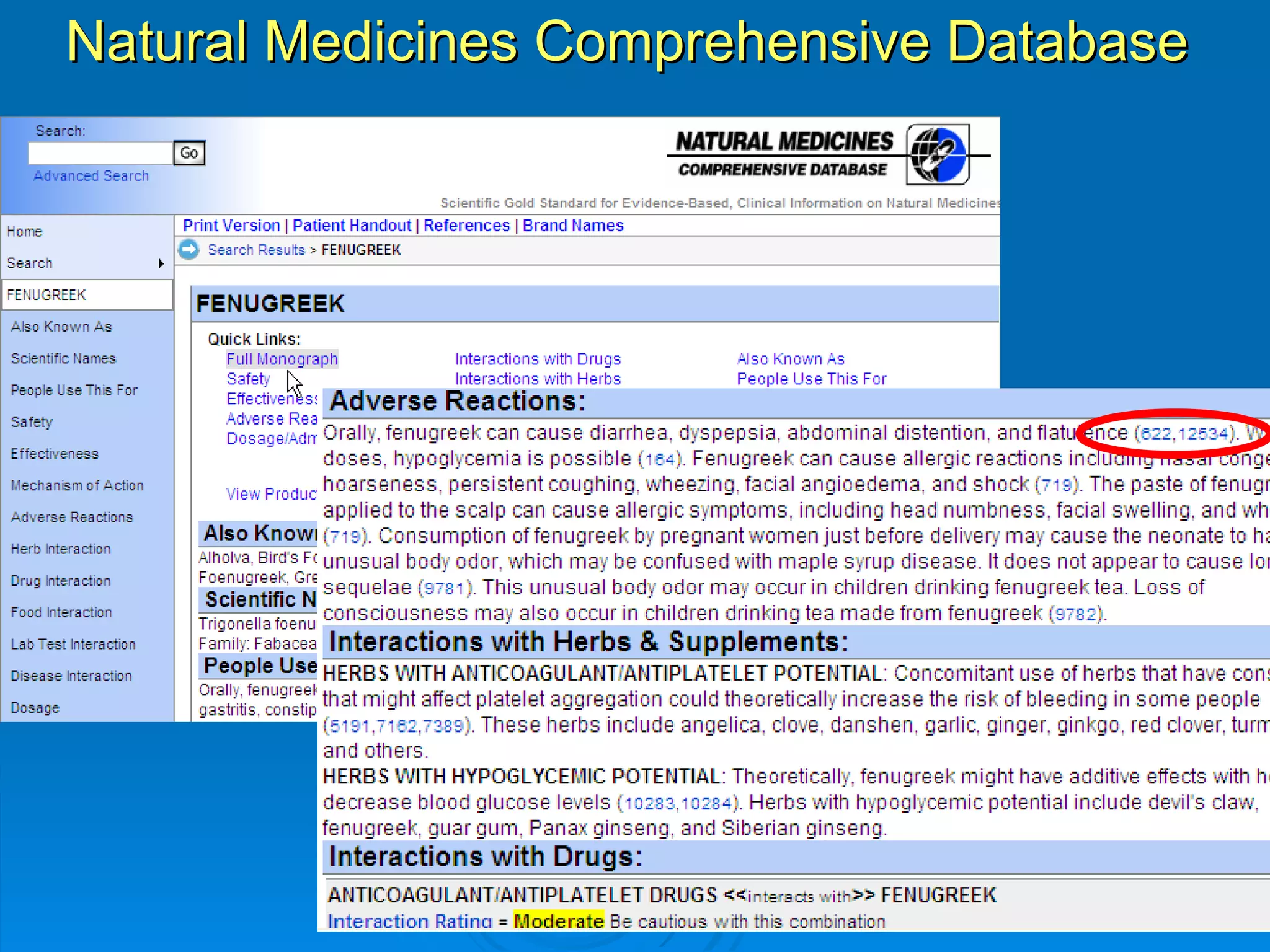
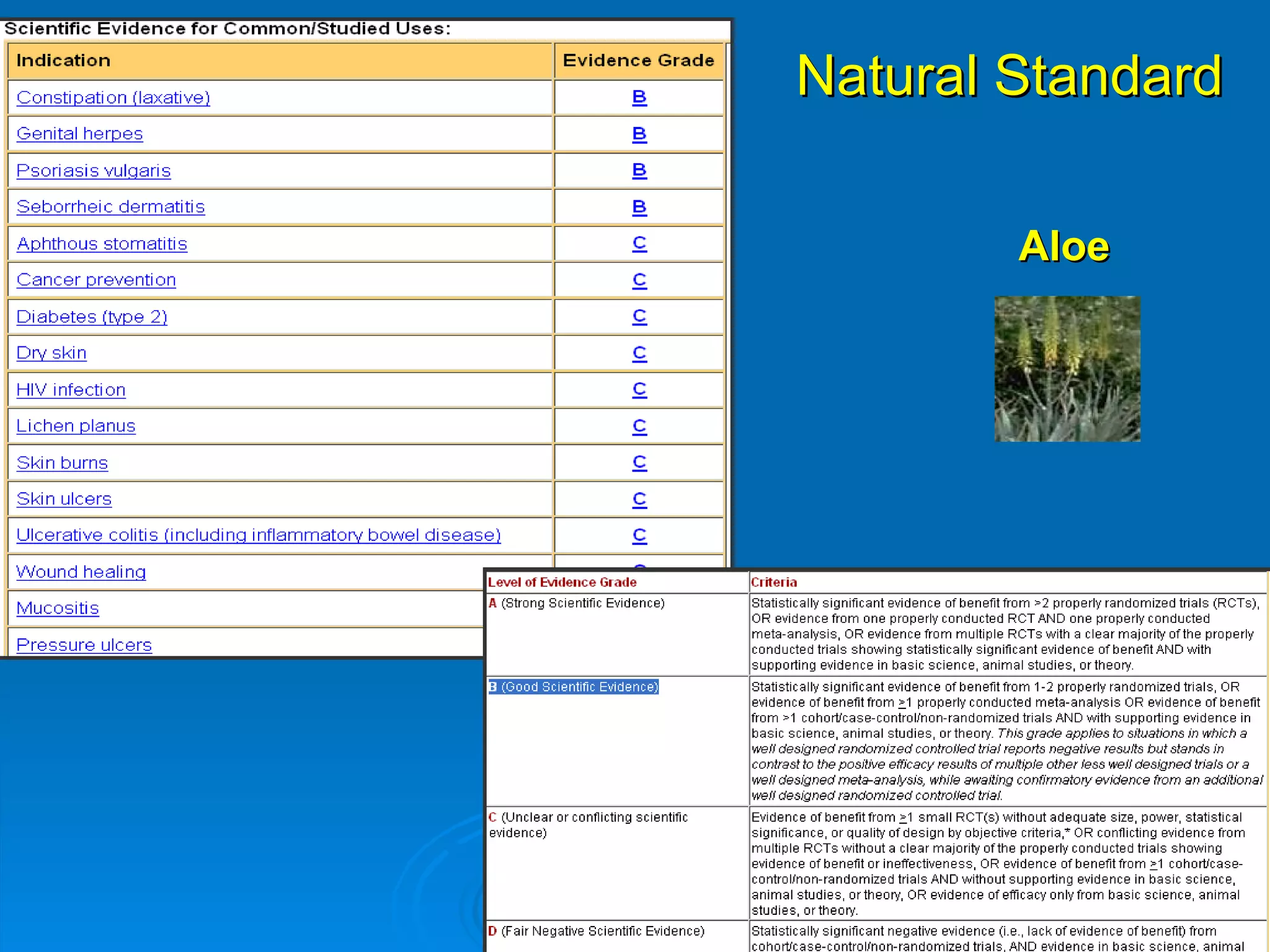
