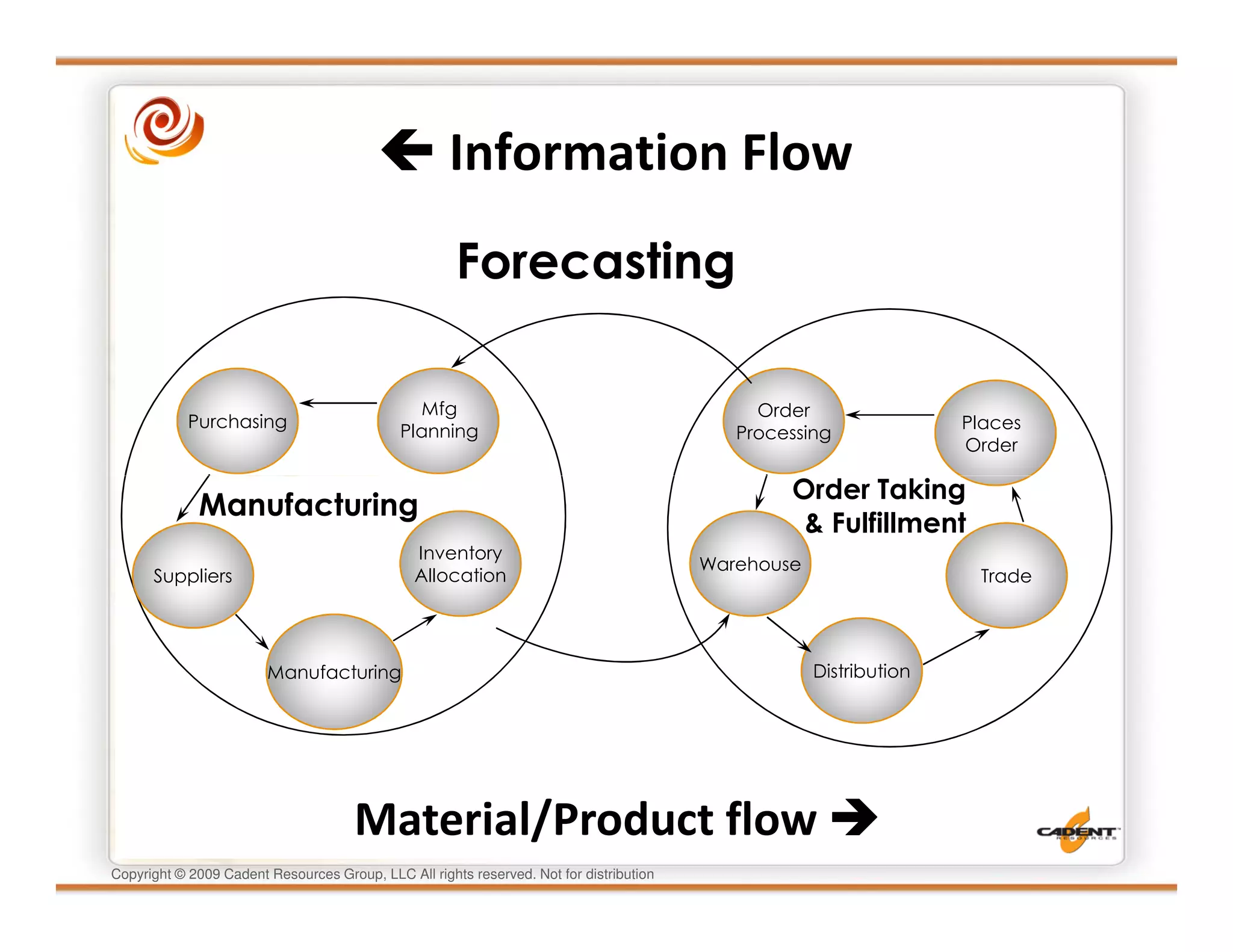
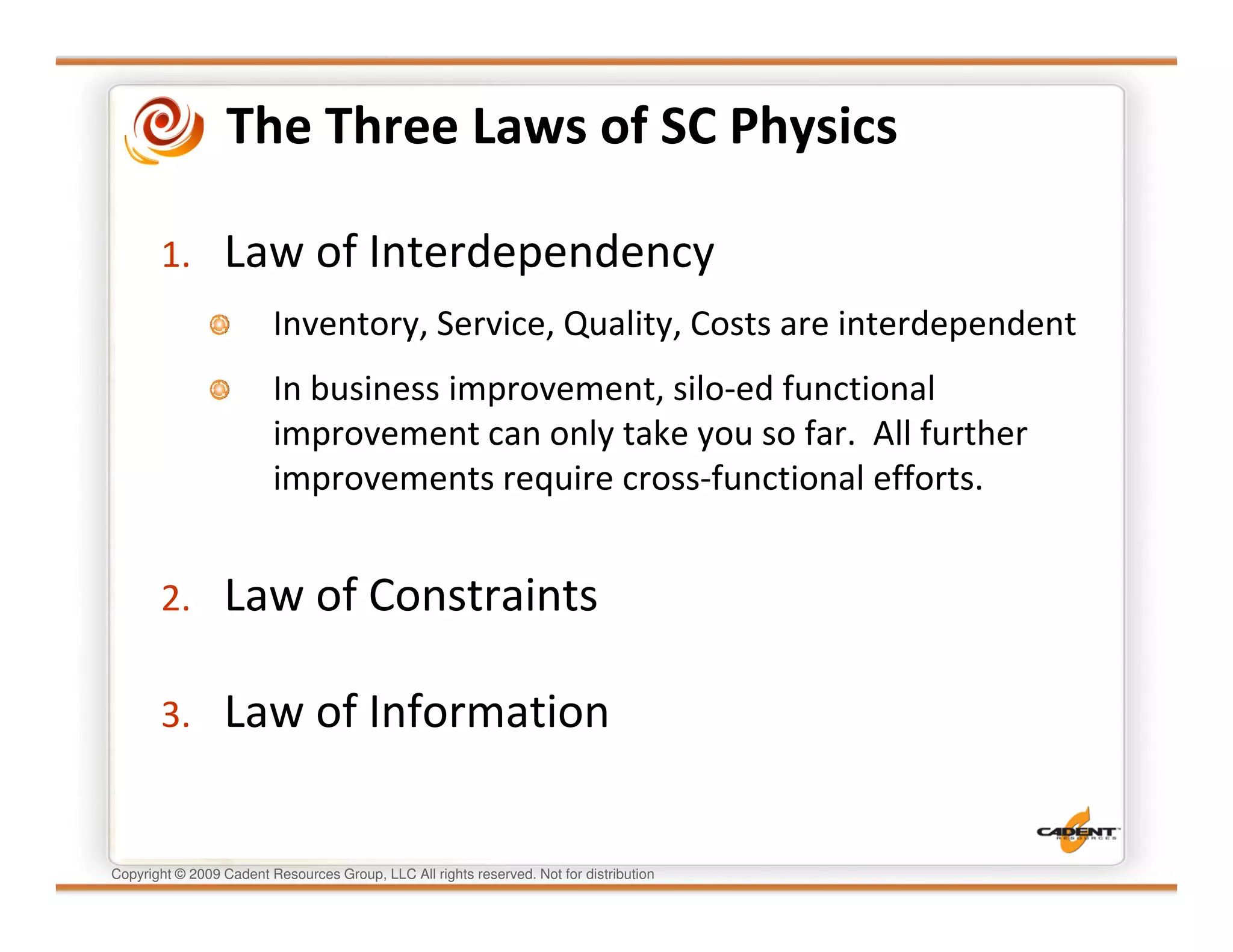
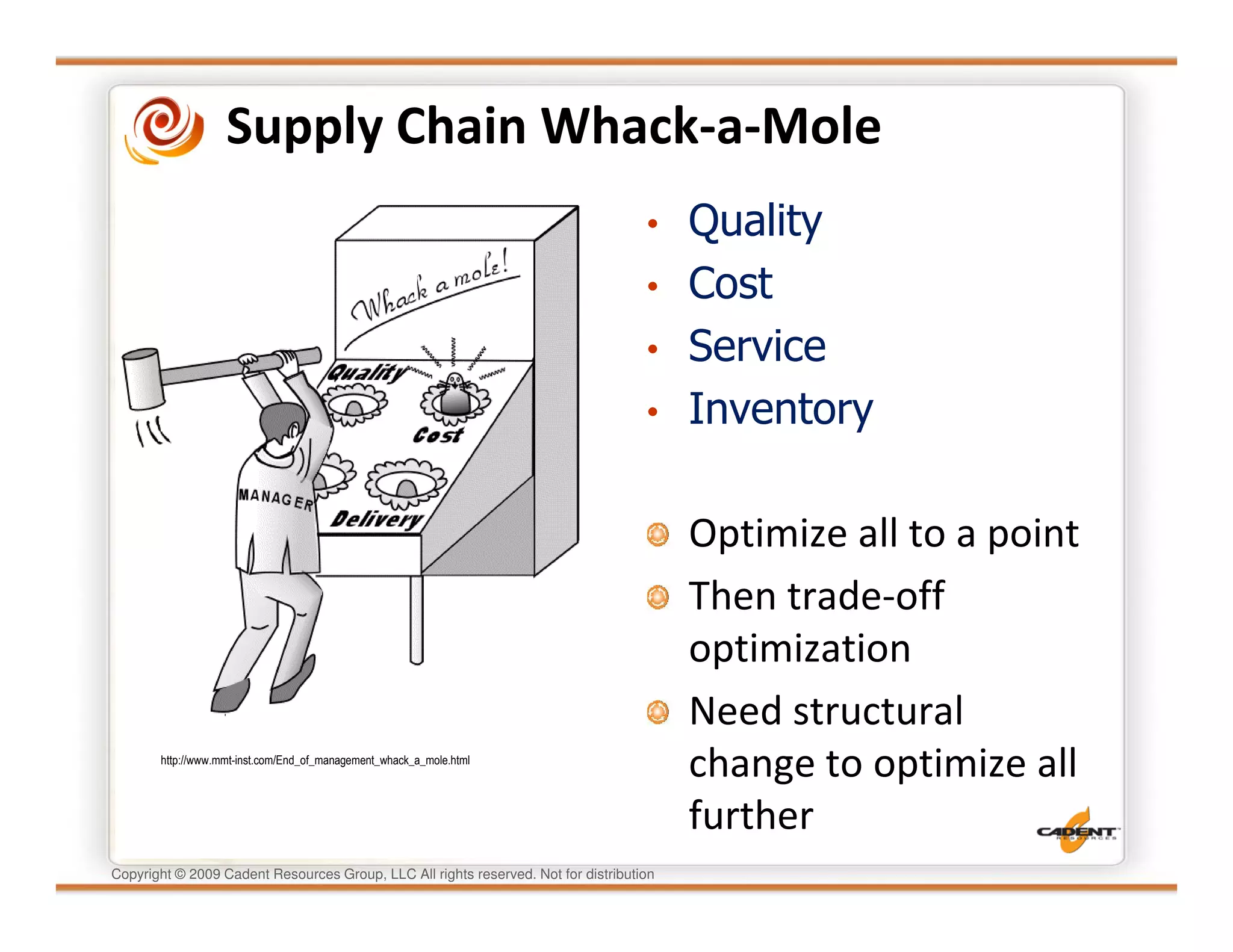
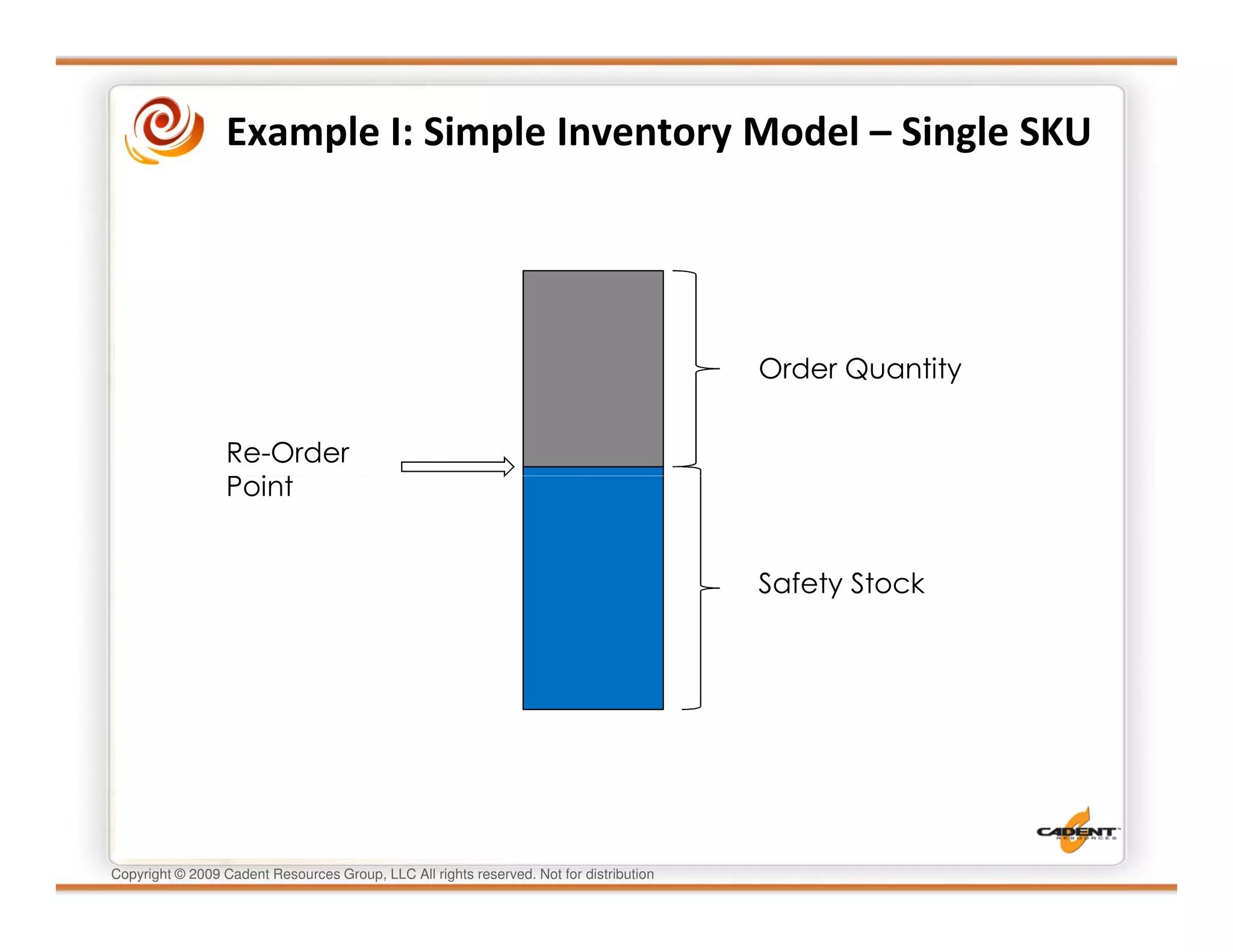
