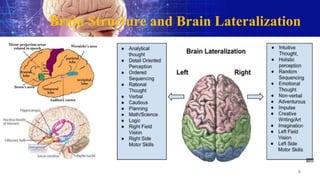
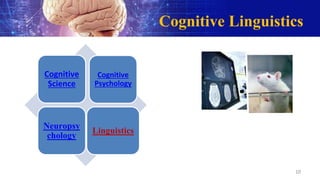
The document discusses various theories related to language learning and acquisition. It covers theories on the origin of language, including natural evolution, invention, and theories related to human communication sounds. It also discusses theories of language acquisition, including Plato's theory of innate knowledge, Descartes' theory of innate rationality and language, Locke's tabula rasa theory, Skinner's behaviorism theory, Chomsky's universal grammar theory, Schumann's acculturation model, and Krashen's monitor model. Finally, it discusses cognitive linguistics and theoretical linguistics frameworks like structuralism, functionalism, and formalism that relate to language.