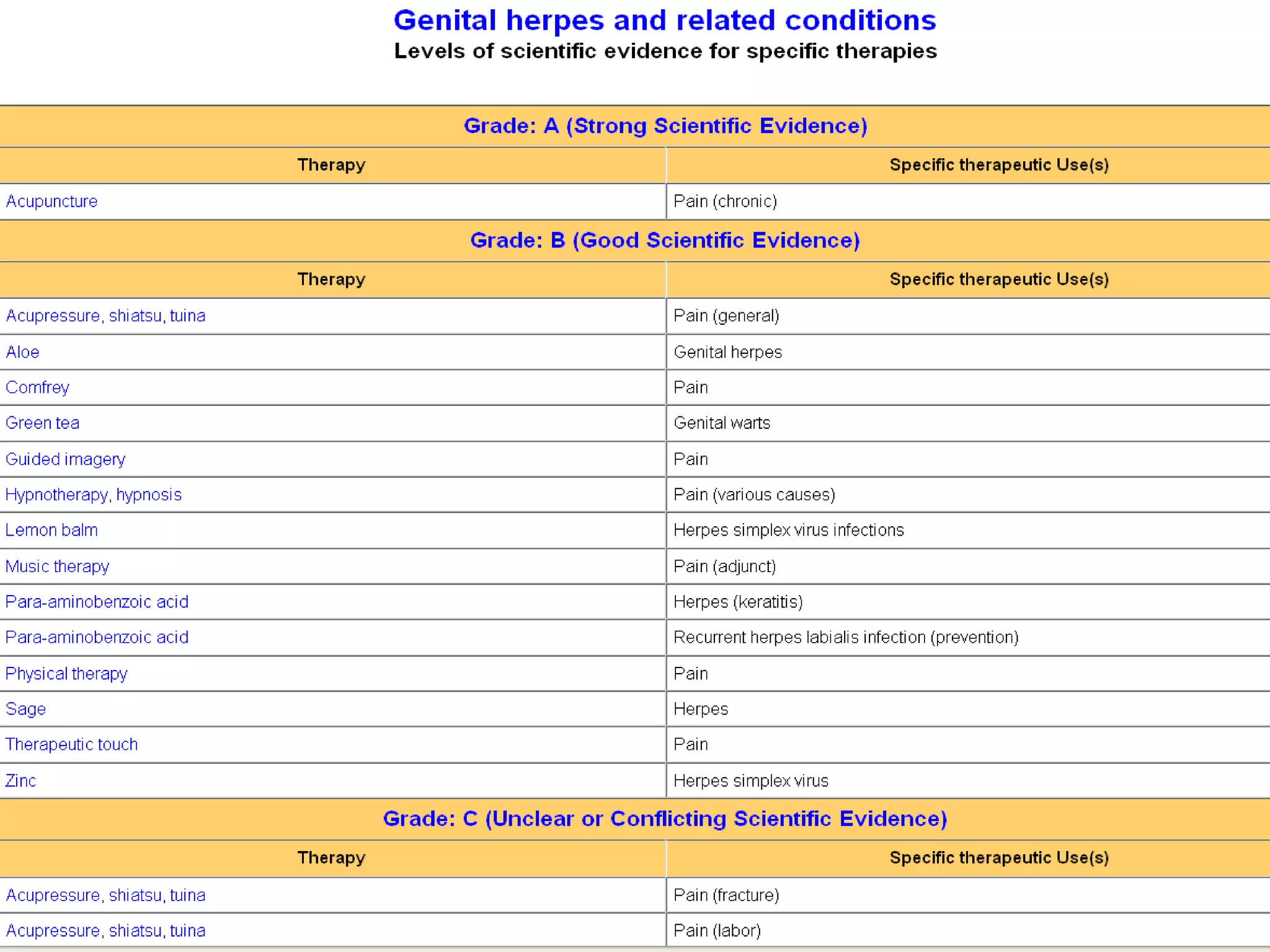
