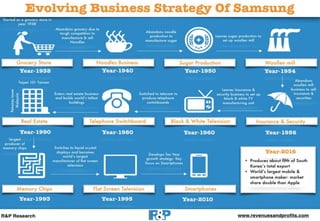
Samsung was founded in 1938 and is headquartered in Seoul, South Korea. It has annual revenue of $224.64 billion and employs 489,000 people across its divisions which include Samsung Electronics, Samsung C&T Corporation, and Samsung Heavy Industries. The document provides a SWOT analysis of Samsung's strengths such as innovative designs and brand reputation, weaknesses like low profit margins, and opportunities and threats in the mobile phone market. It also analyzes Samsung's business strategy using Porter's Five Forces and discusses Samsung's competitive advantage of vertical integration across its supply chain.