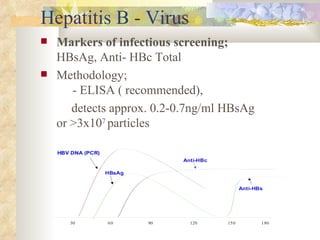
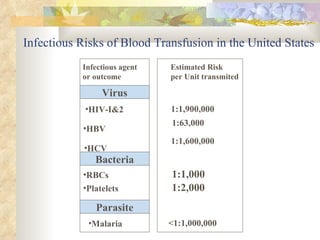
International standards for screening blood donations require testing for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, syphilis, and malaria. While screening has improved blood safety, risks remain as new infectious agents may emerge and current tests have window periods where early infections are not detected. In Pakistan, screening is not uniform across centers and some use substandard methods, like pooling donor samples, which increases transmission risk. Future directions include fully implementing standard screening tests, minimizing residual risks through new tests, encouraging healthy volunteer donors, and increasing awareness of transfusion risks.