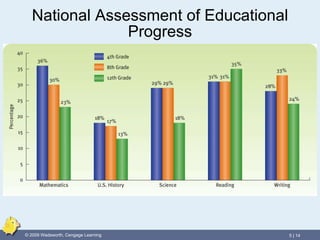
The document discusses key aspects of curriculum including the formal curriculum that is explicitly taught versus the hidden curriculum that is taught informally. It also discusses current curriculum topics like language arts, mathematics, science, social studies, foreign languages, the arts, physical education, electives, career and technical education. For each topic it outlines the general goals and current issues and trends. It concludes by discussing approaches like cooperative learning, critical thinking, differentiated instruction, and debates around the curriculum.