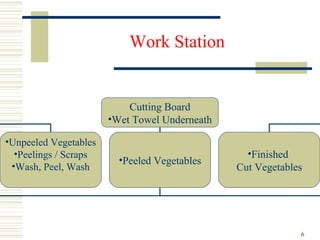
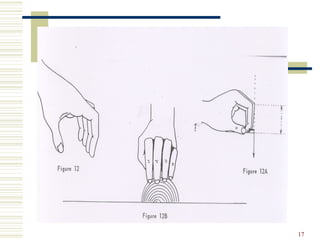
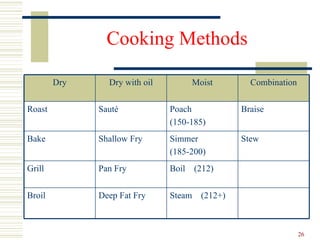
The document discusses several topics related to culinary arts including classroom policies, HACCP food safety principles, mise en place, knife cuts, cooking methods, and boiling versus simmering. Classroom policies require proper uniform and attendance. HACCP identifies seven principles for food safety including critical control points. Mise en place means having all ingredients prepared beforehand. Different knife cuts are used for various vegetable shapes. Cooking methods involve heat transfer and moisture levels. Boiling is faster than simmering due to more liquid movement.