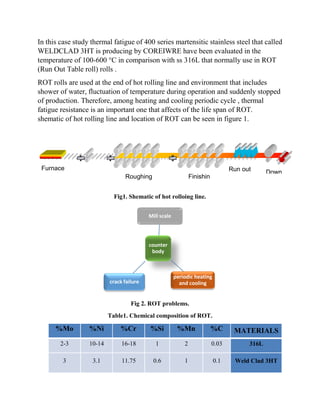
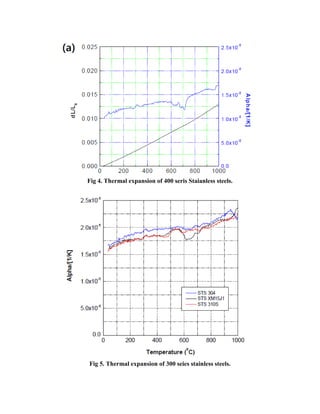
This case study evaluates the thermal fatigue resistance of 400 series martensitic stainless steel, specifically weldclad 3ht, compared to 316l stainless steel used in run out table rolls (rot), focusing on their behavior under temperature fluctuations. The findings indicate that the weld clad 3ht exhibits lower maximum stress and better fatigue resistance compared to 316l, which translates into longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs for the rolling process. Additionally, the differences in thermal expansion and microstructure further contribute to the performance advantages of weld clad 3ht in these applications.