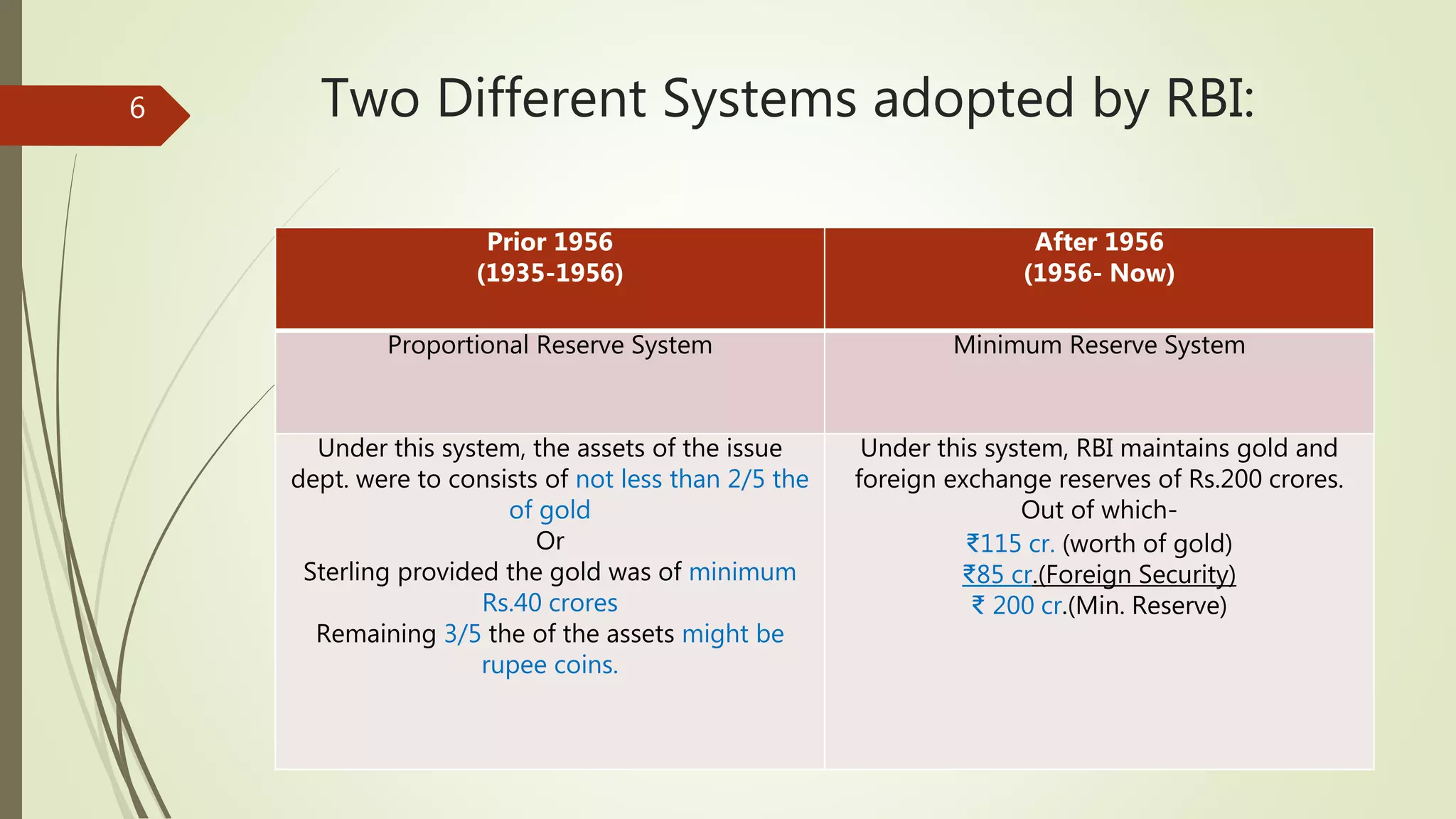
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was established in 1935 according to the Reserve Bank of India Act of 1934. It has several important roles, including being the sole issuer of currency notes, the banker's bank (holding reserves for commercial banks and providing clearing and remittance facilities), the banker to the government of India, controlling credit in the economy through various instruments, managing foreign exchange and representing India in the IMF, collecting and publishing various economic data, and promoting development through institutions that support agriculture, industry, and safeguard depositors. The RBI was initially privately owned but is now fully owned by the Government of India.