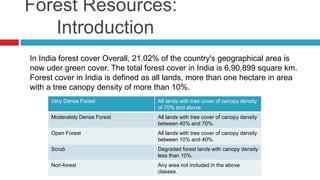
This document discusses forest resources and the importance of forests. It covers:
1) The key functions of forests including protective, productive, regulatory and accessory functions that benefit both humans and the natural world.
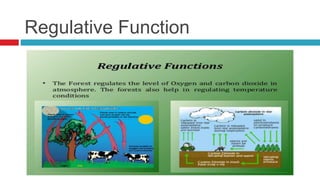
2) The types and ecological importance of forests in regulating climate, providing habitat, producing oxygen and controlling water flow.
3) The economic importance of forests in providing timber, fuelwood, materials for industry and food.
4) The causes and effects of deforestation including population growth, shifting cultivation, infrastructure development and forest fires.
5) The need for afforestation to control deforestation and its objectives such as preventing soil erosion and regulating climate.