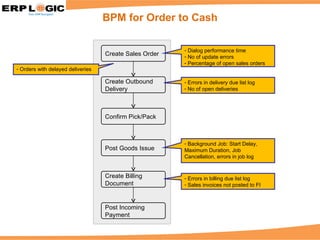
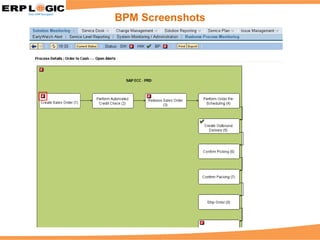
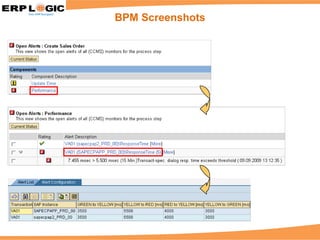
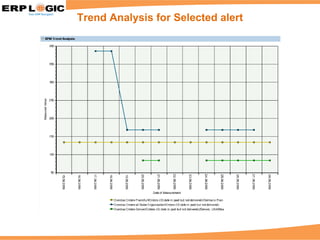
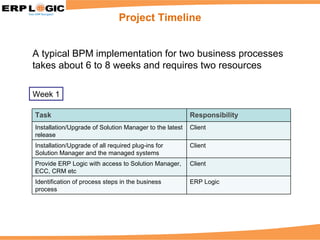
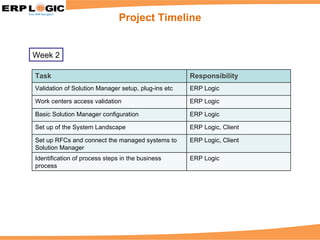
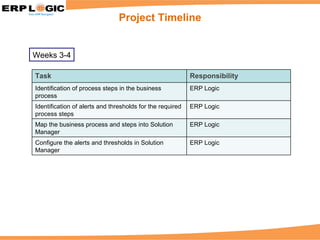
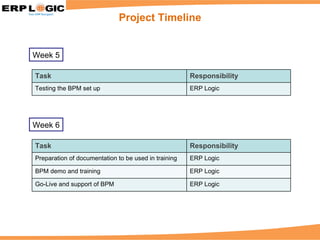
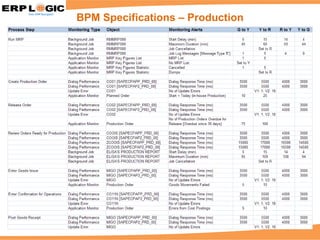
Business Process Monitoring (BPM) allows companies to proactively monitor their core business processes. BPM detects problems early, enabling faster resolution before major impacts. It provides visibility into key process metrics like order status, delivery issues, and invoice posting. BPM implementation involves configuring the monitoring of specific processes in SAP Solution Manager over 6-8 weeks. Benefits include reduced downtime, improved service levels, and avoidance of costly manual monitoring.