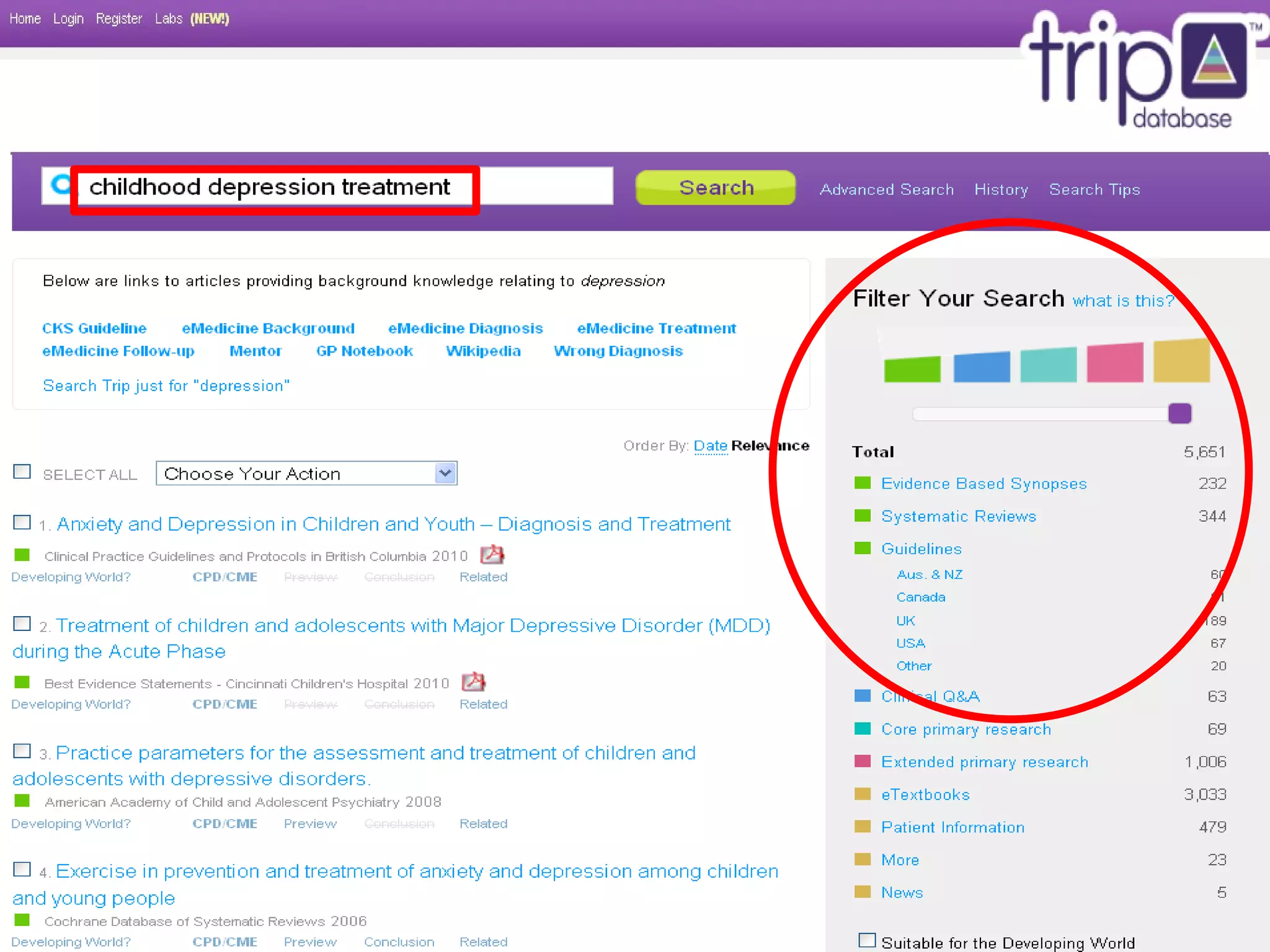
