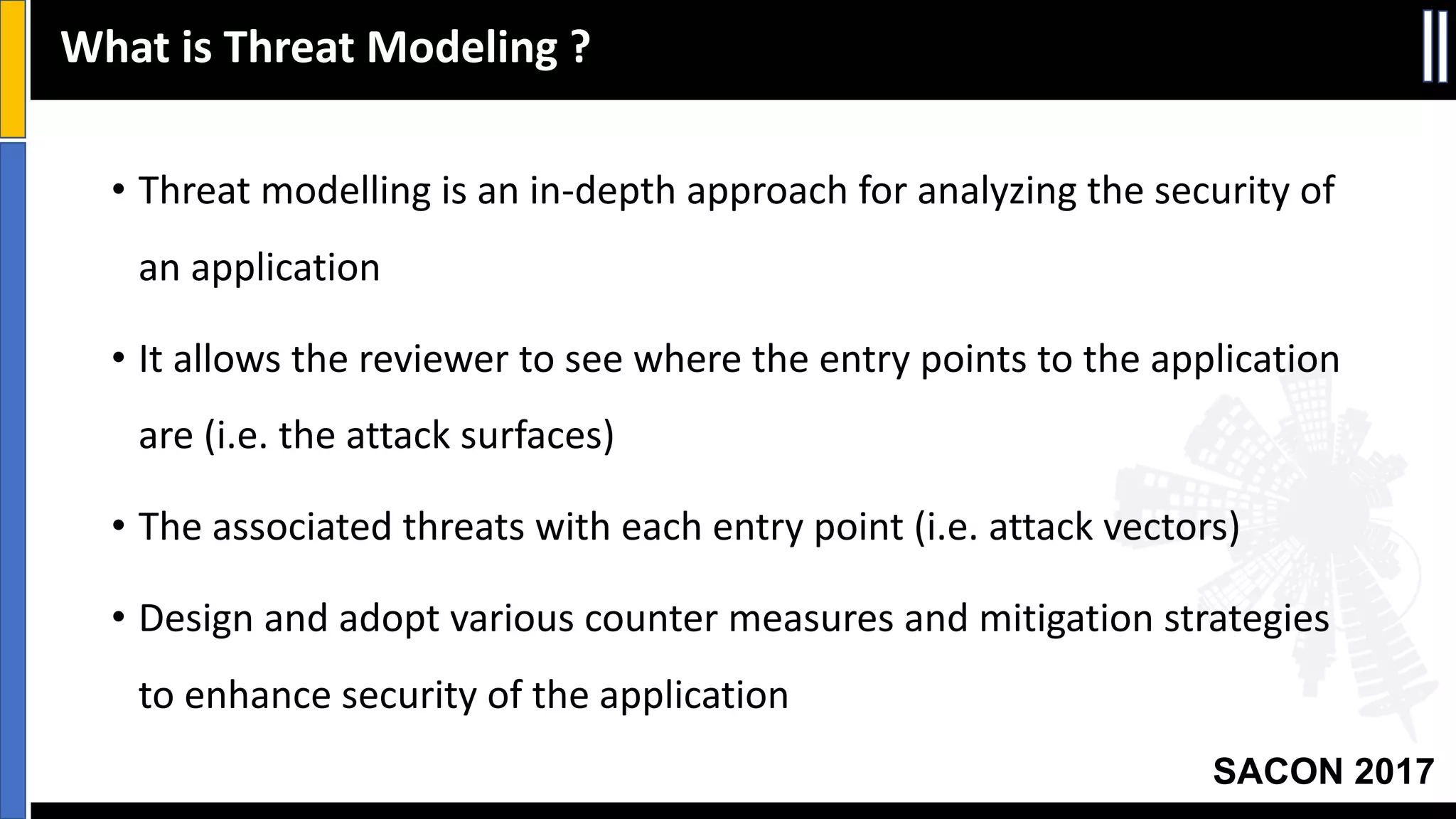
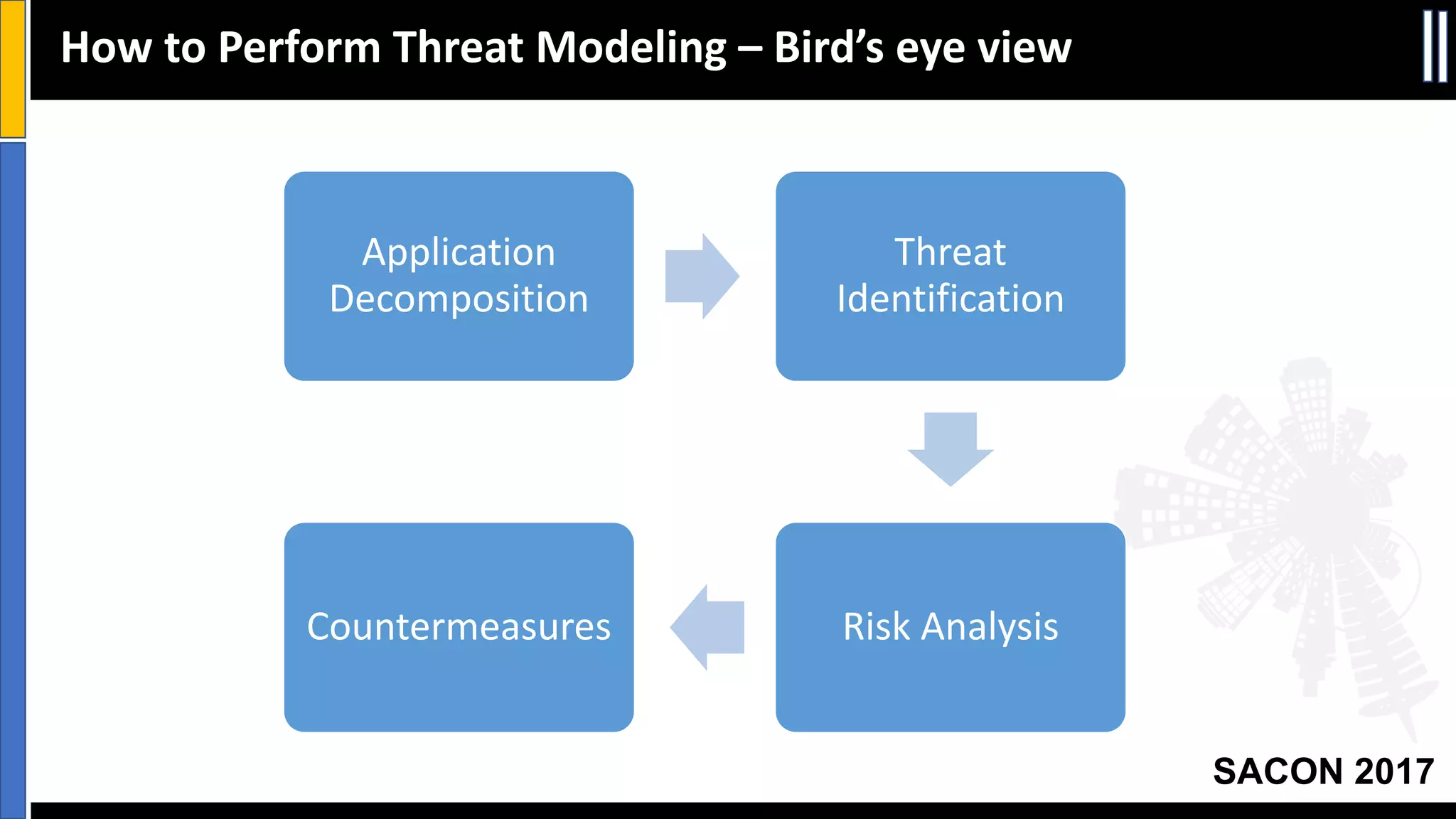
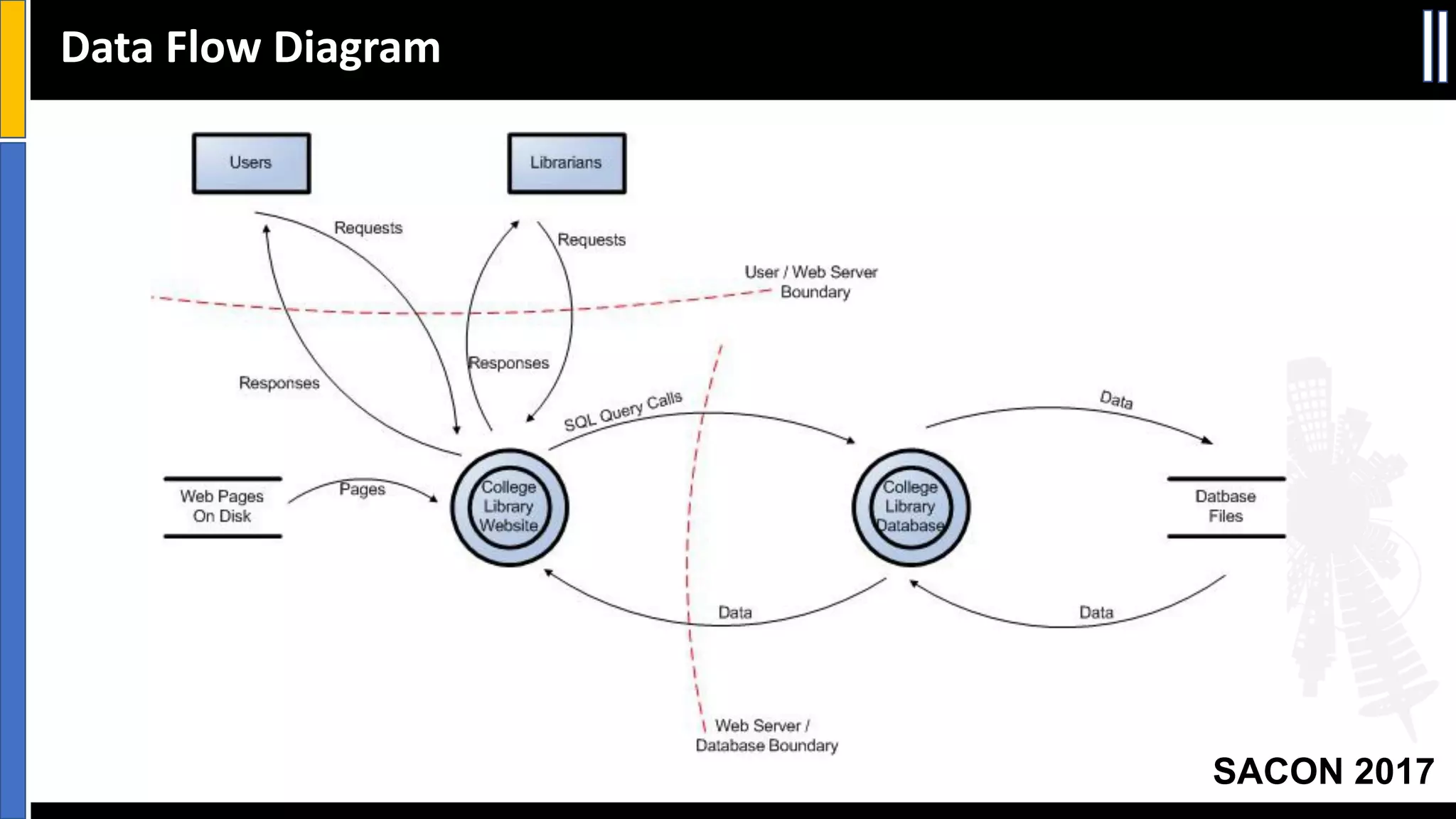
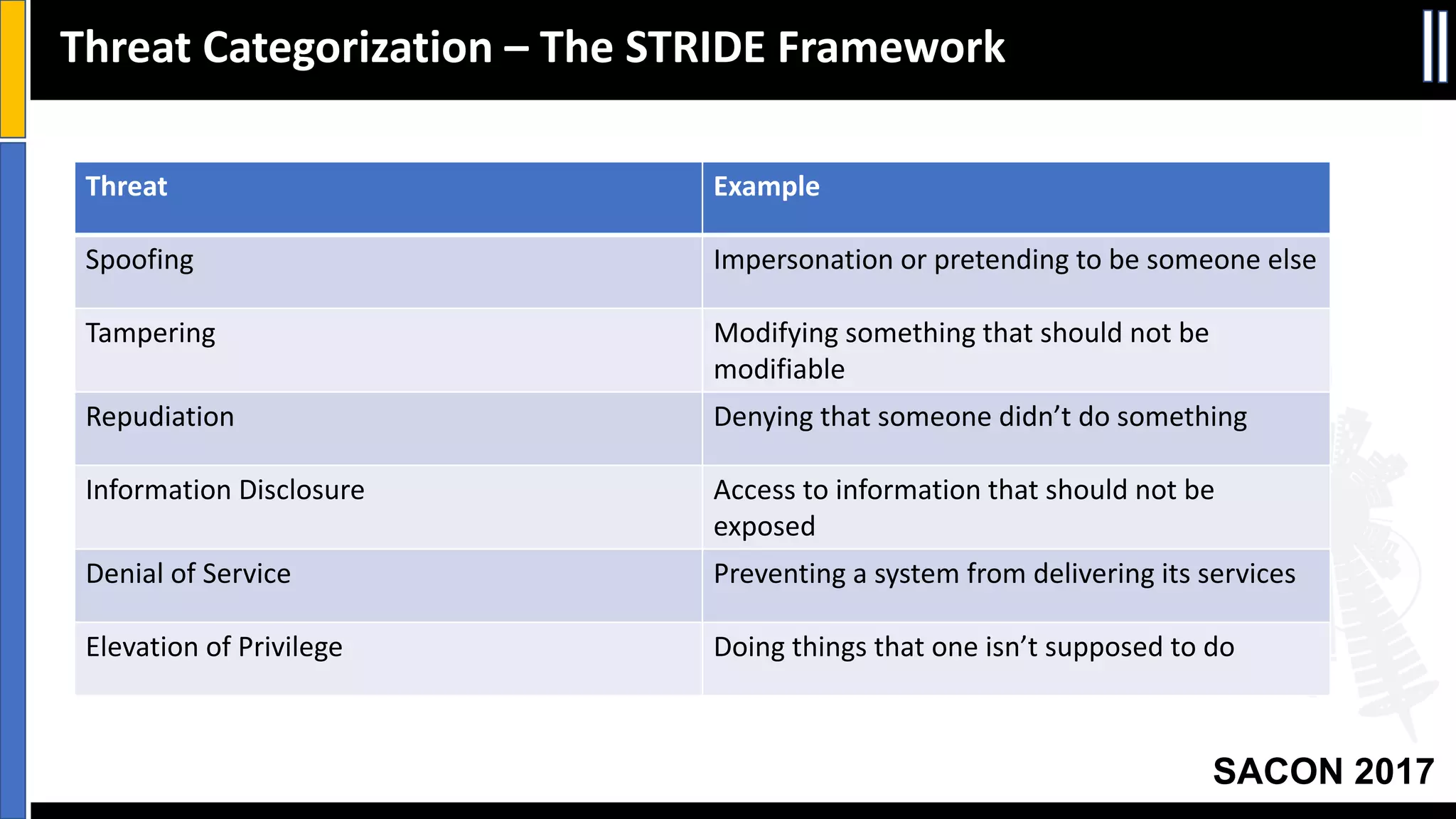