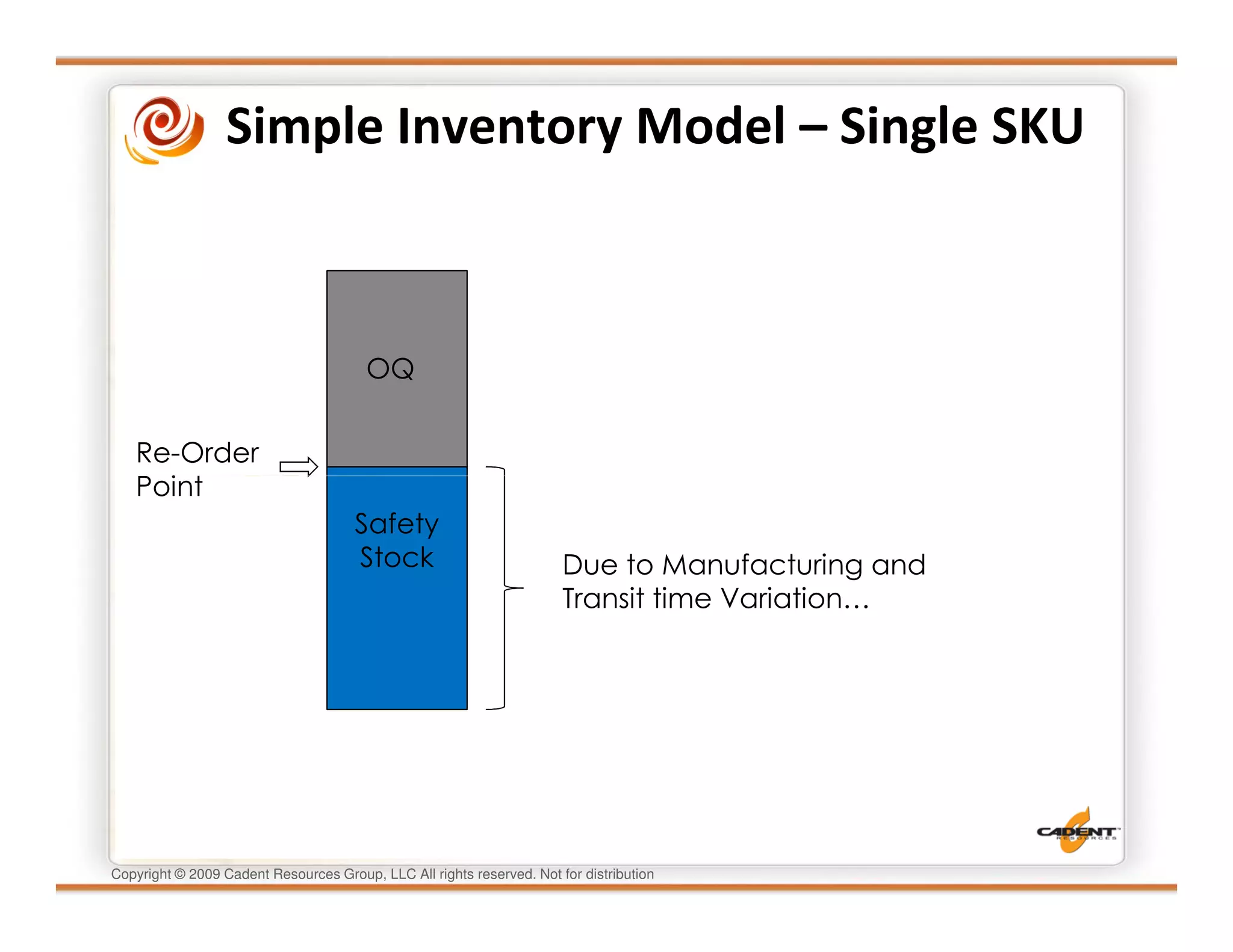
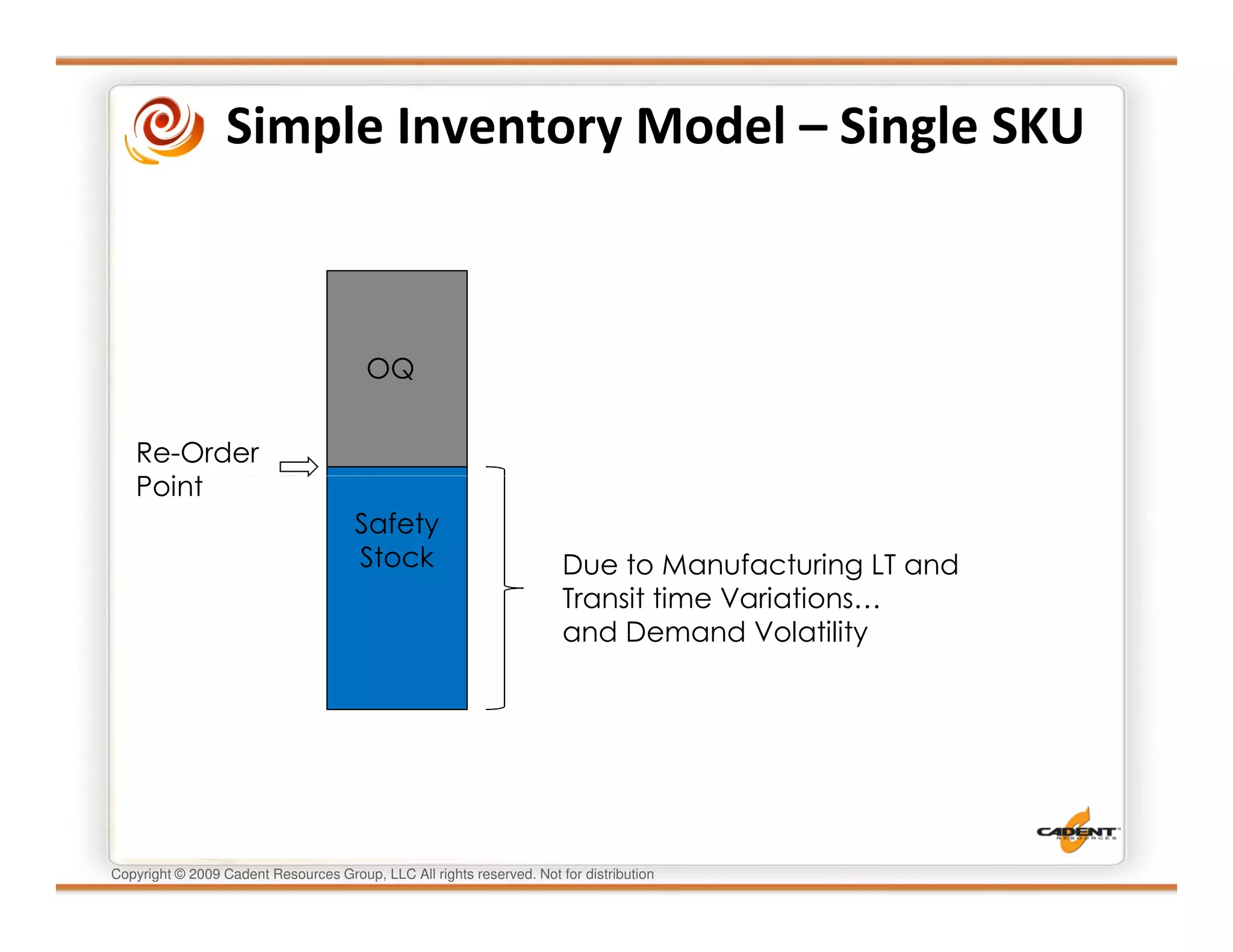
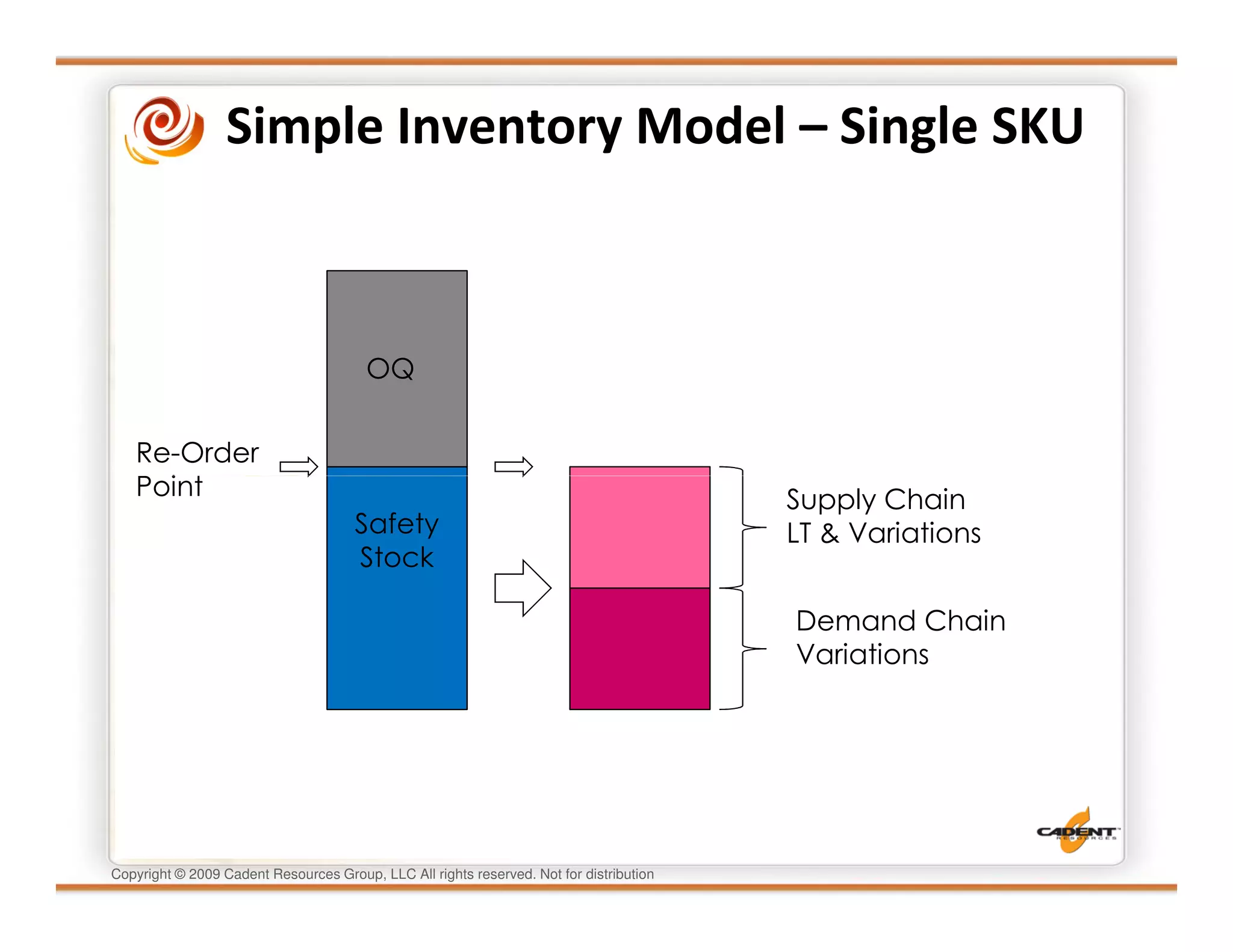
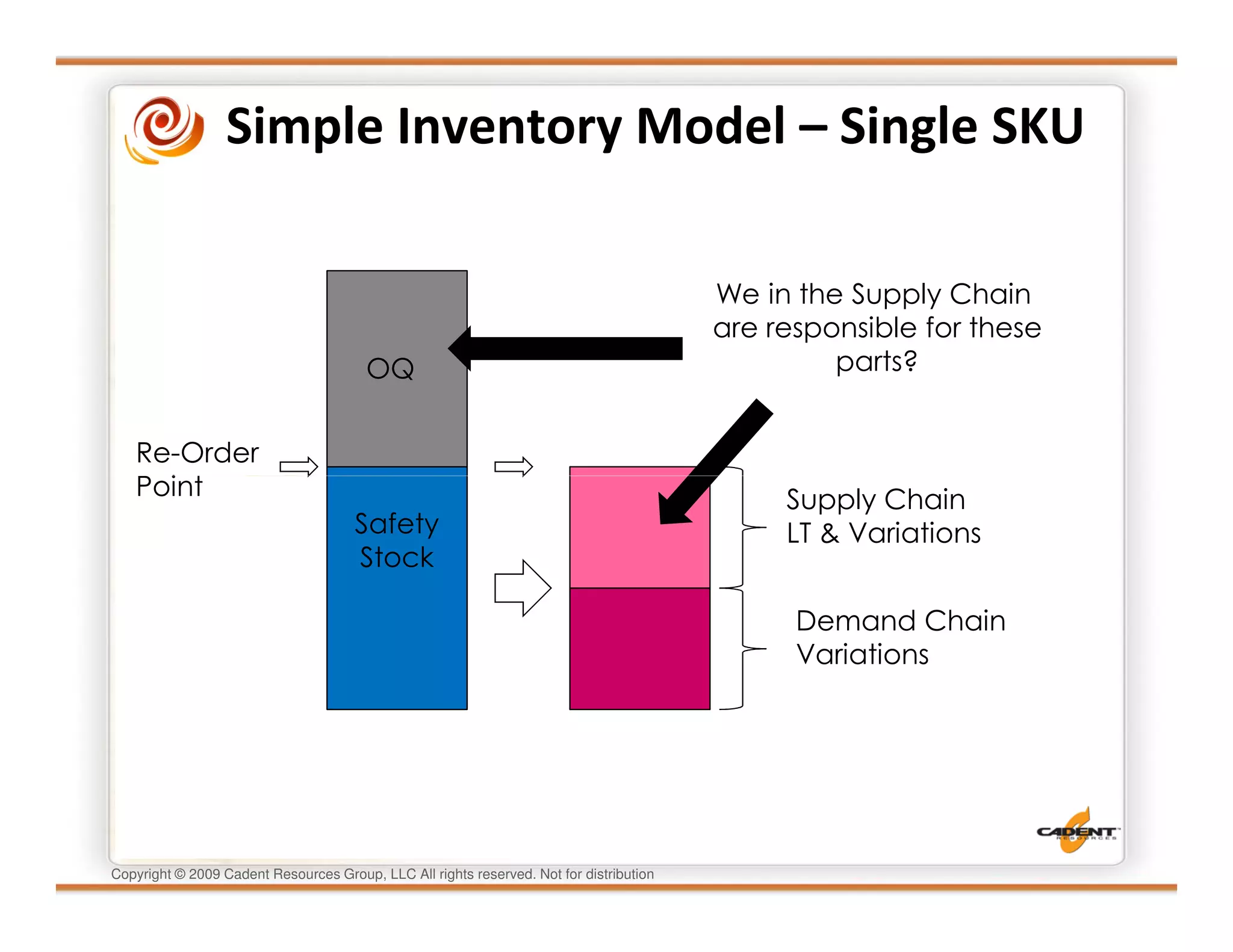
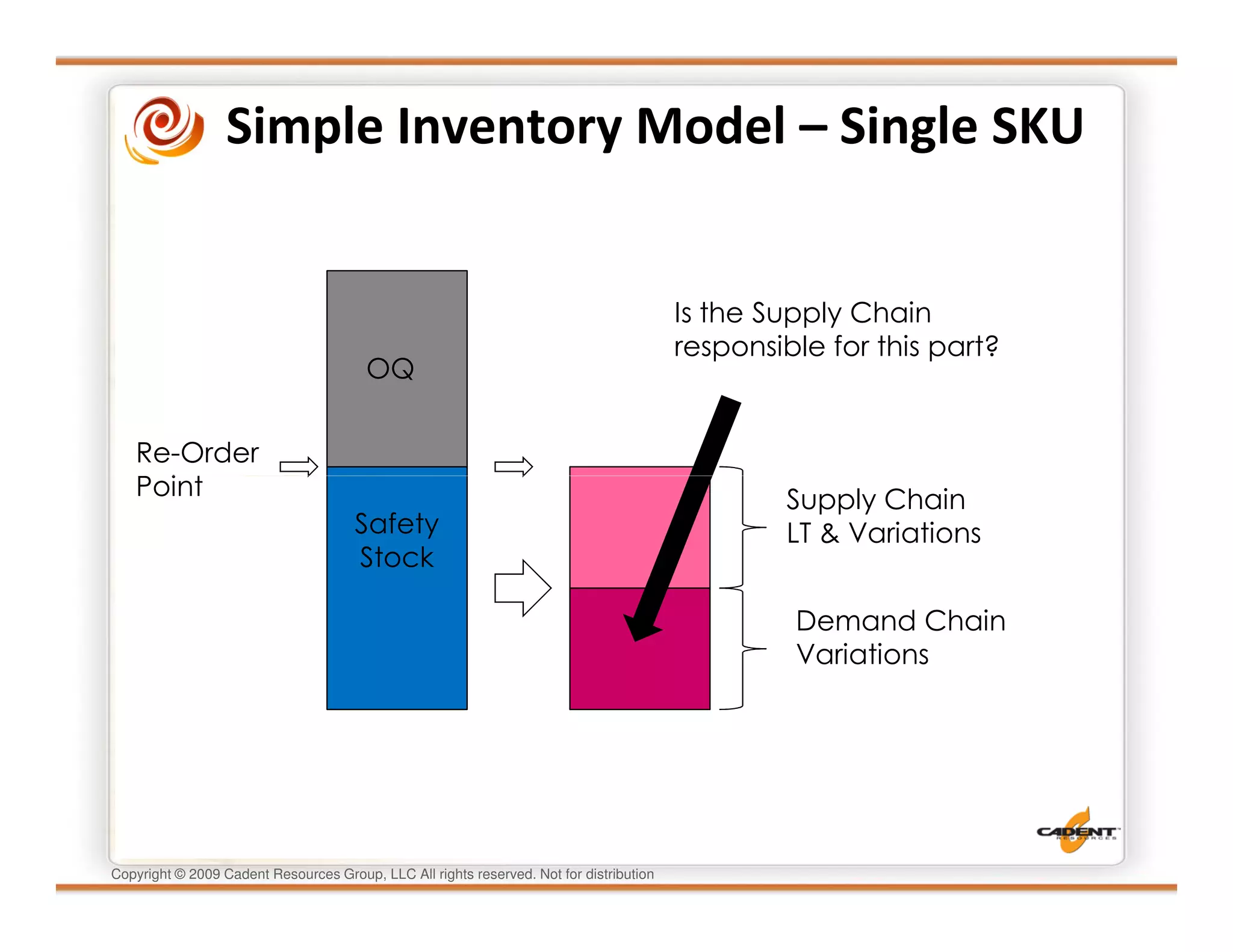