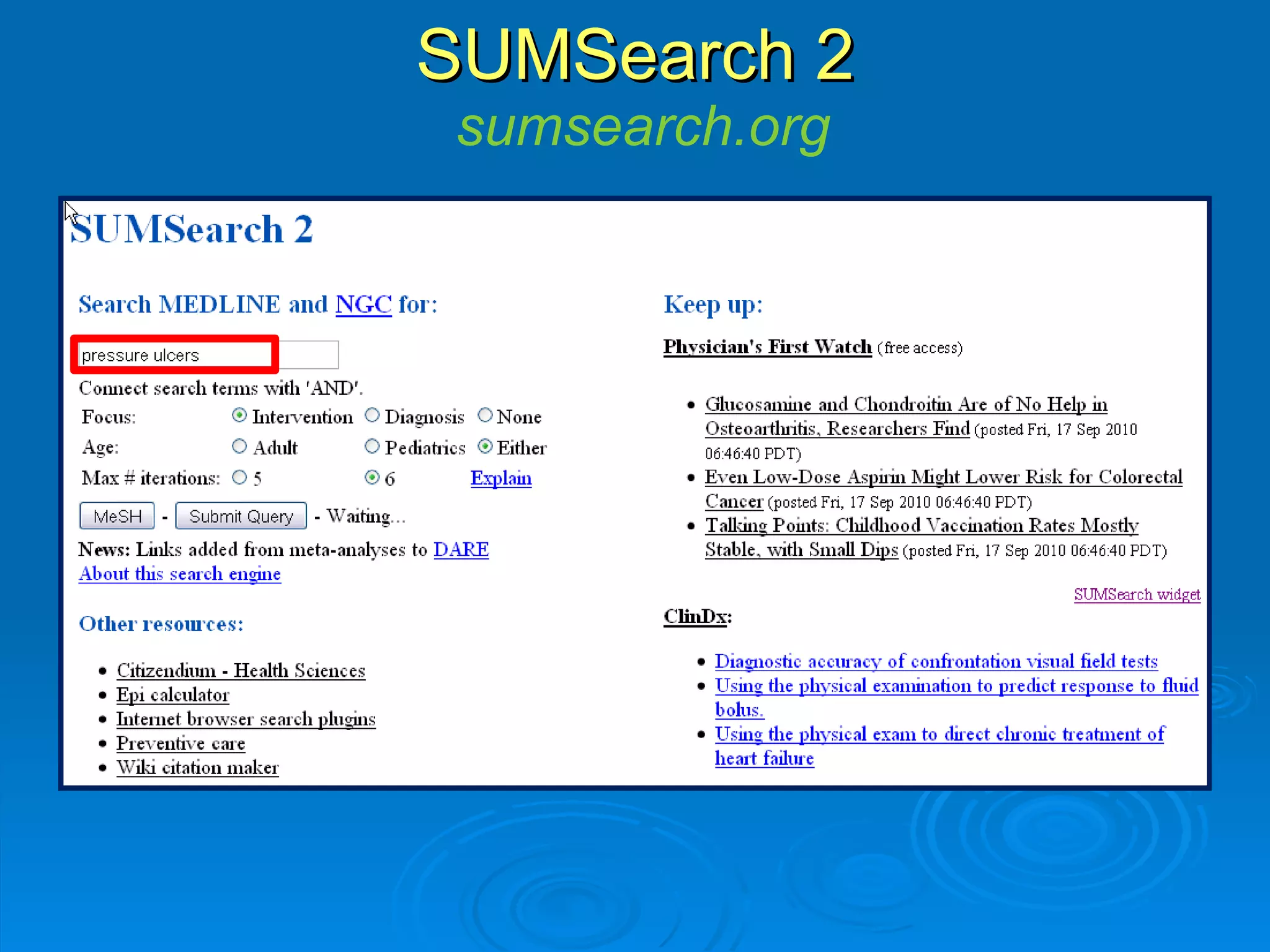
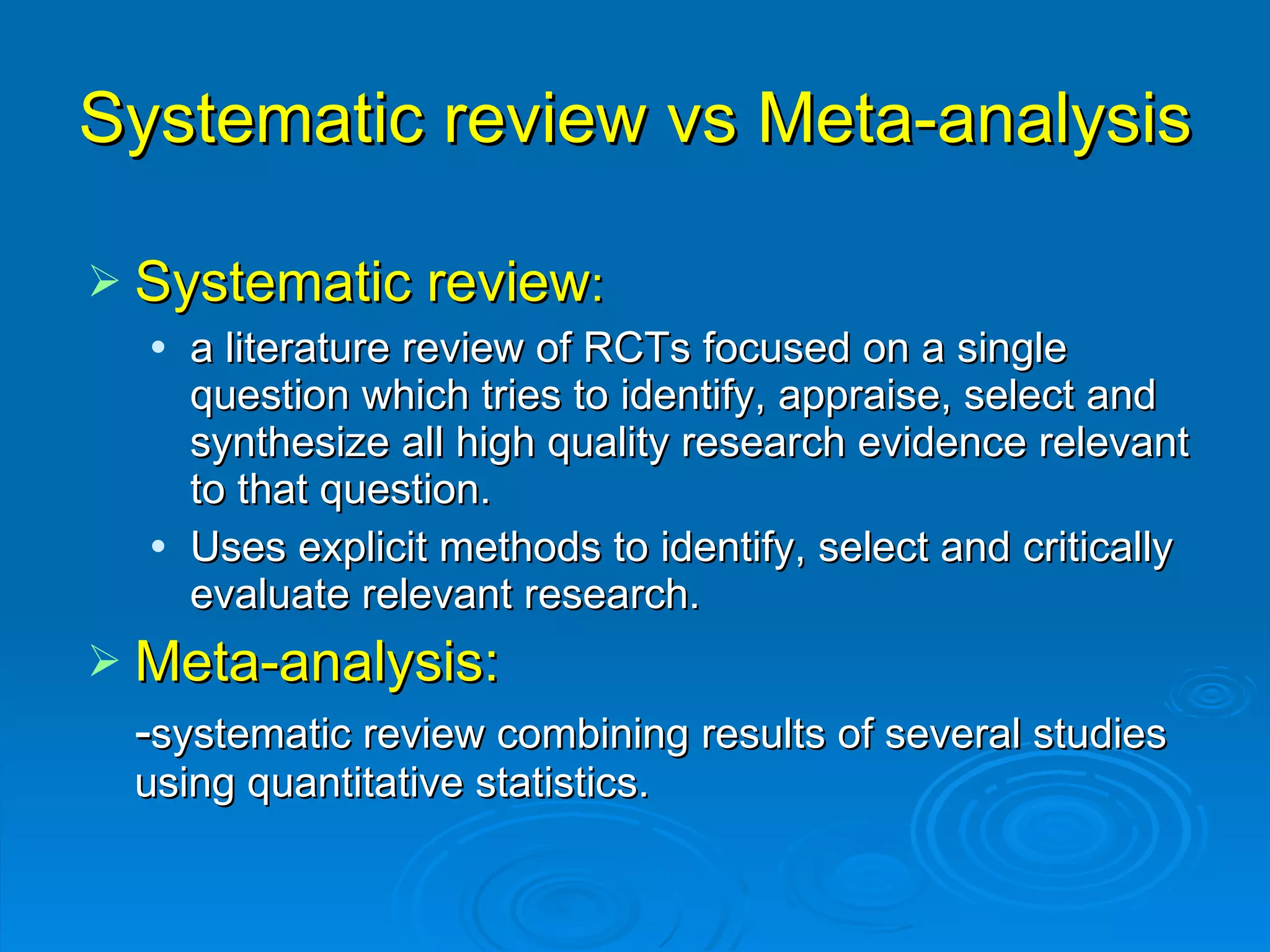