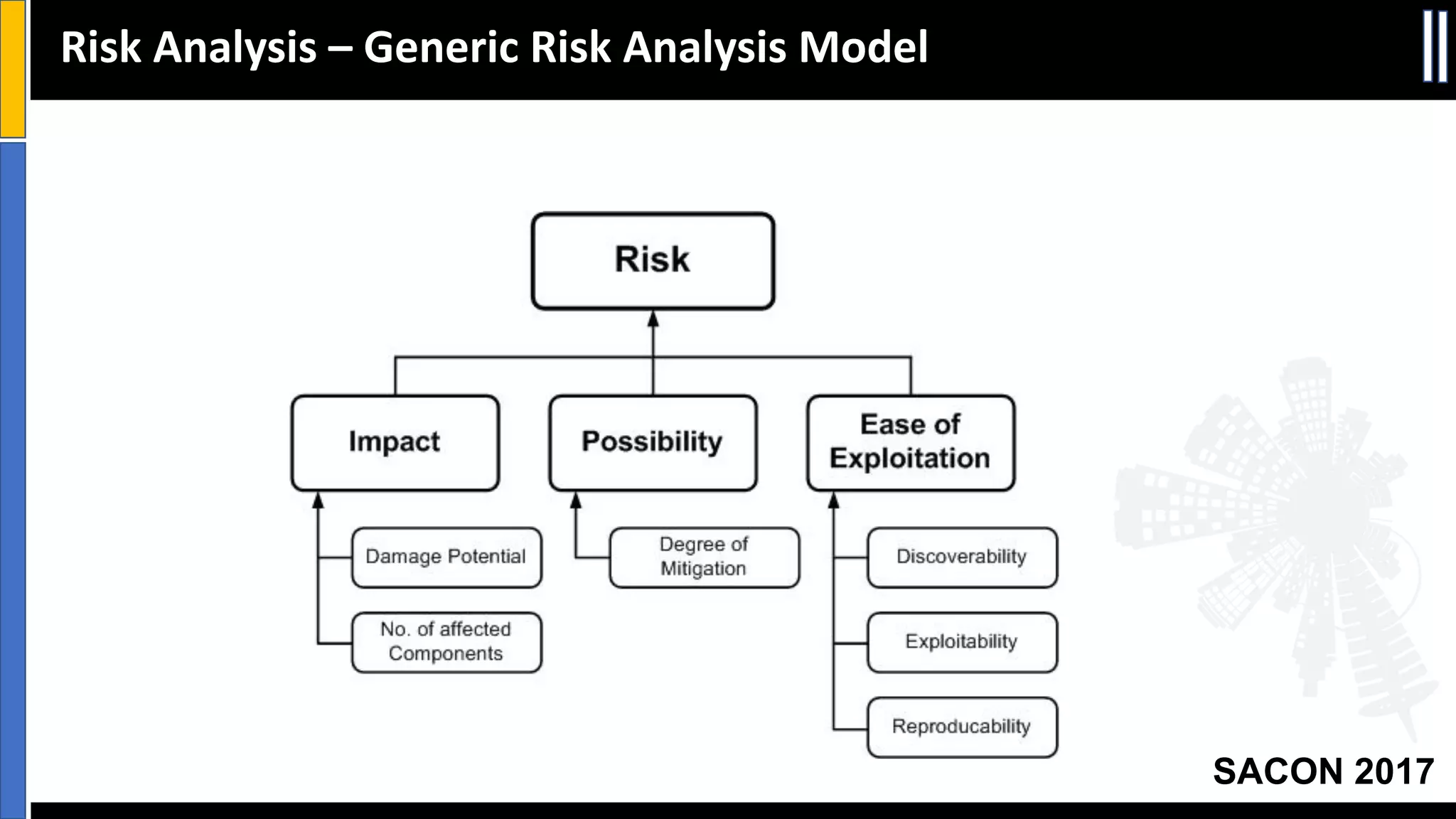
This document discusses threat modeling and provides an overview of the threat modeling process. It explains that threat modeling involves decomposing an application, identifying threats, analyzing risks, and defining countermeasures. The key steps are decomposing the application into components and data flows, identifying threats using techniques like STRIDE categorization, prioritizing risks using frameworks like DREAD, and specifying security controls to mitigate threats. The goal of threat modeling is to understand vulnerabilities and design secure applications.