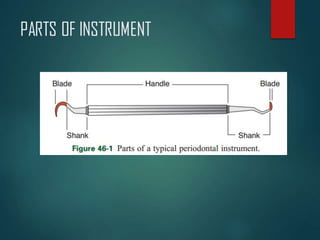
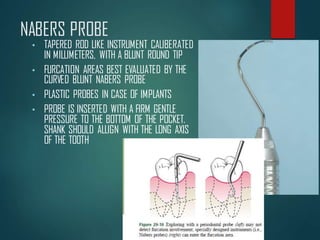
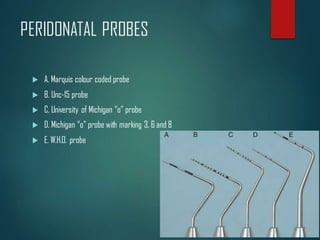
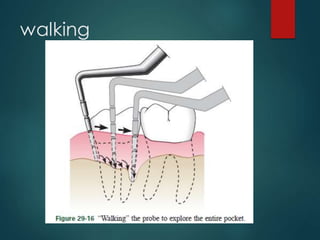
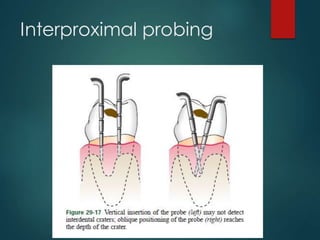
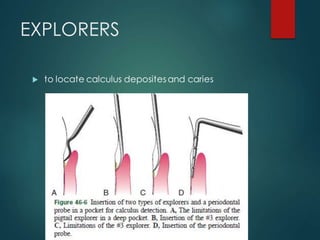
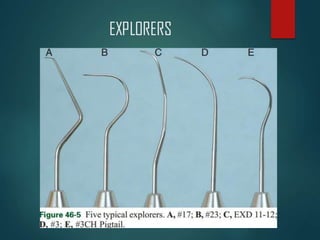
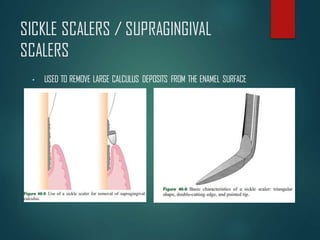
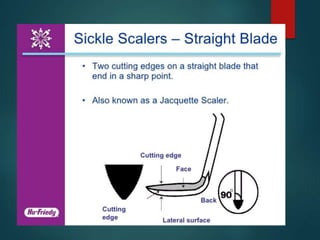
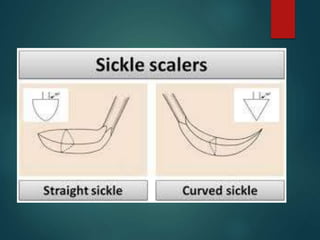
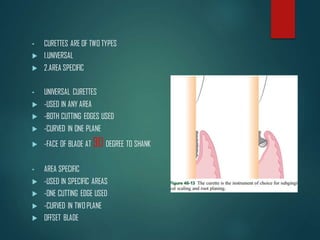
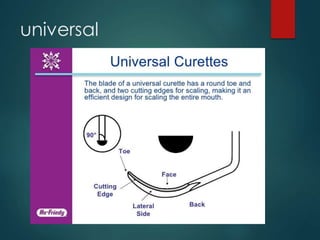
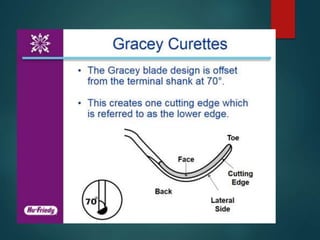
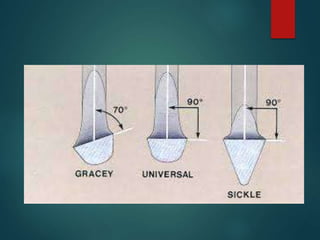
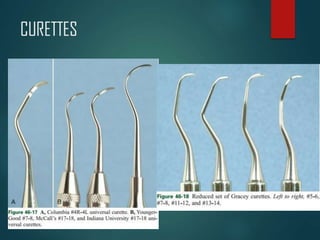
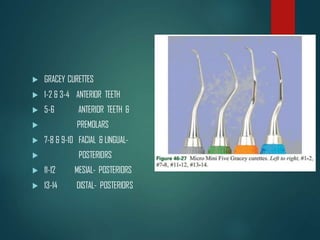
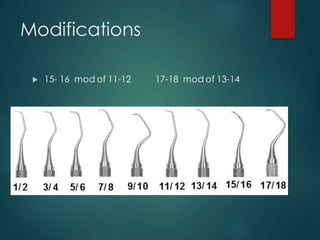
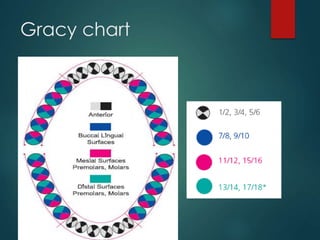
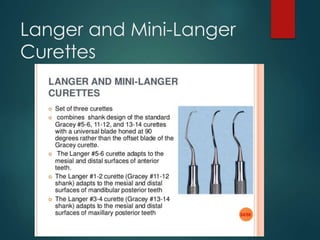
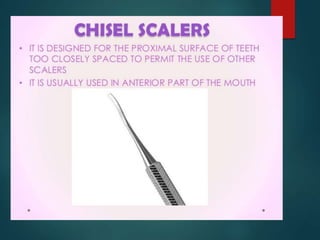
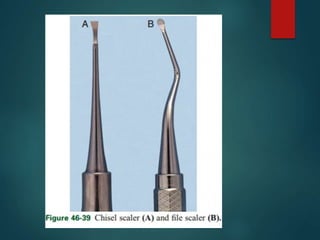
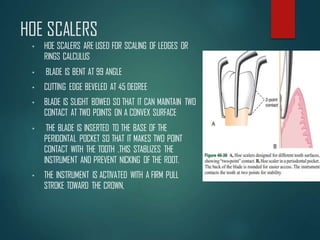
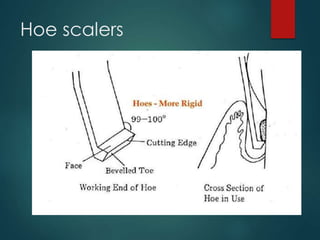
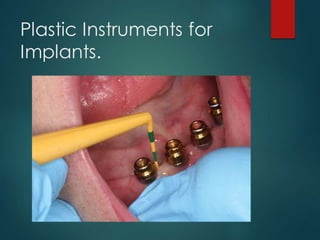
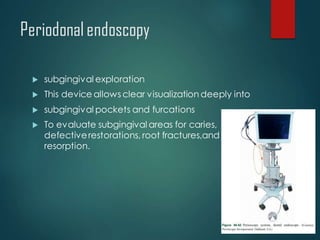
This document discusses different types of periodontal instruments and their uses. It describes five main classifications of instruments: periodontal probes, explorers, scaling/root planing/curettage instruments, periodontal endoscopes, and cleansing/polishing instruments. Specific instruments are discussed in detail within each classification, including their parts, designs, uses, and benefits. Gracey curettes, sickle scalers, hoe scalers, files, and ultrasonic instruments are some of the instruments explained in the document.