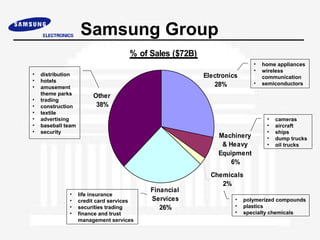
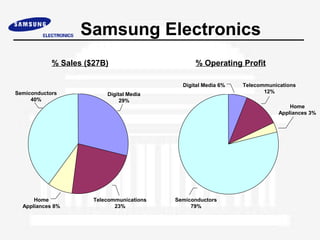
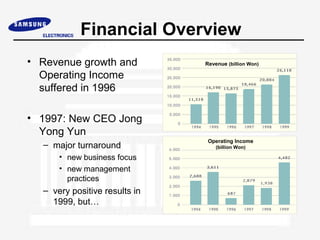
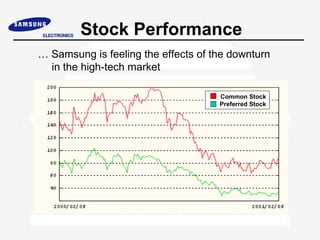
Samsung Electronics was established in 1969 and has since become a leading global electronics company. It is organized into 4 main groups covering digital media, semiconductors, information and communications, and home appliances. While it has experienced strong growth and financial success, Samsung faces ongoing challenges to maintain innovation, recruit and retain top talent, and improve corporate governance practices.