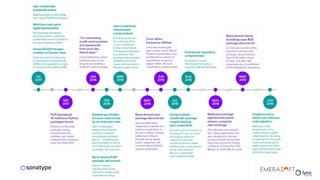
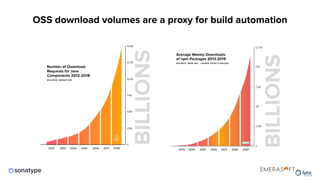
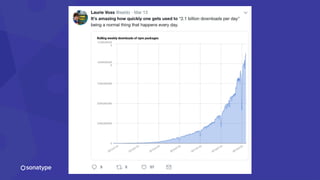
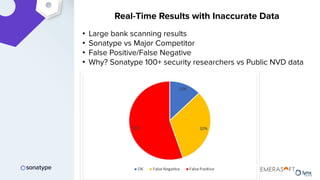
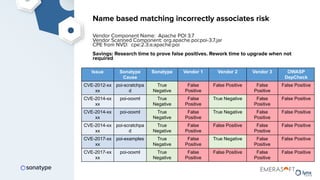
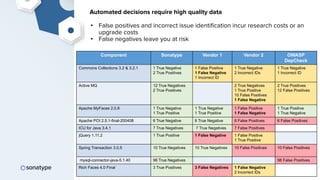
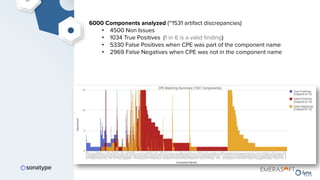
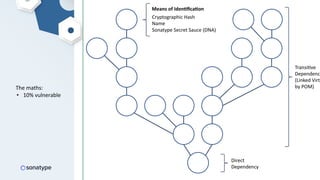
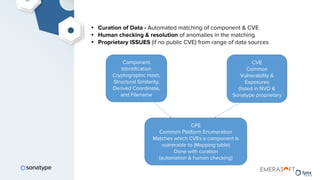
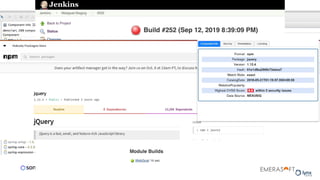
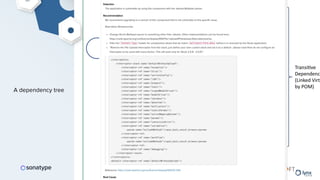
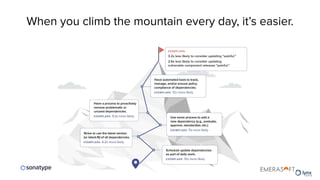
The document discusses the importance of accurate data for automating software security processes, particularly in the context of open-source software. It emphasizes that relying on public vulnerability databases can lead to excessive false positives and negatives, potentially hindering innovation and developer trust. Recommendations include using proprietary intelligence, curating data, and providing developers with contextual remediation guidance to enhance security practices without creating friction.