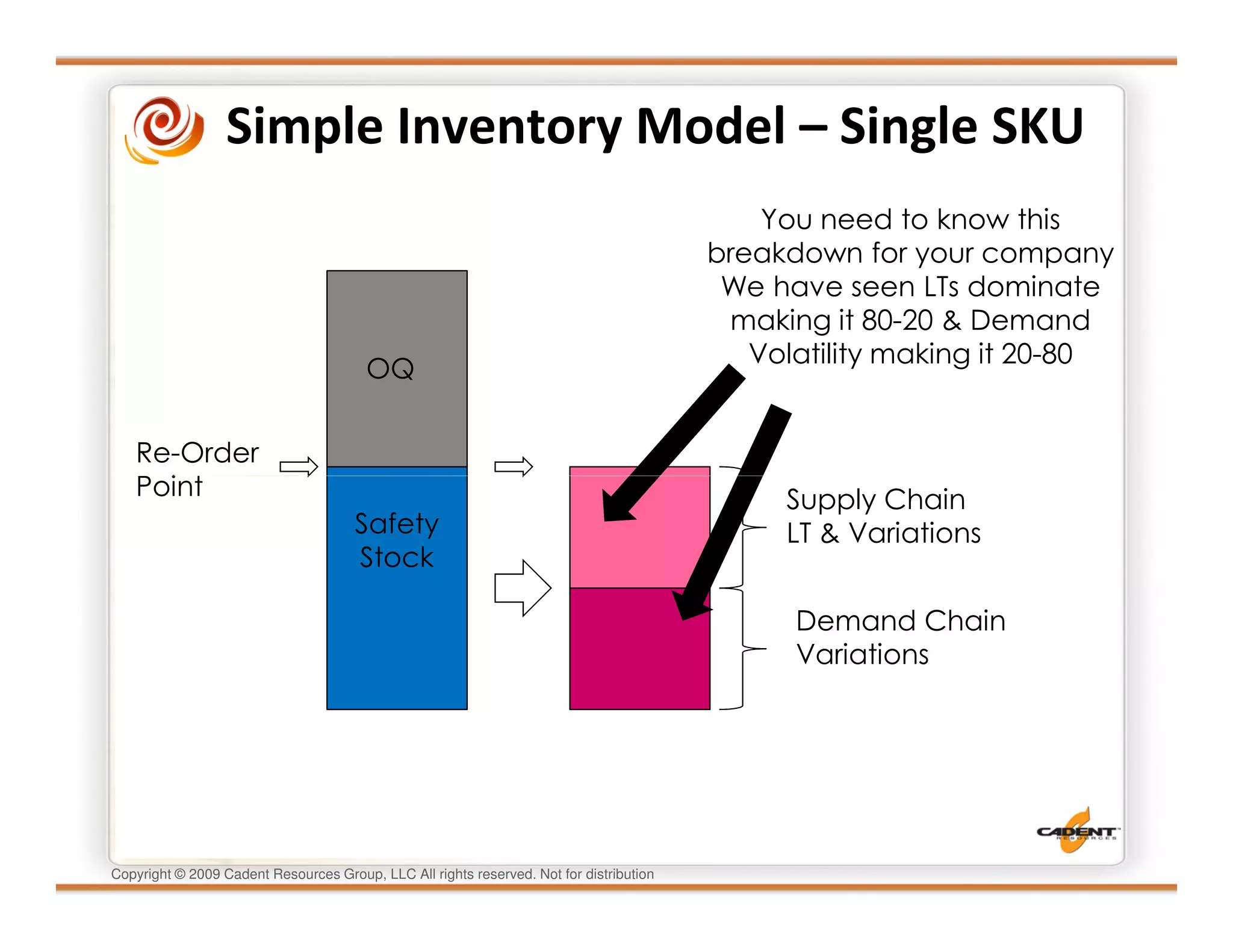
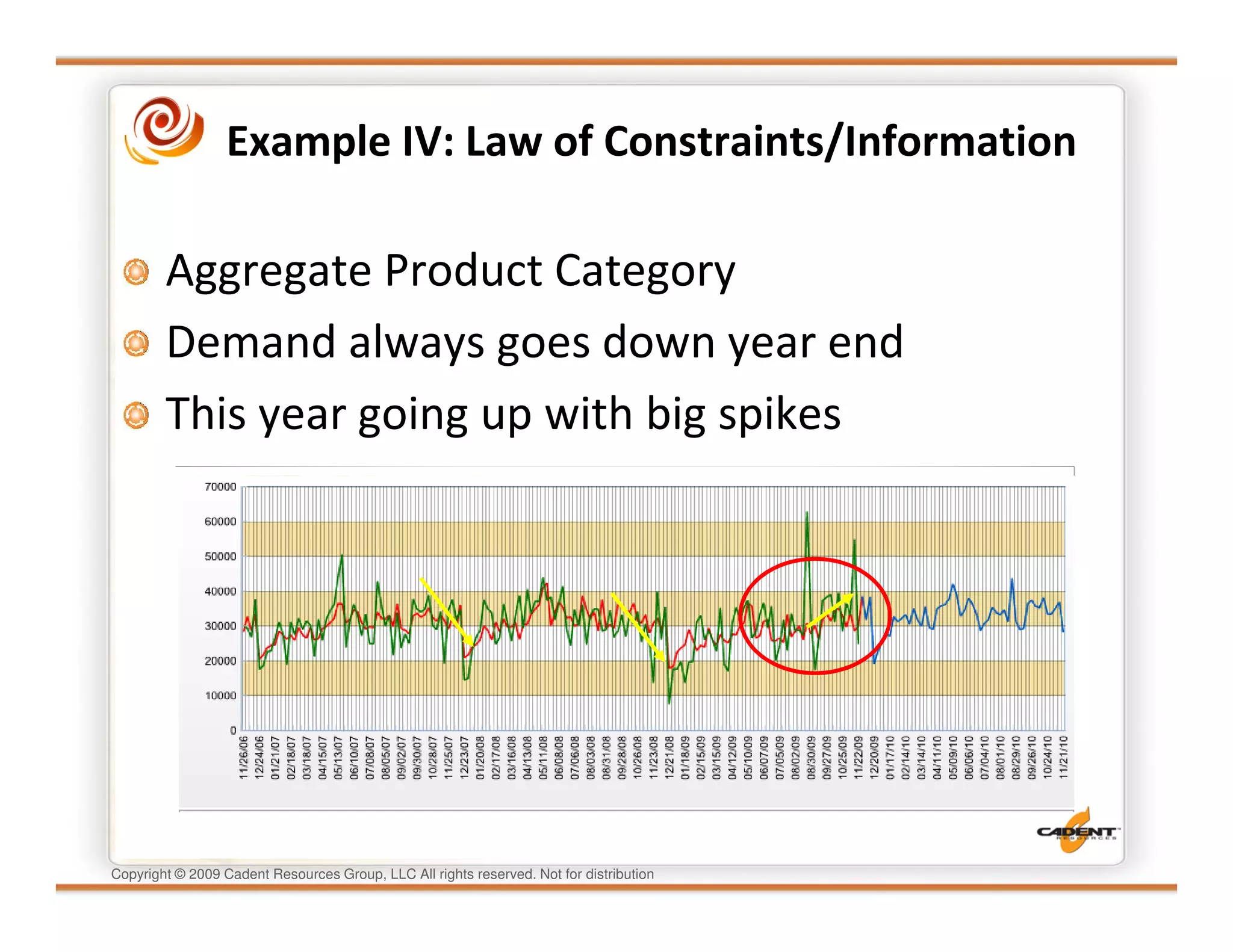
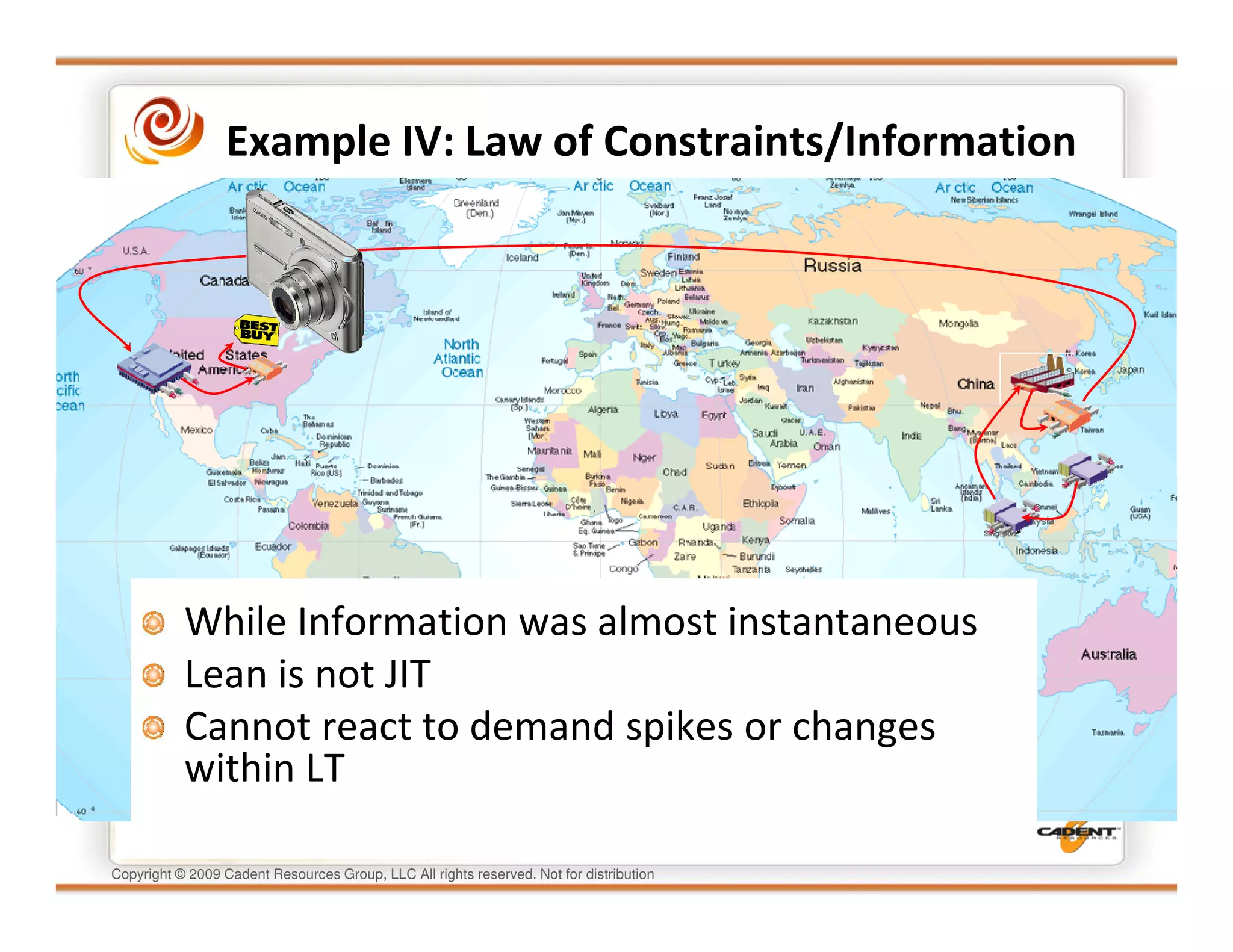
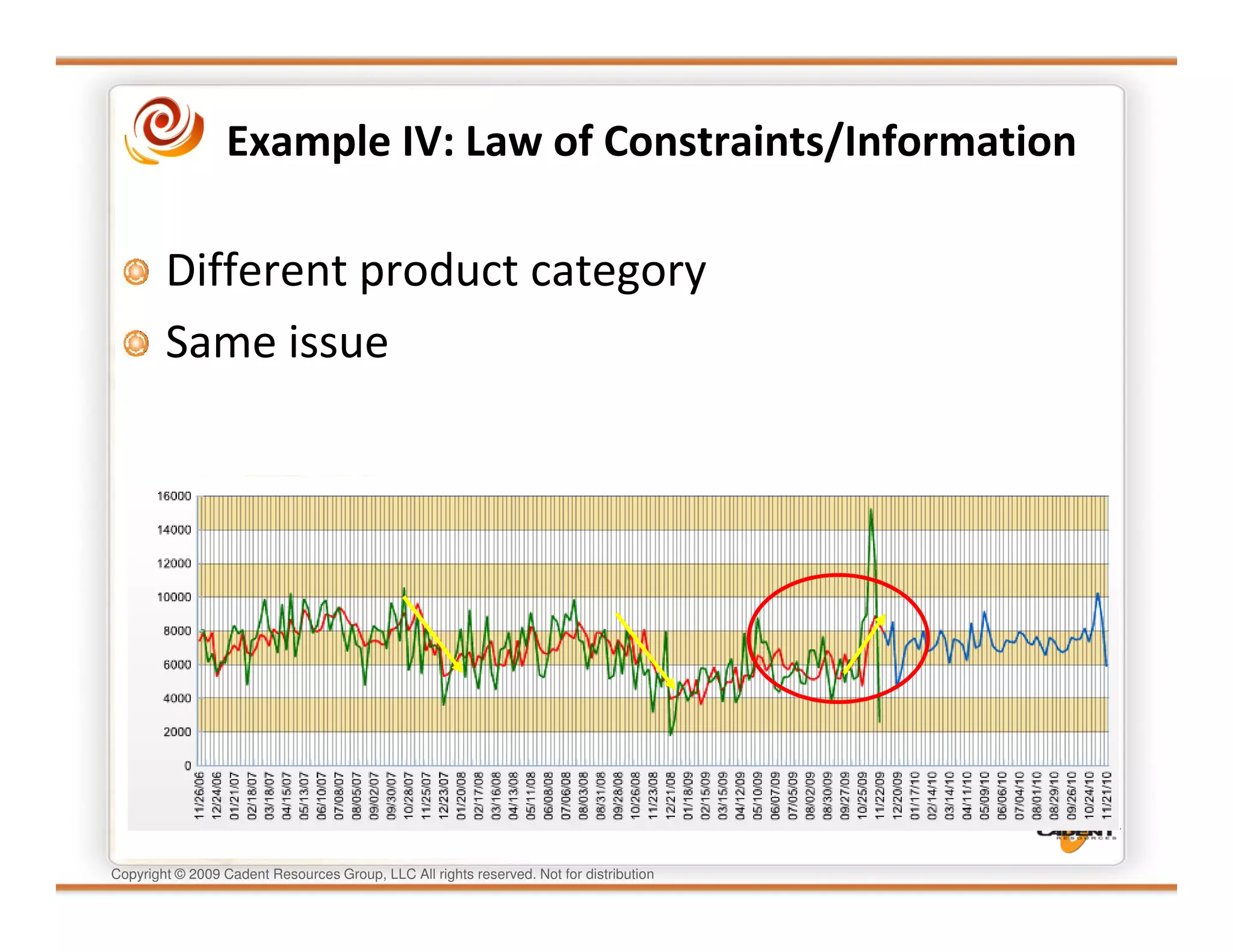