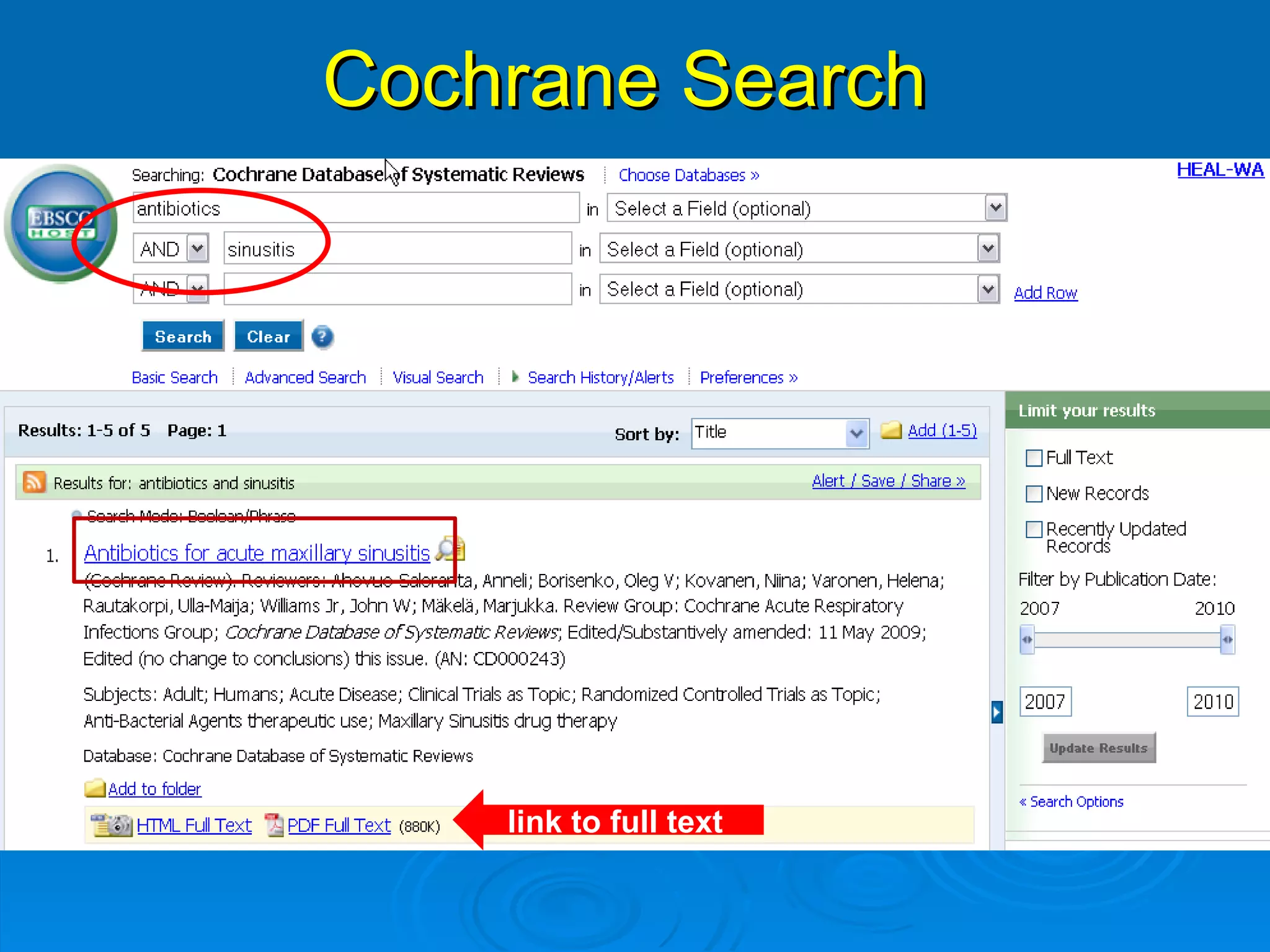
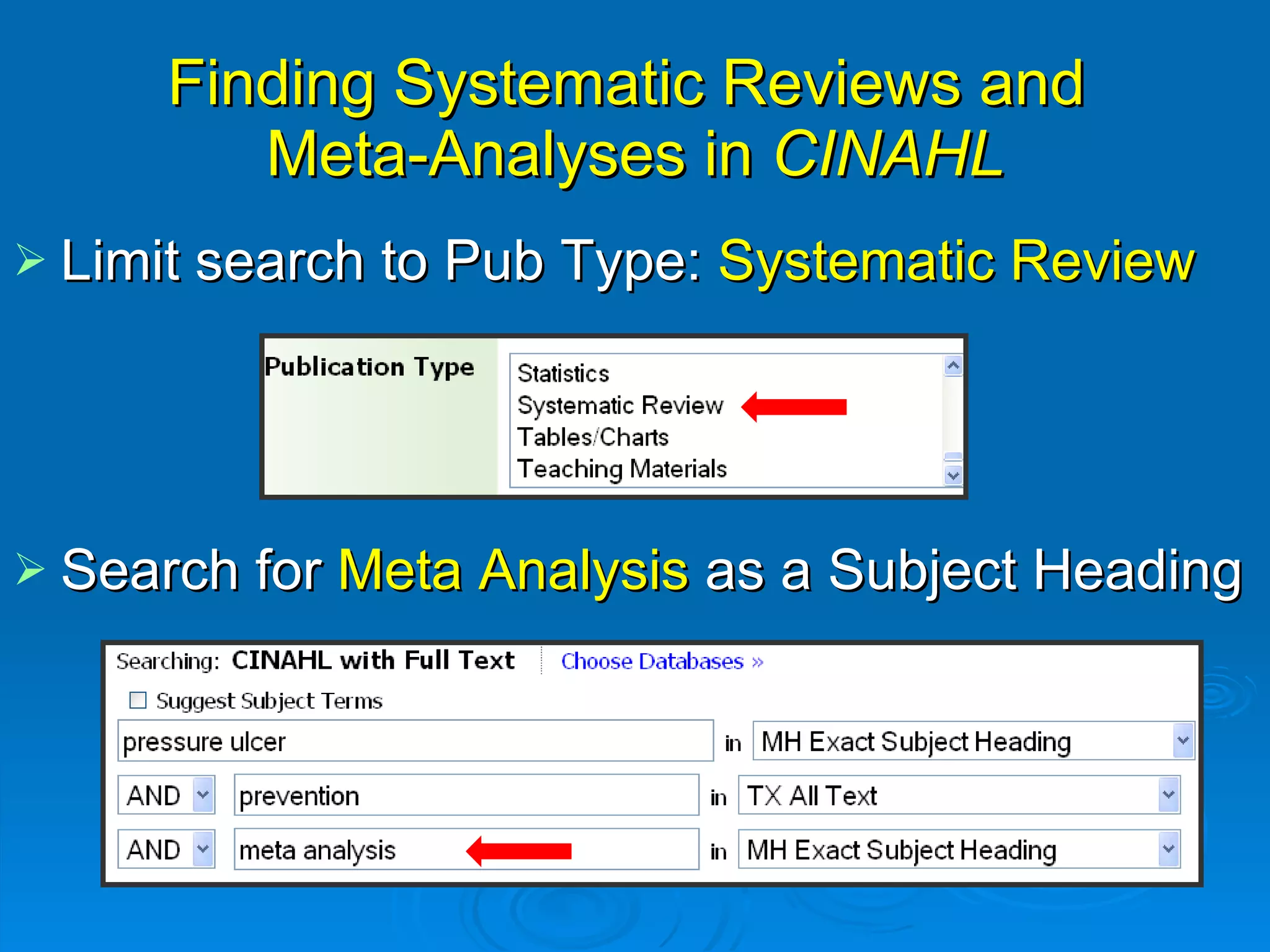
