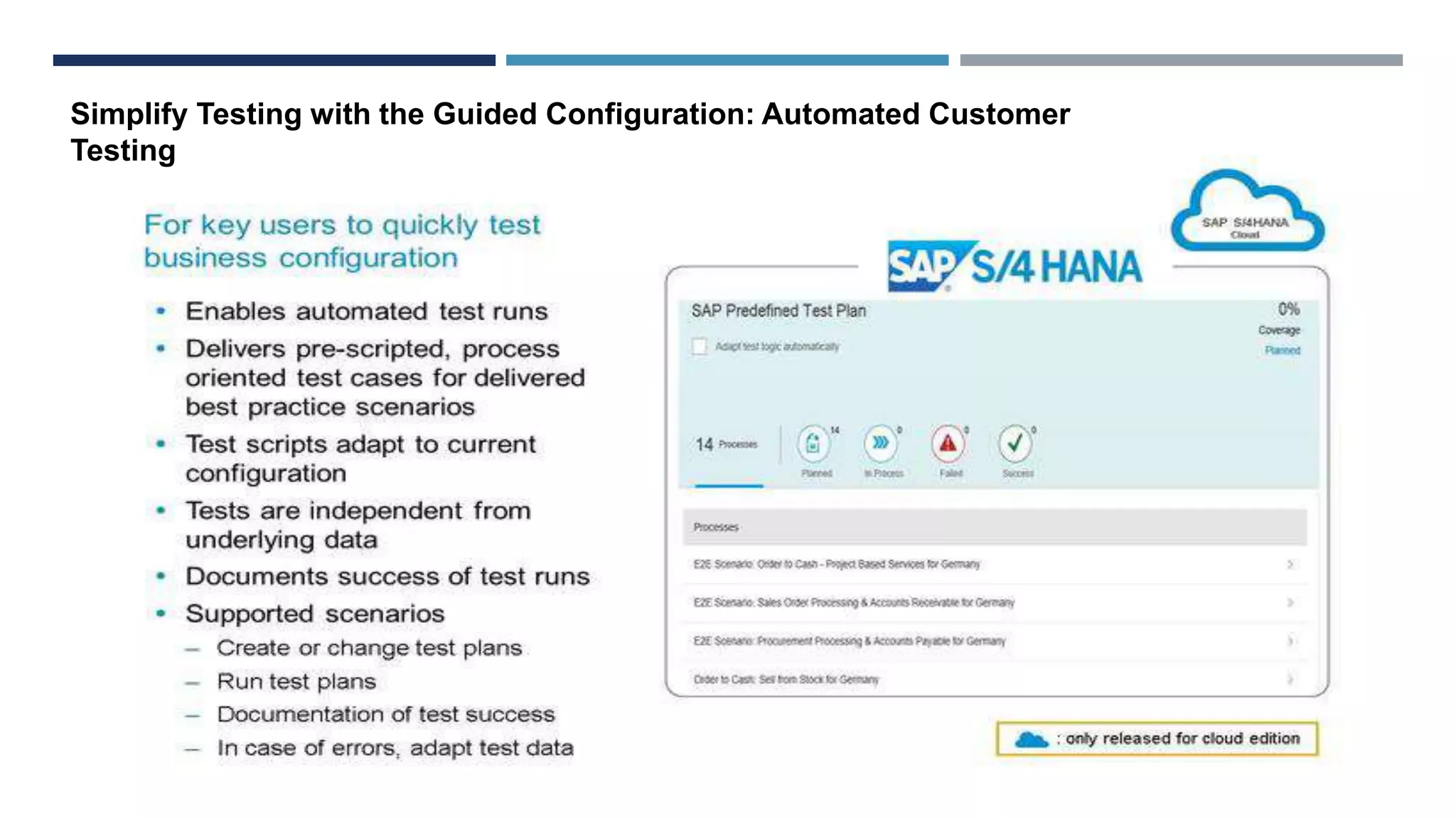
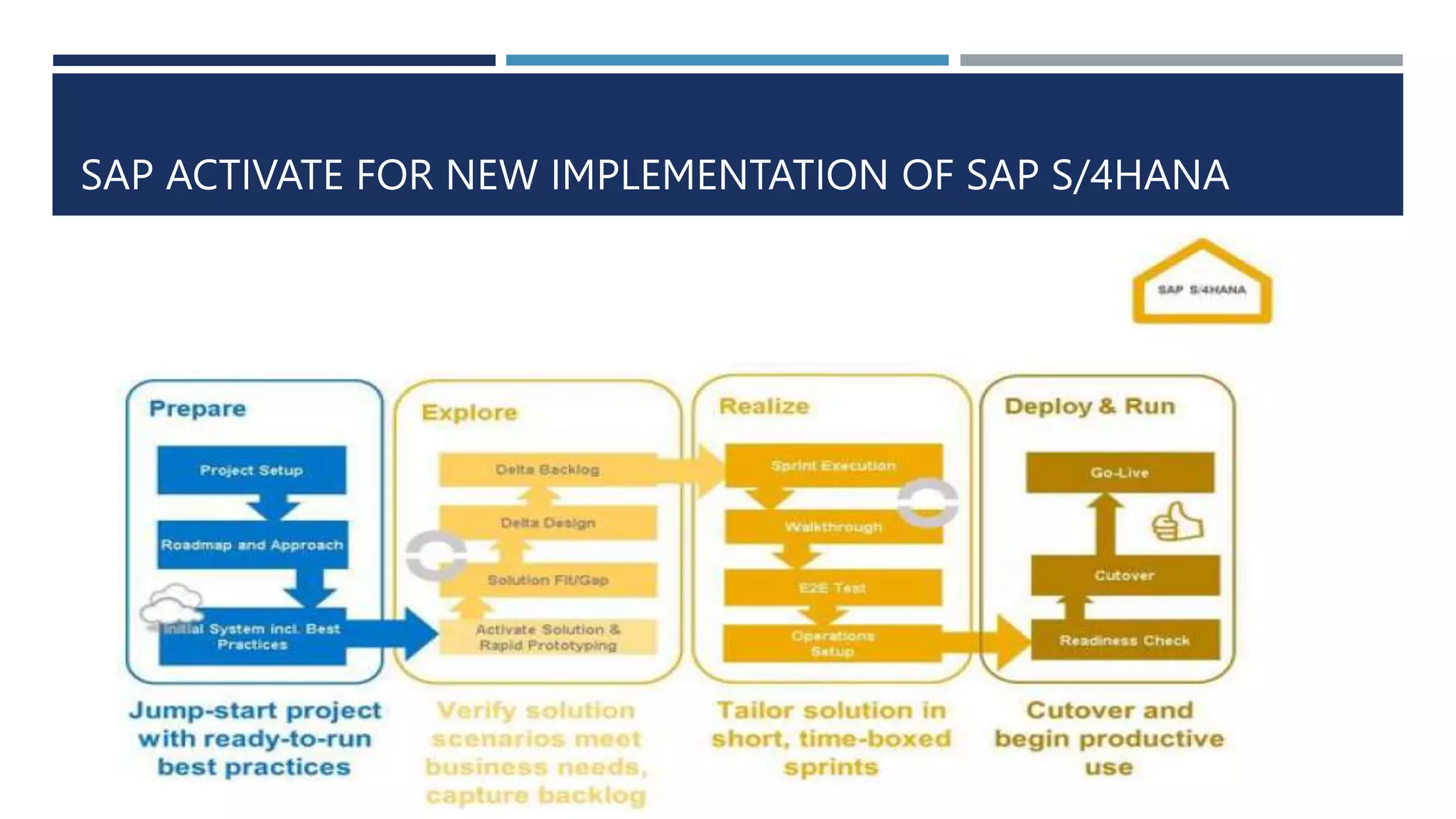
This document provides an overview of the SAP Activate methodology for implementing SAP solutions in the cloud. It outlines the key phases and deliverables of the methodology, including Prepare, Explore, Realize, and Deploy. In the Prepare phase, the cloud system is provisioned and the customer team is enabled. The Explore phase involves fit-to-standard analysis and configuration definition. In Realize, the solution is configured using guided configuration tools. Deploy involves data migration, testing, and go-live activities. Differences for on-premise implementations are also highlighted, such as using a sandbox environment and transporting objects between systems.