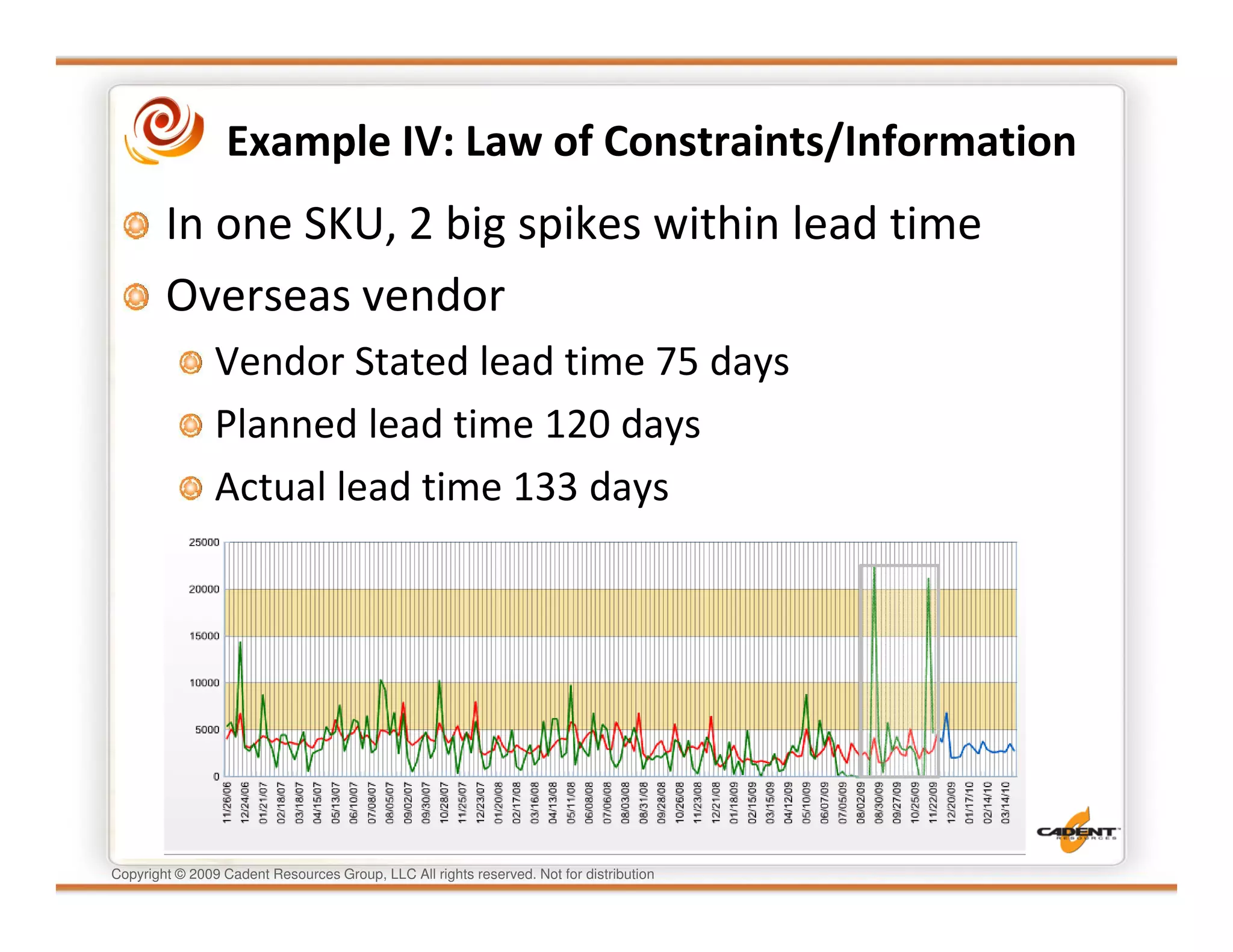
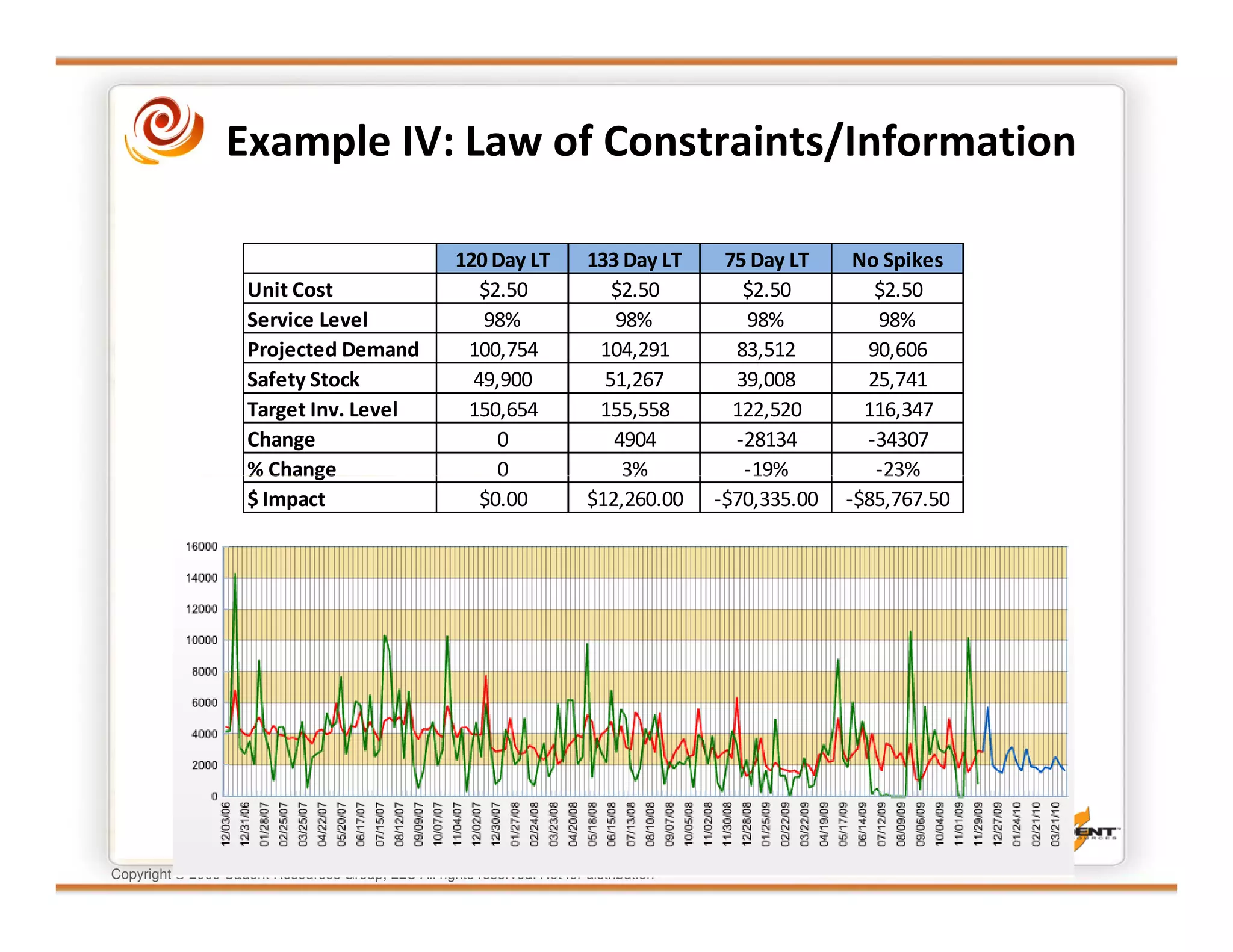
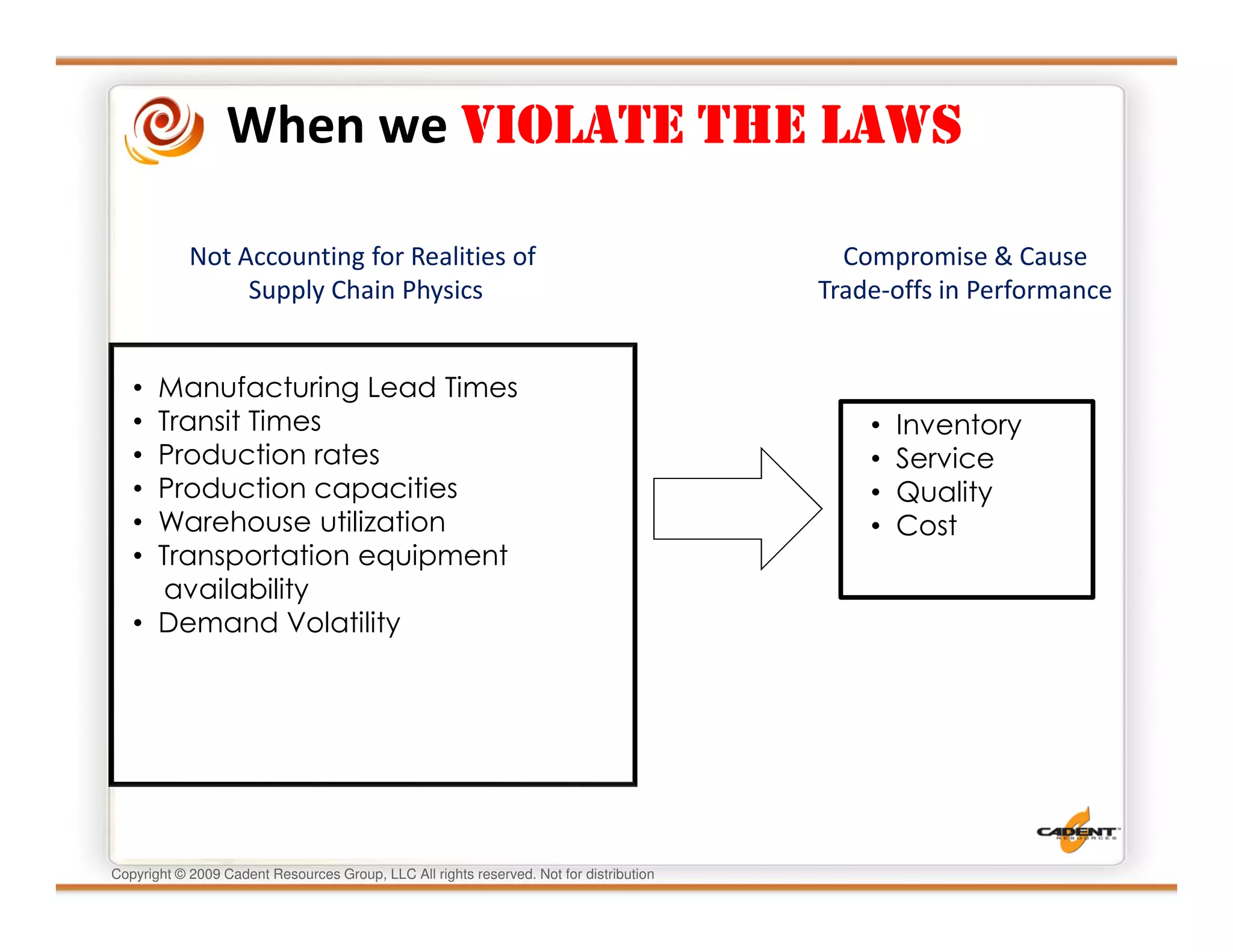
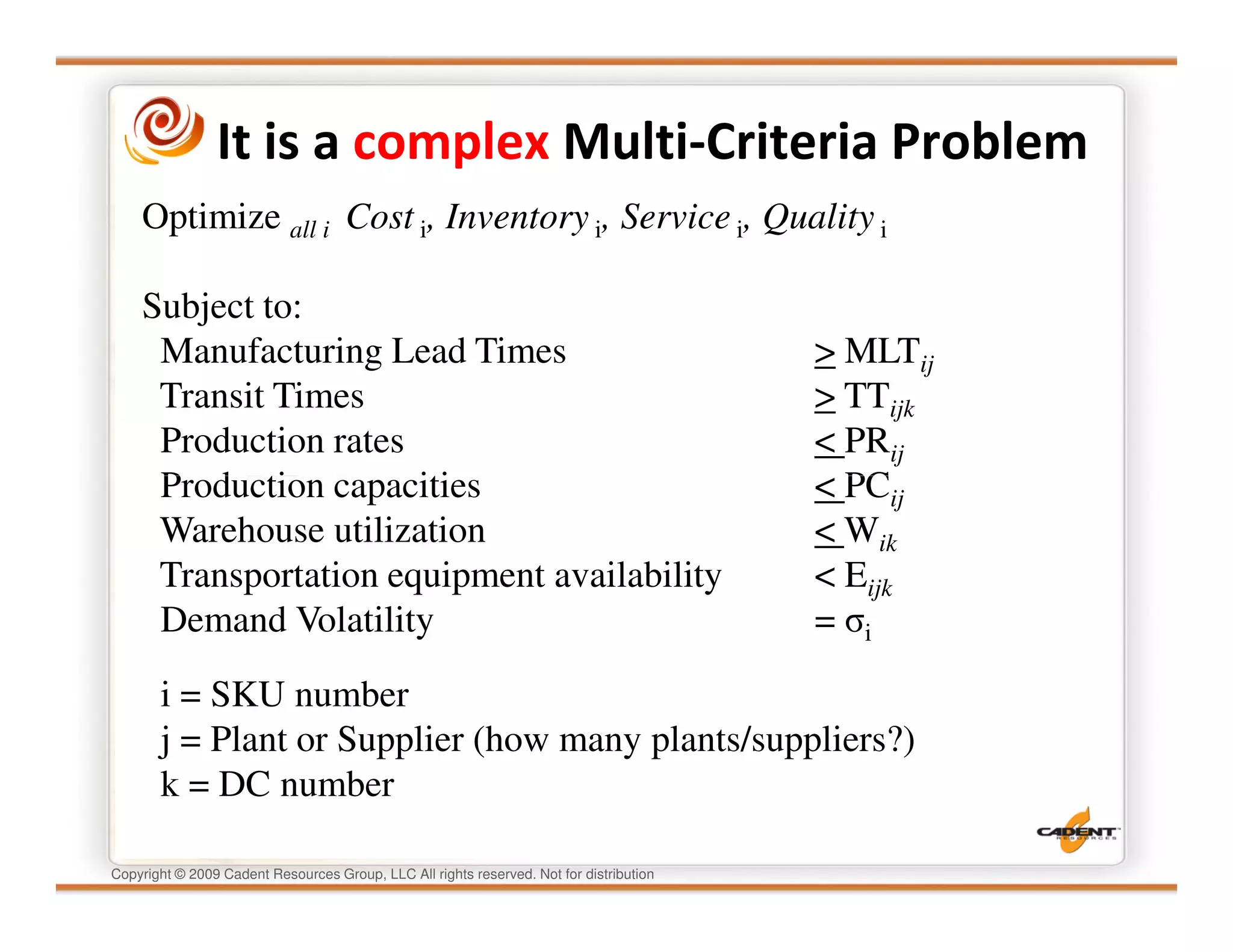
