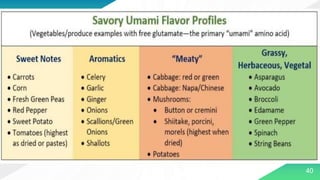
The document discusses cooking and basic cooking principles. It defines cooking as using heat to prepare food for consumption and lists five purposes of cooking: to make nutrients available, enhance flavor, improve digestibility, increase palatability, and destroy pathogens. It identifies the key questions to consider when cooking: what utensils to use, ingredients, amount of heat, and which recipe to follow. The document then provides an overview of common cooking utensils and their uses before discussing ingredients, methods of cooking including dry and moist heat methods, and the five parts of a standard recipe: yield, ingredients, directions, equipment needs, and temperature/time.