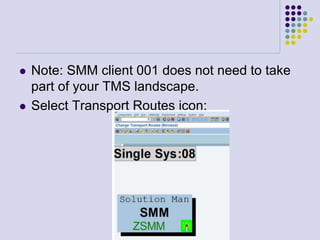
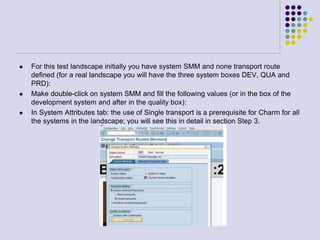
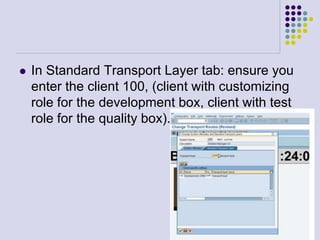
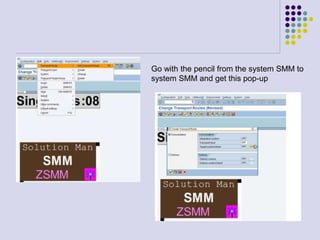
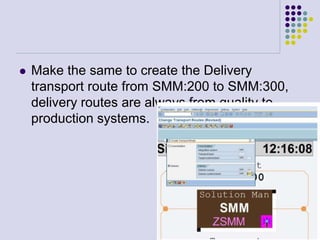
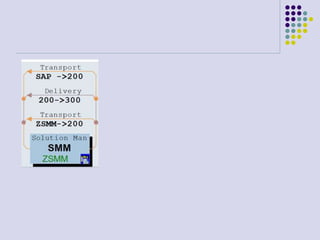
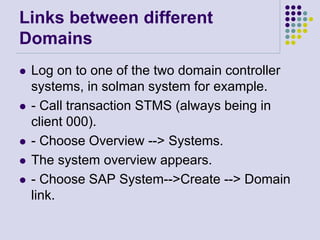
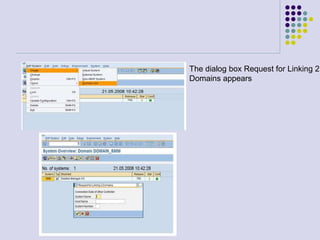
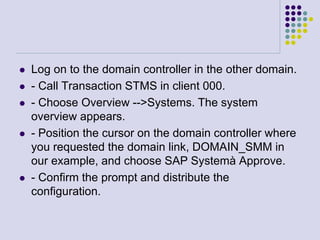
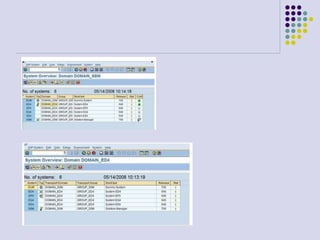
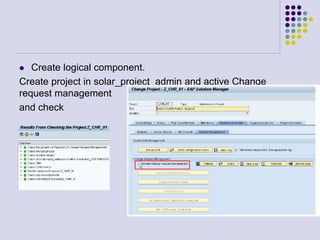
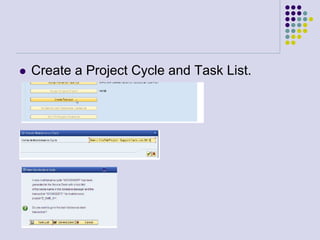
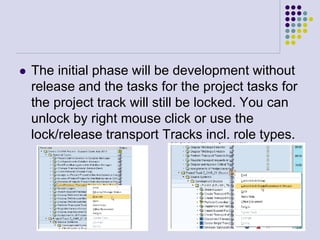
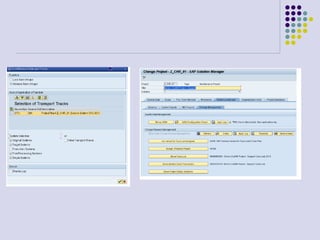
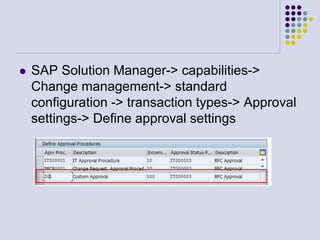
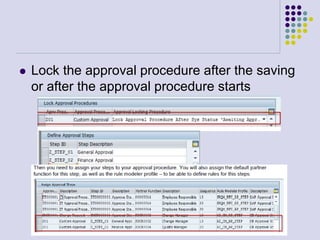
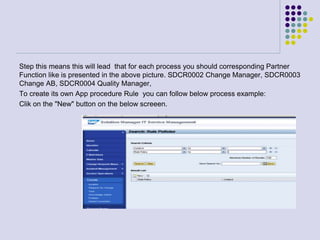
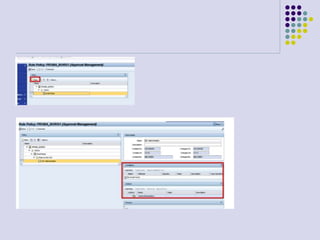
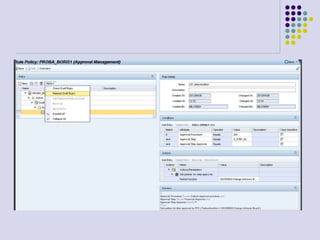
This document outlines the prerequisites, configuration, and lessons for a change request management training. It includes setting up transport management systems and approval procedures in SAP. The training contains 3 lessons on change request content and process, with objectives, teaching materials, and wrap-ups for each lesson. It concludes with an assessment of the training and evaluation of participant feedback.