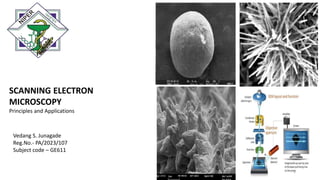
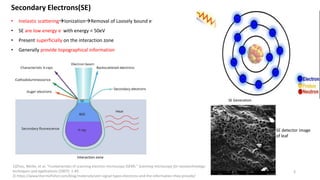
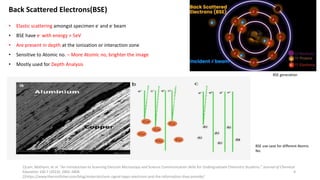
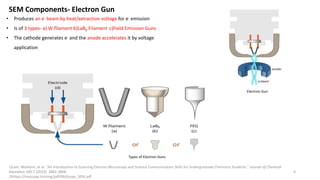
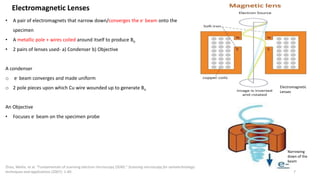
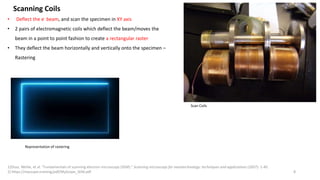
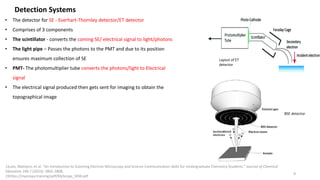
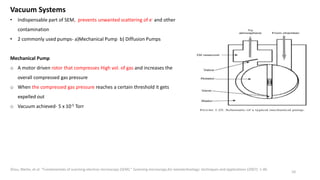
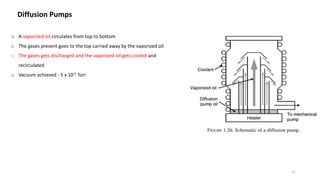
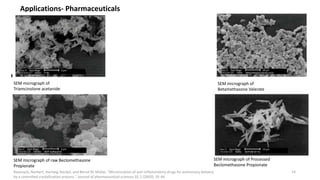
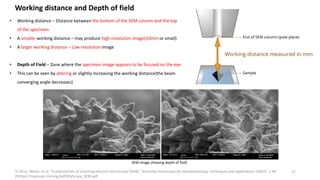
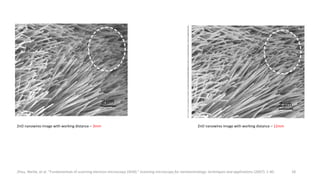
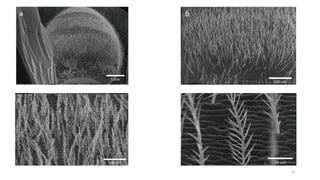
The document presents an overview of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), detailing the generation of secondary and back-scattered electrons, and the components involved, including electron guns, electromagnetic lenses, and detection systems. It outlines key applications in biological sciences, geology, and pharmaceuticals, as well as factors affecting image quality. Additionally, it discusses specimen preparation techniques to enhance imaging results.