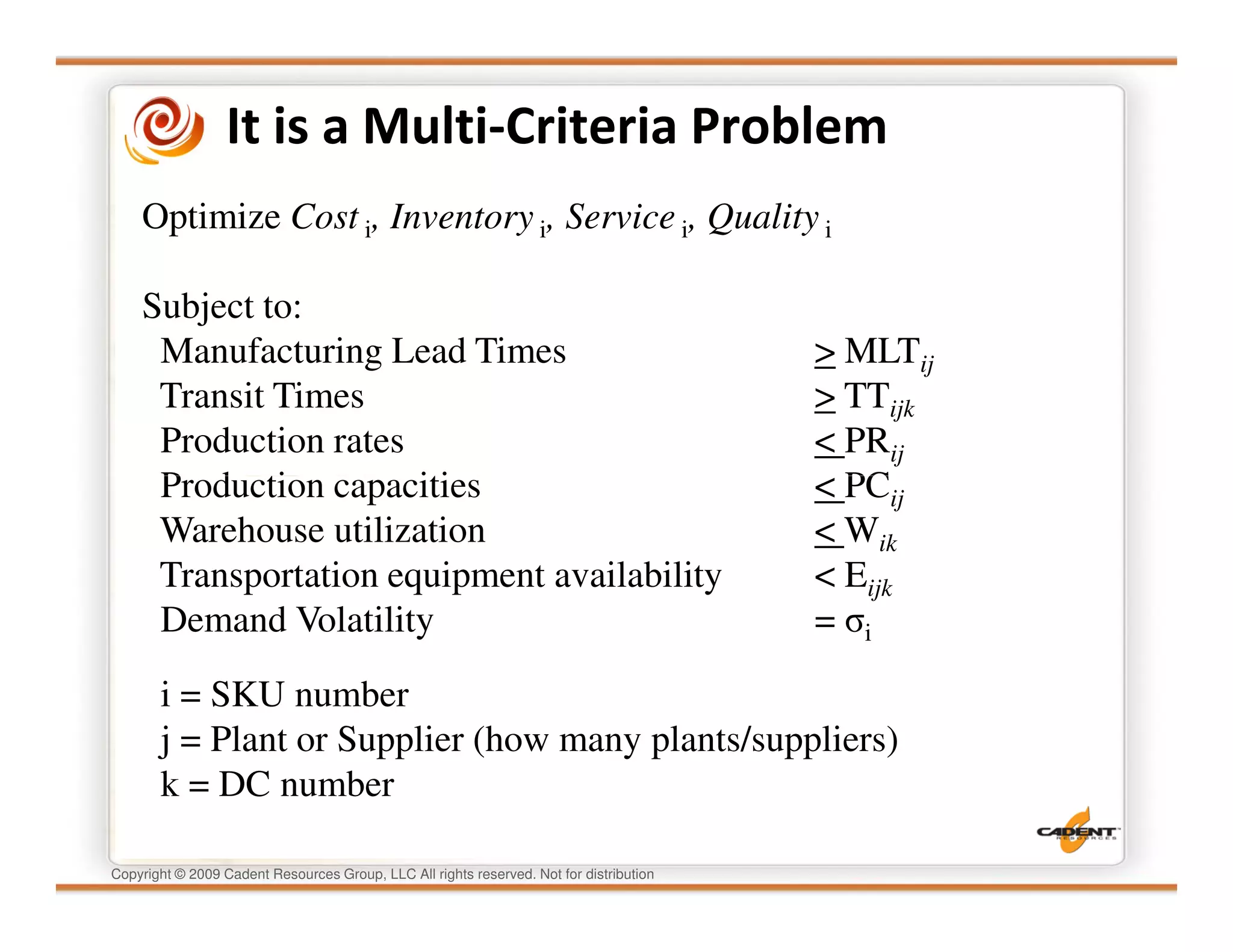
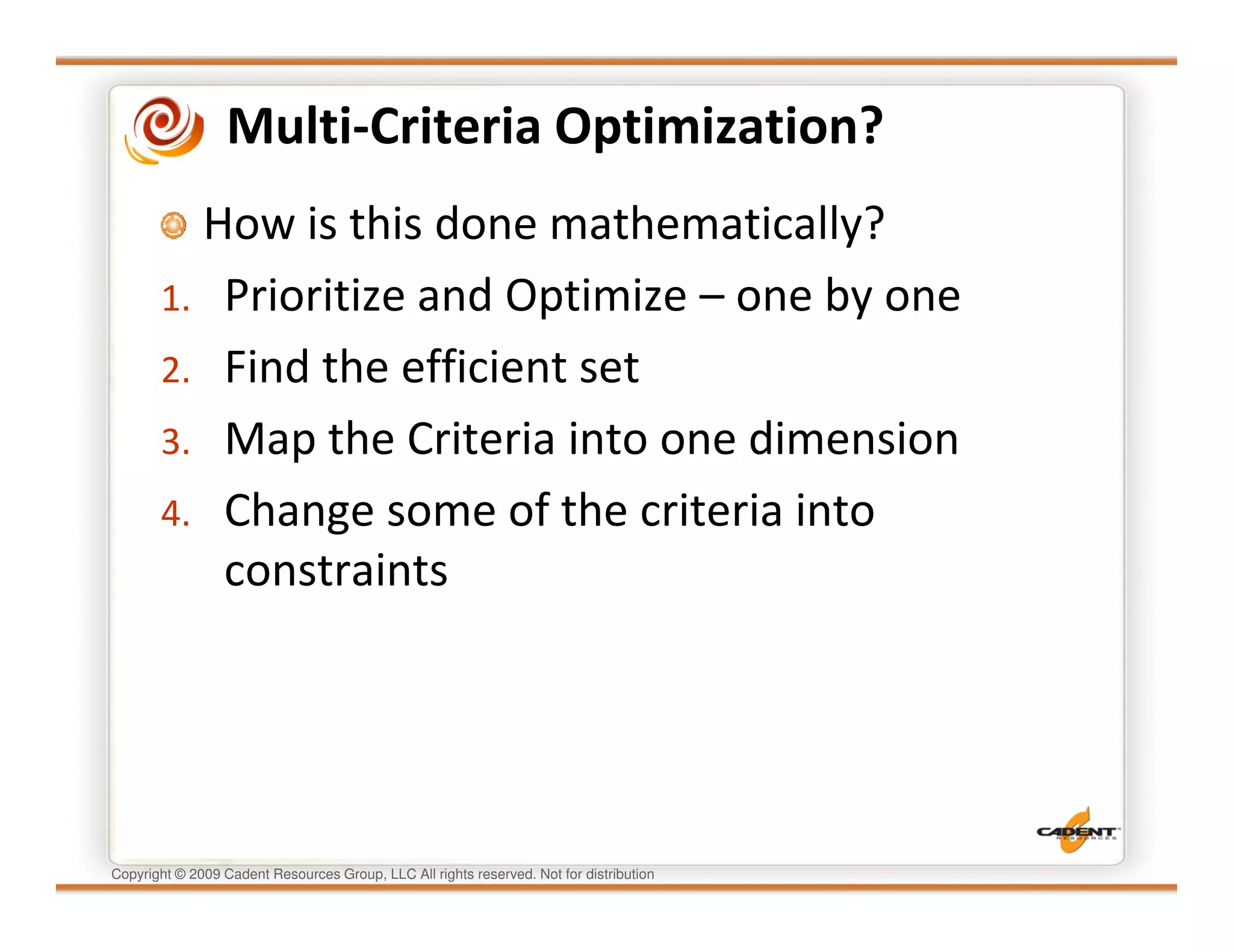
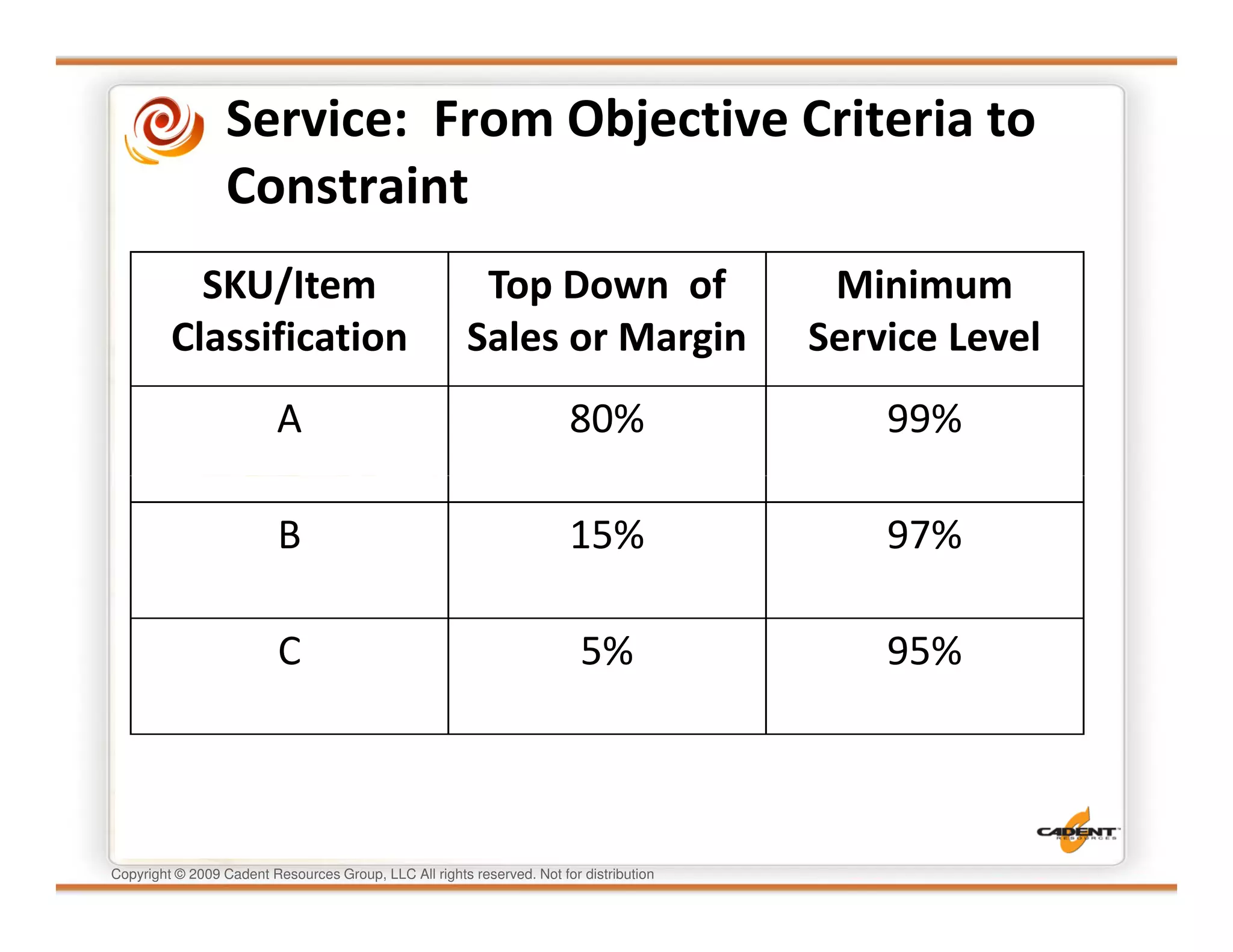
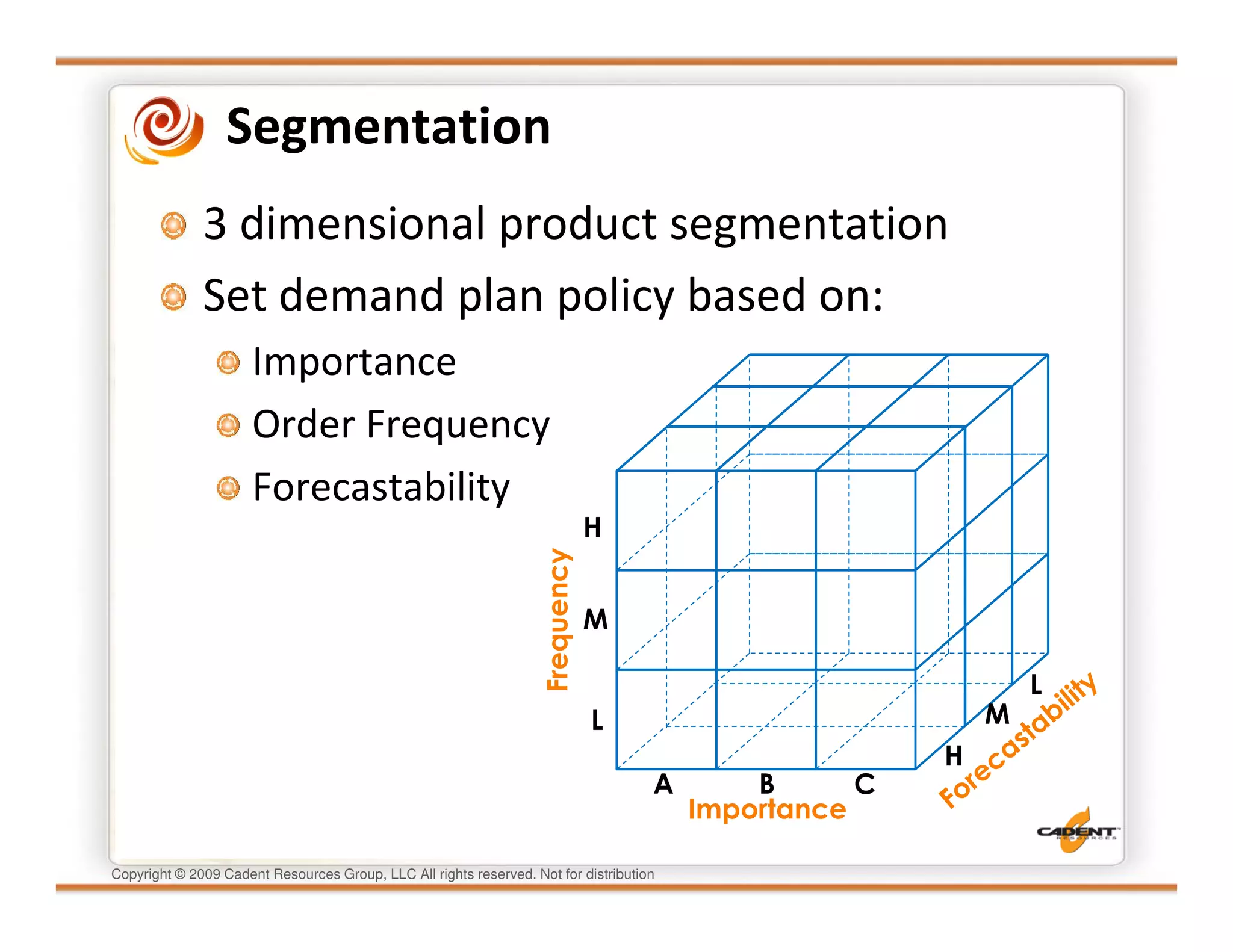
This document discusses supply chain physics and the real decision space involved. It provides four examples of inventory issues, including a simple inventory model, excess and obsolete inventory, and situations where the laws of constraints and information are violated. It explains that optimizing supply chains is a complex multi-criteria problem that involves balancing factors like costs, inventory levels, service, quality and constraints like lead times. Violating the laws of supply chain physics can compromise performance in these areas.