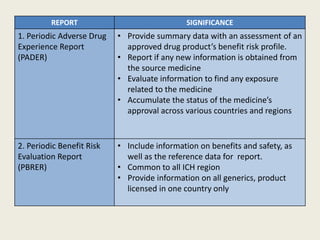
This document discusses various types of aggregate safety reports that are submitted to regulatory agencies, including Periodic Benefit Risk Evaluation Reports (PBRER), Periodic Adverse Drug Experience Reports (PADER), Development Safety Update Reports (DSUR), and Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSUR). It provides details on the purpose, format, and submission requirements for PSURs to agencies in countries like India, Europe, Singapore, Canada, Japan, and Australia. The significance of each report is also summarized.