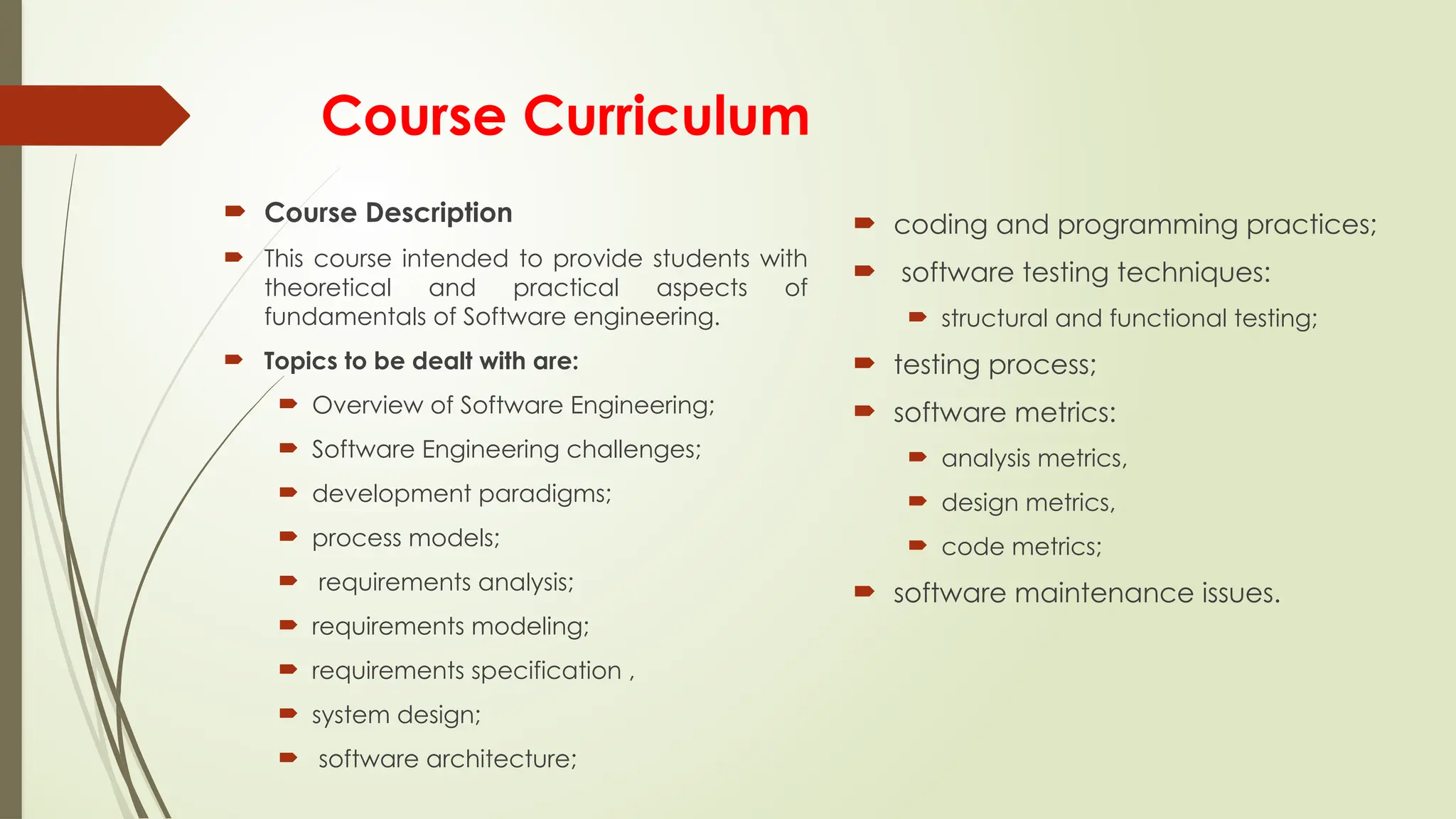
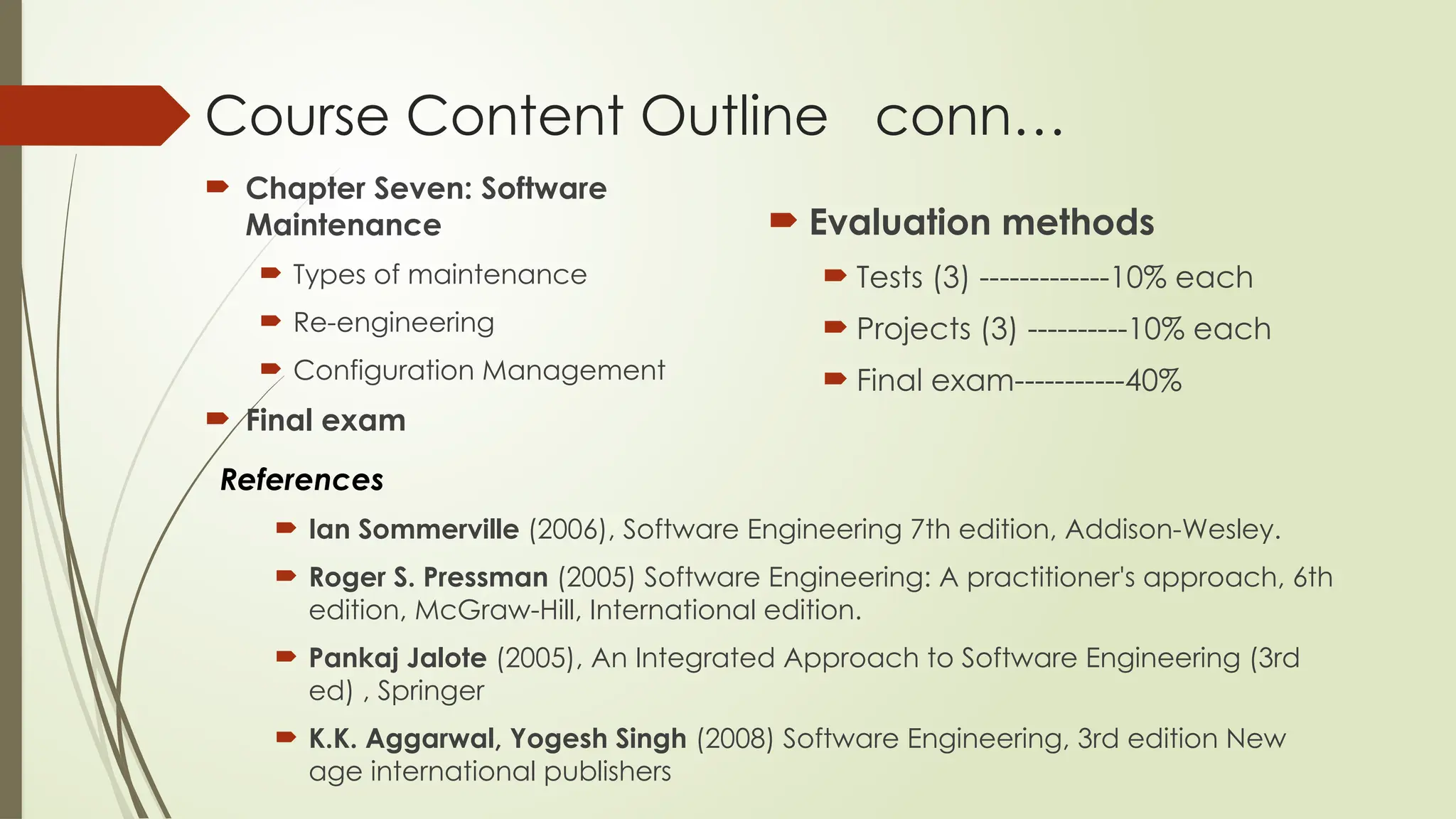