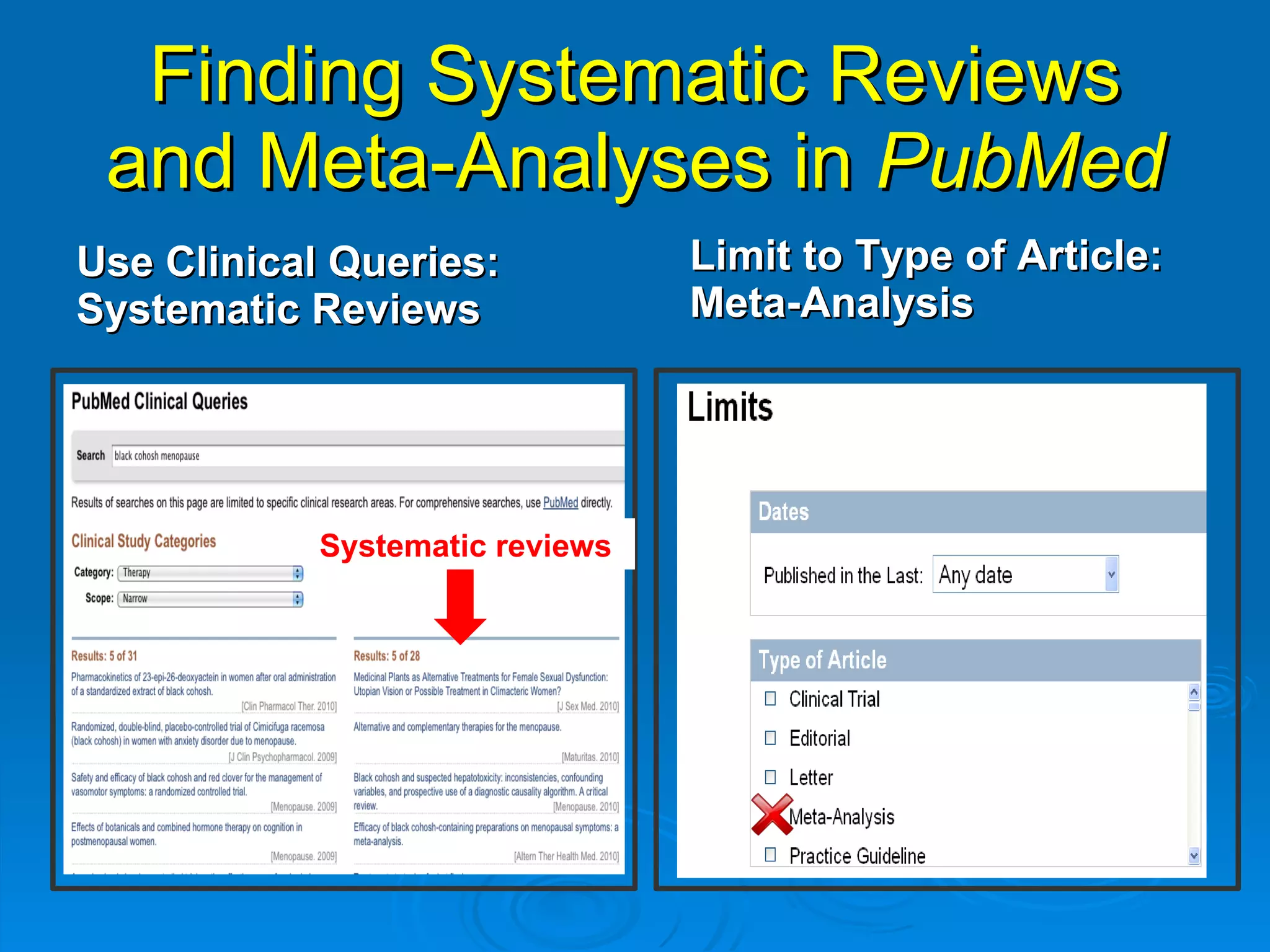
