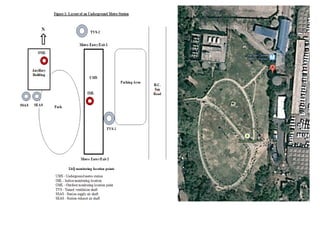
1) The document presents a case study analyzing indoor air pollution and sick building syndrome (SBS) in the underground Chandi Chowk metro station in New Delhi, India.
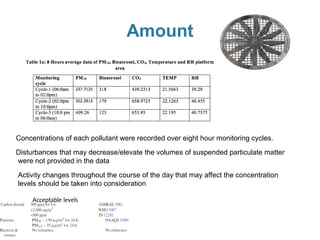
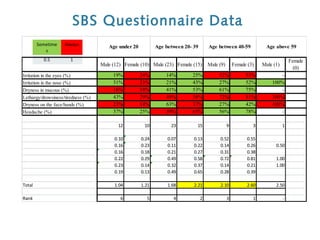
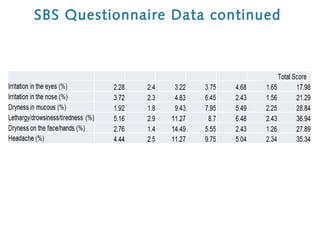
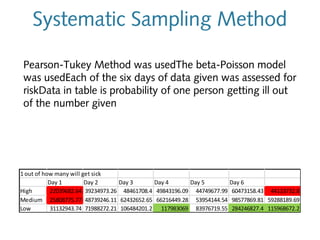
2) It identifies various air pollutants like particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, bioaerosols, and carbon dioxide that could be contributing to SBS. Questionnaires were used to assess SBS symptoms in station workers.
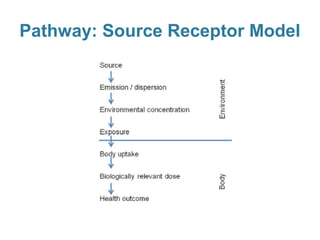
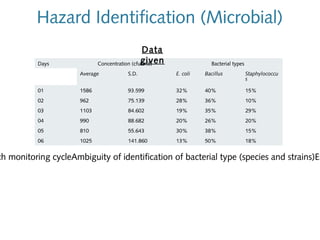
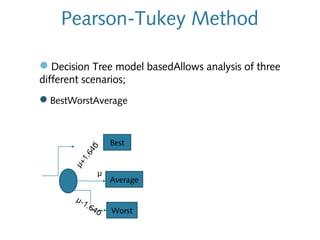
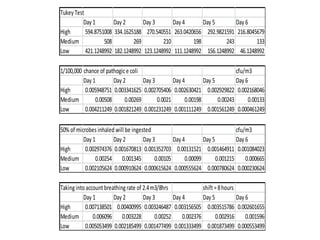
3) Exposure to the pollutants was assessed by measuring their concentrations over time, identifying sources, inhalation pathways, and establishing dose-response relationships between pollutant levels and SBS symptoms. More data is needed to better understand these relationships.