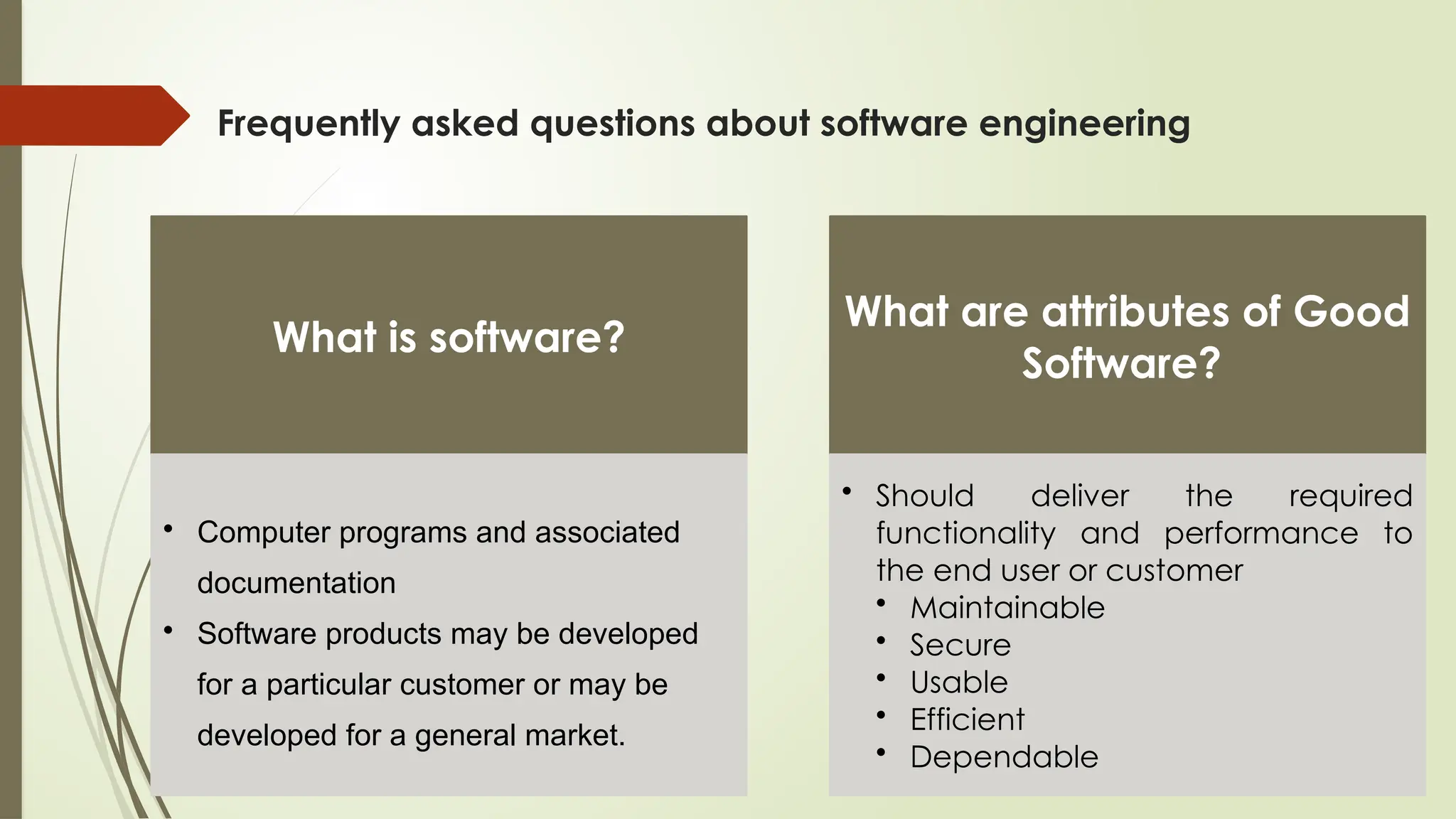
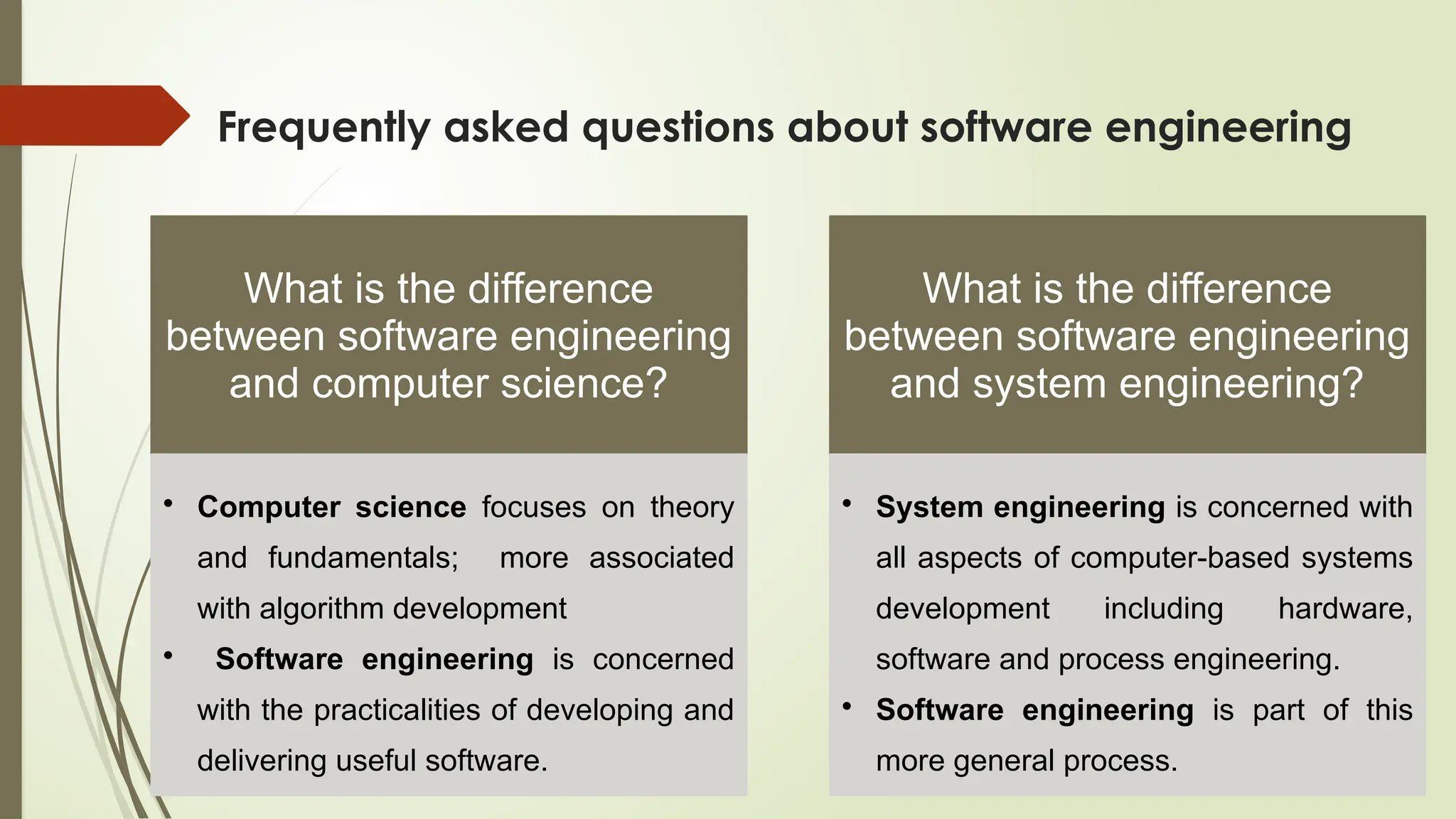
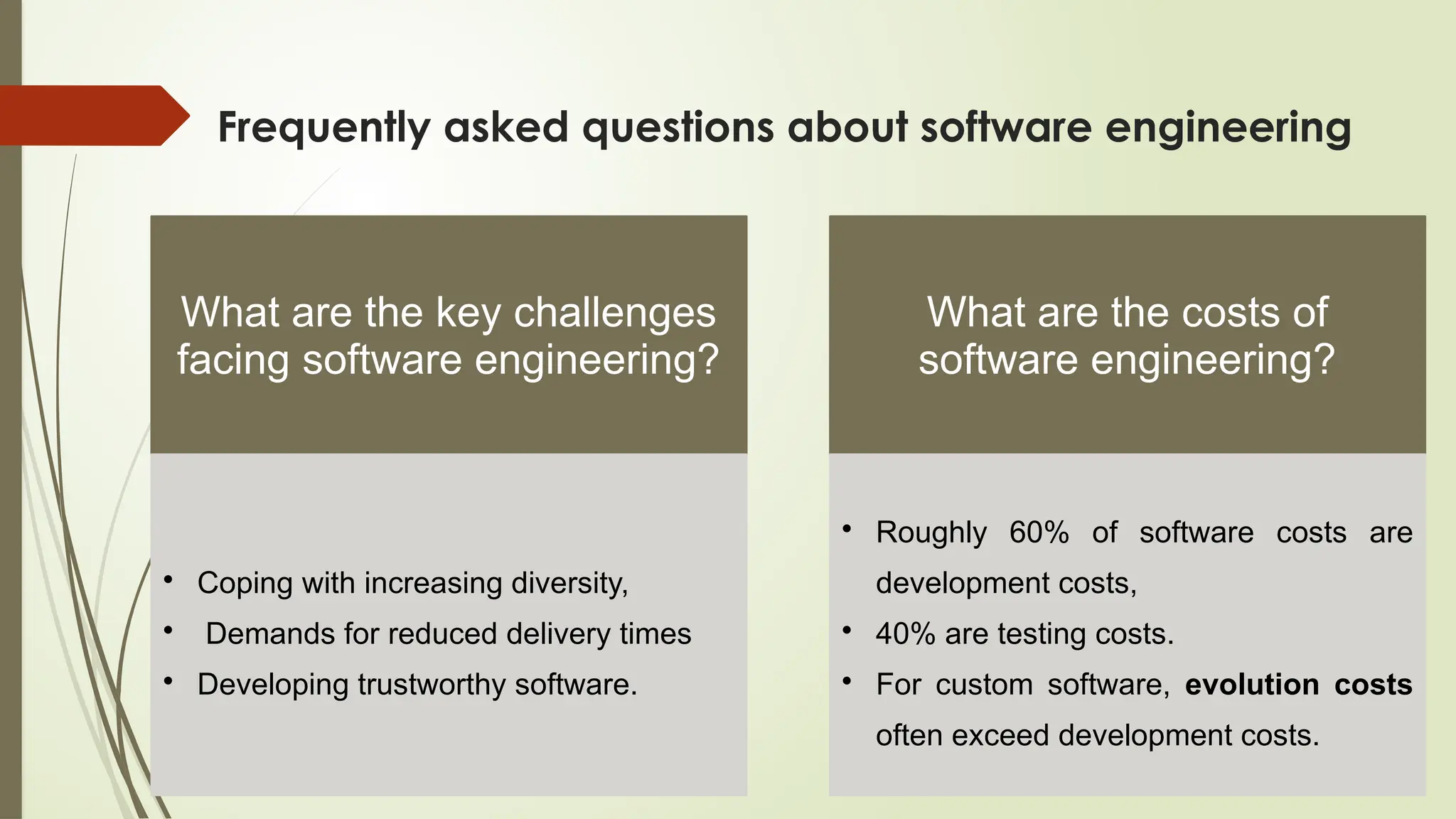