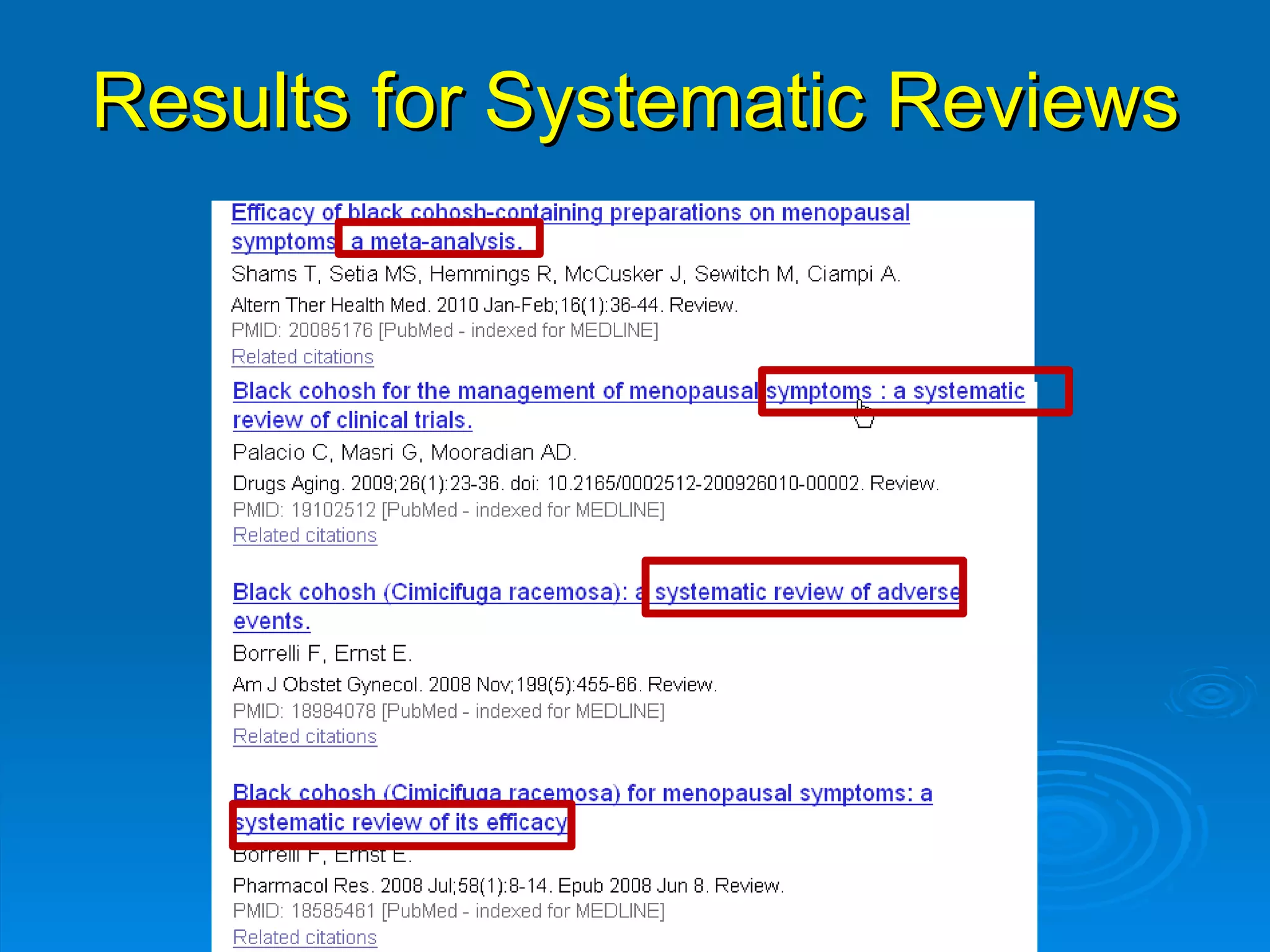
