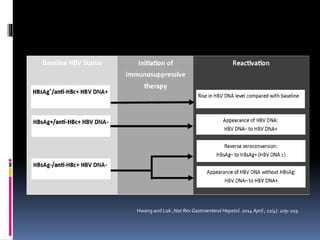
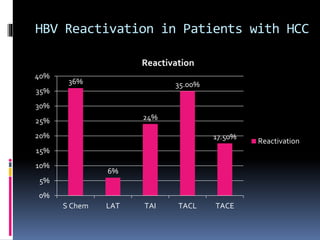
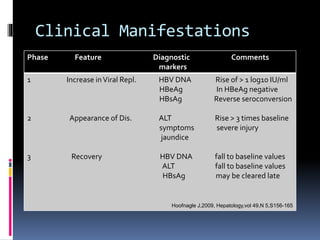
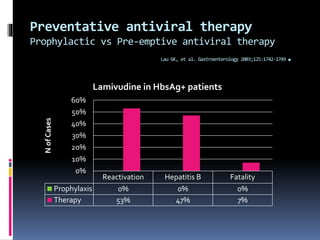
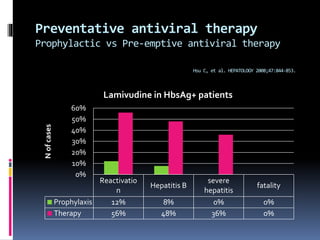
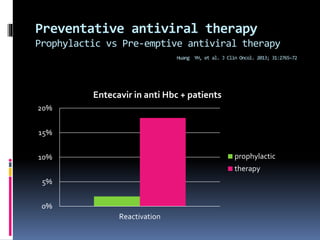
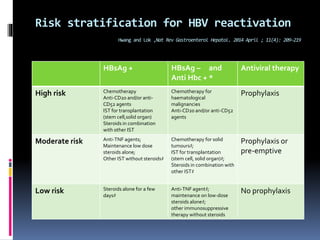
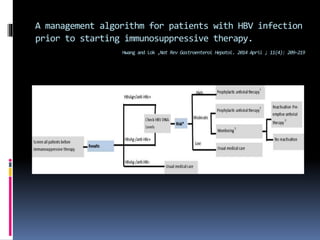
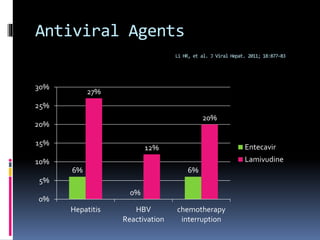
Reactivation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) can occur when a patient with resolved or inactive HBV undergoes immunosuppression. This document discusses the definition, causes, incidence, risk factors, clinical manifestations, outcomes, prevention and treatment of HBV reactivation. Key points include: screening patients for HBV before immunosuppression, using prophylactic antiviral therapy for high risk patients, and monitoring or using pre-emptive therapy for moderate risk patients. Entecavir is recommended over lamivudine or tenofovir for prevention due to lower resistance risk. Therapy should begin before and continue after immunosuppression.