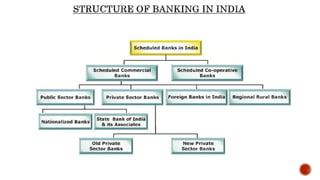
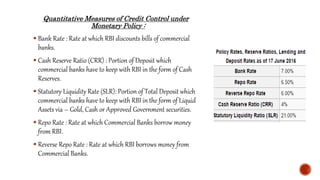
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India's central bank and was established in 1935. It controls monetary policy and regulates the banking system. As the central bank, RBI acts as a bank for banks by facilitating inter-bank transactions and maintaining statutory reserves. It also acts as a lender of last resort for banks during financial crises. RBI aims to maintain price stability and manage currency, credit, and foreign exchange to promote balanced economic growth in India.