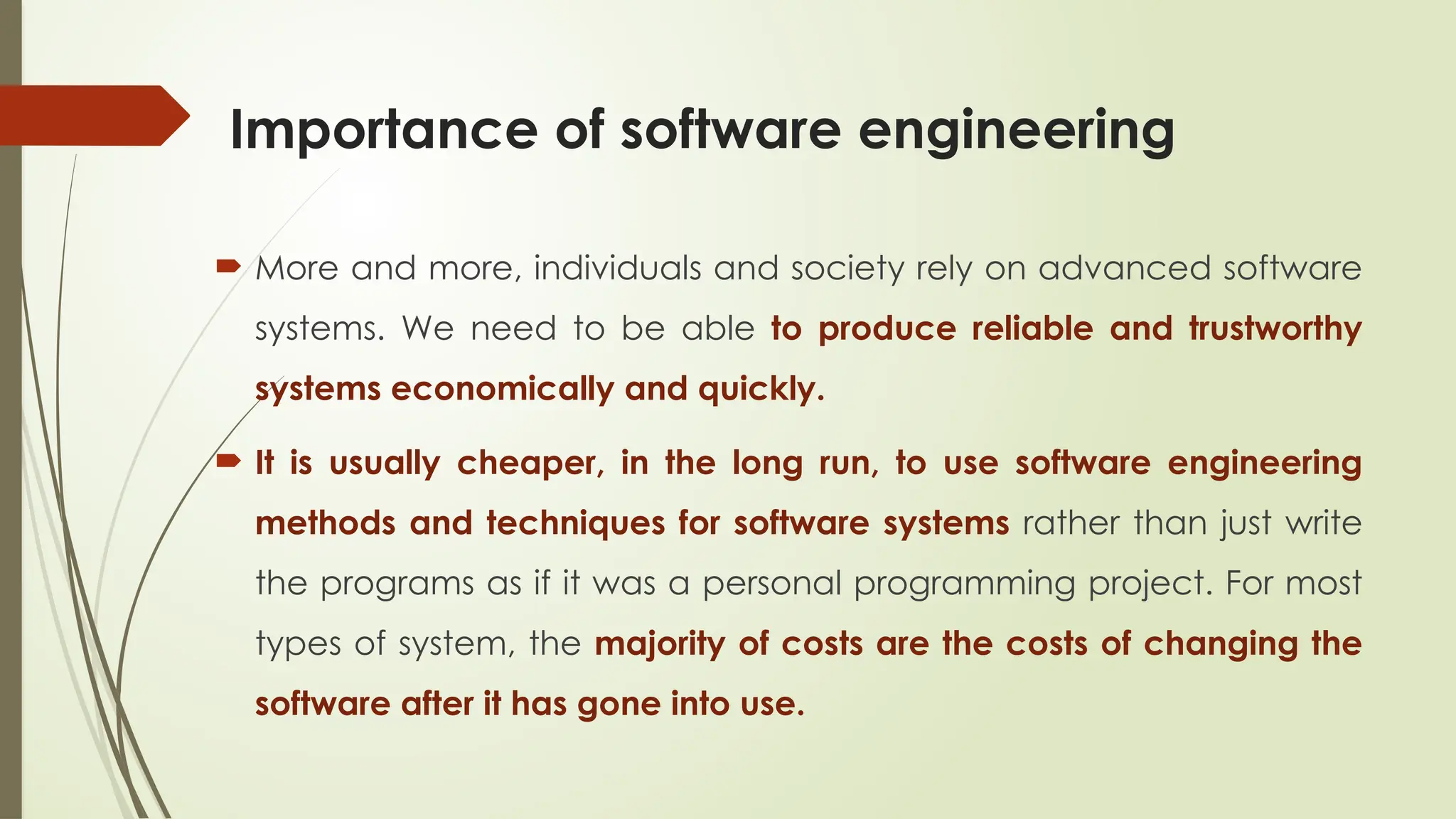
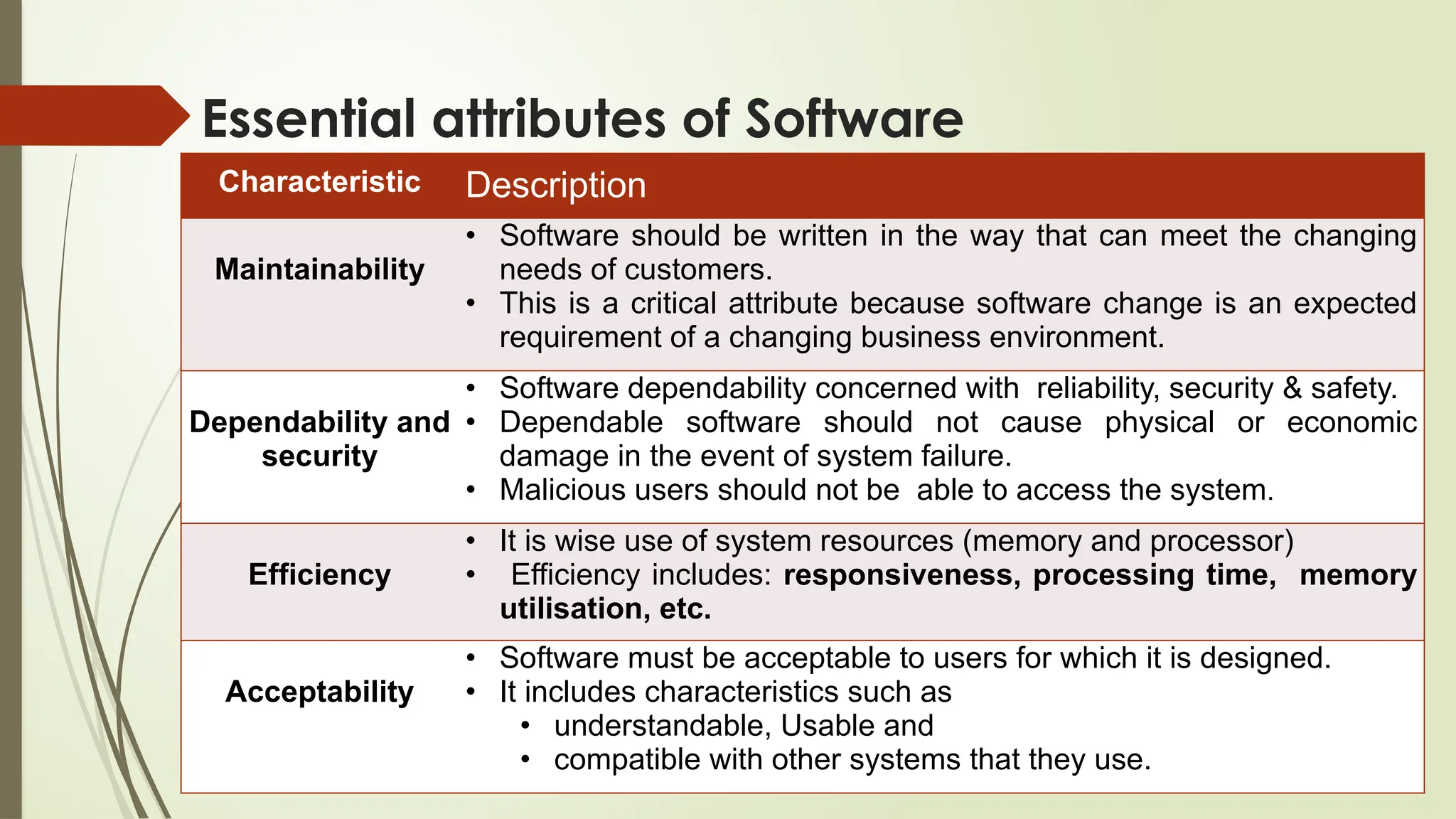
The document outlines a course on the fundamentals of software engineering, covering both theoretical and practical aspects. Key topics include software development processes, requirements analysis, system design, testing techniques, and software maintenance. It emphasizes the significance of software engineering in various sectors, the characteristics of software, and the importance of reliable and trustworthy systems.