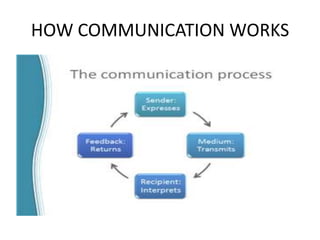
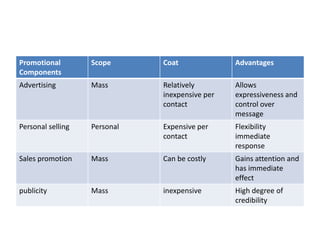
This presentation is from Group Two and includes nine members who will discuss marketing communication. Marketing communication aims to influence customer behavior by bringing products, benefits, features, and prices to the attention of target customers. Effective communication is not complete until the message is understood as intended. The elements of the communication process must be congruent to avoid communication disasters. Promotion is an important part of marketing and includes advertising, personal selling, sales promotion and publicity. The promotional mix and budget are determined based on factors like the product, market, and available funds.