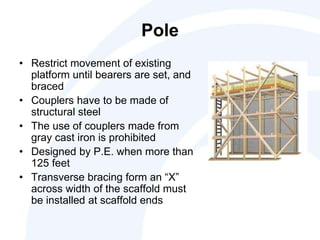
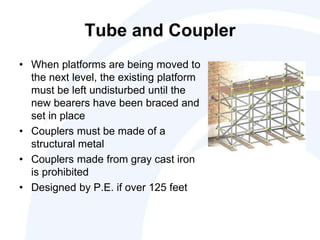
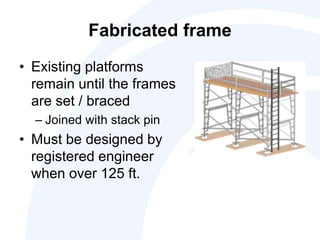
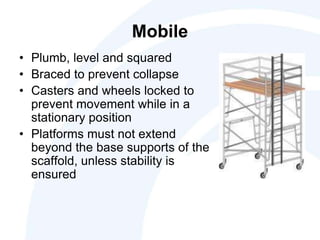
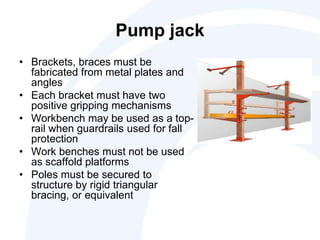
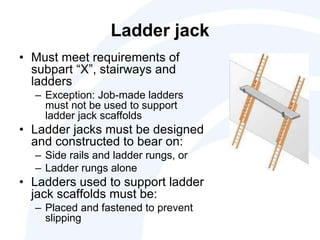
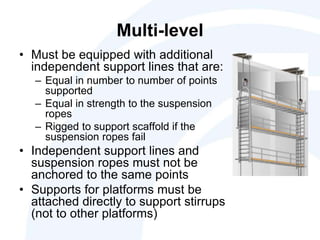
The document outlines the scope, application, and major points of OSHA regulations regarding scaffolding, including fall protection, platform construction, and access requirements. It details the different scaffolding types and their specifications, training requirements for employees, and compliance flexibility for employers. Effective dates and common citation issues are also addressed, along with resources for additional information.