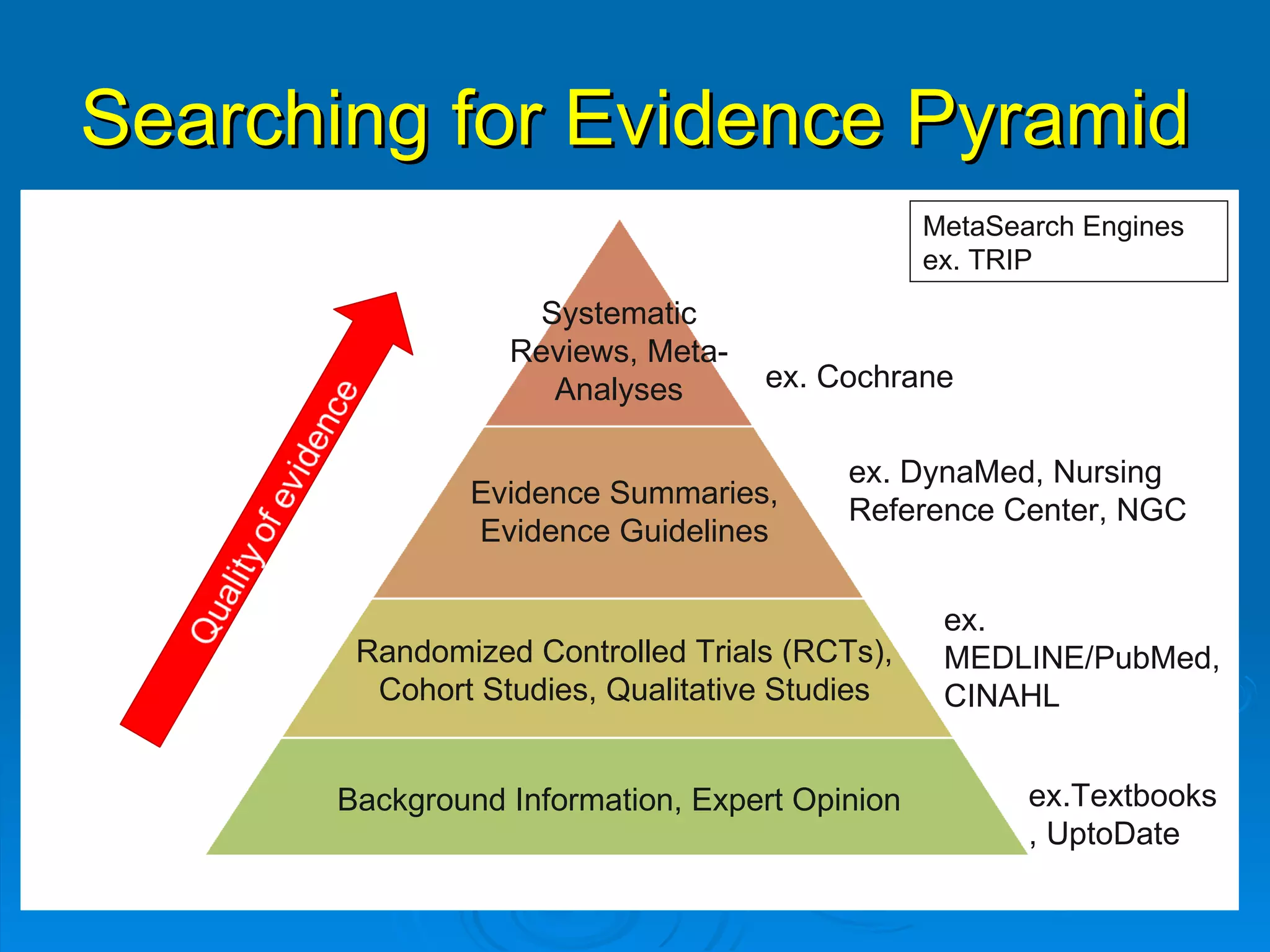
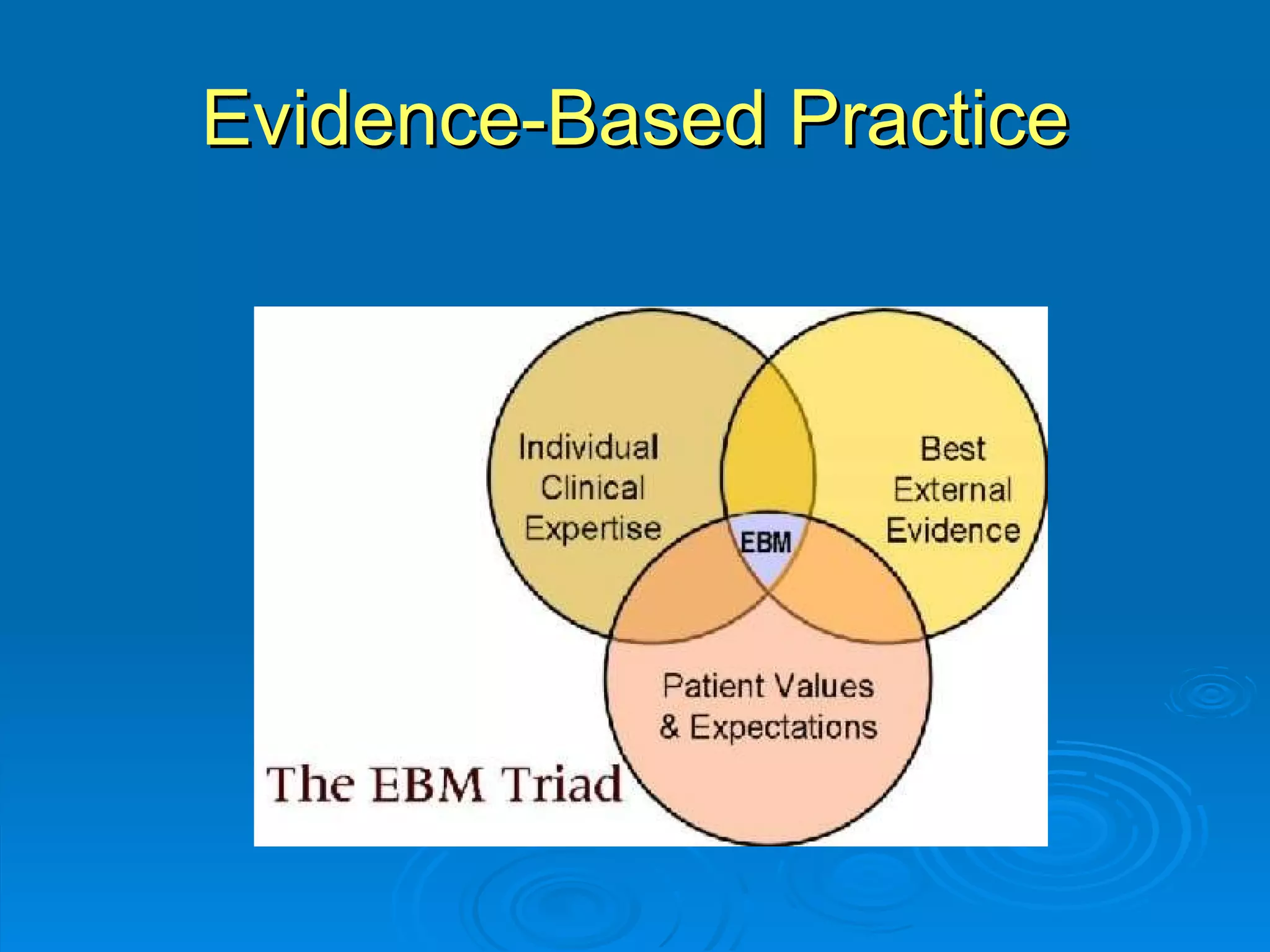
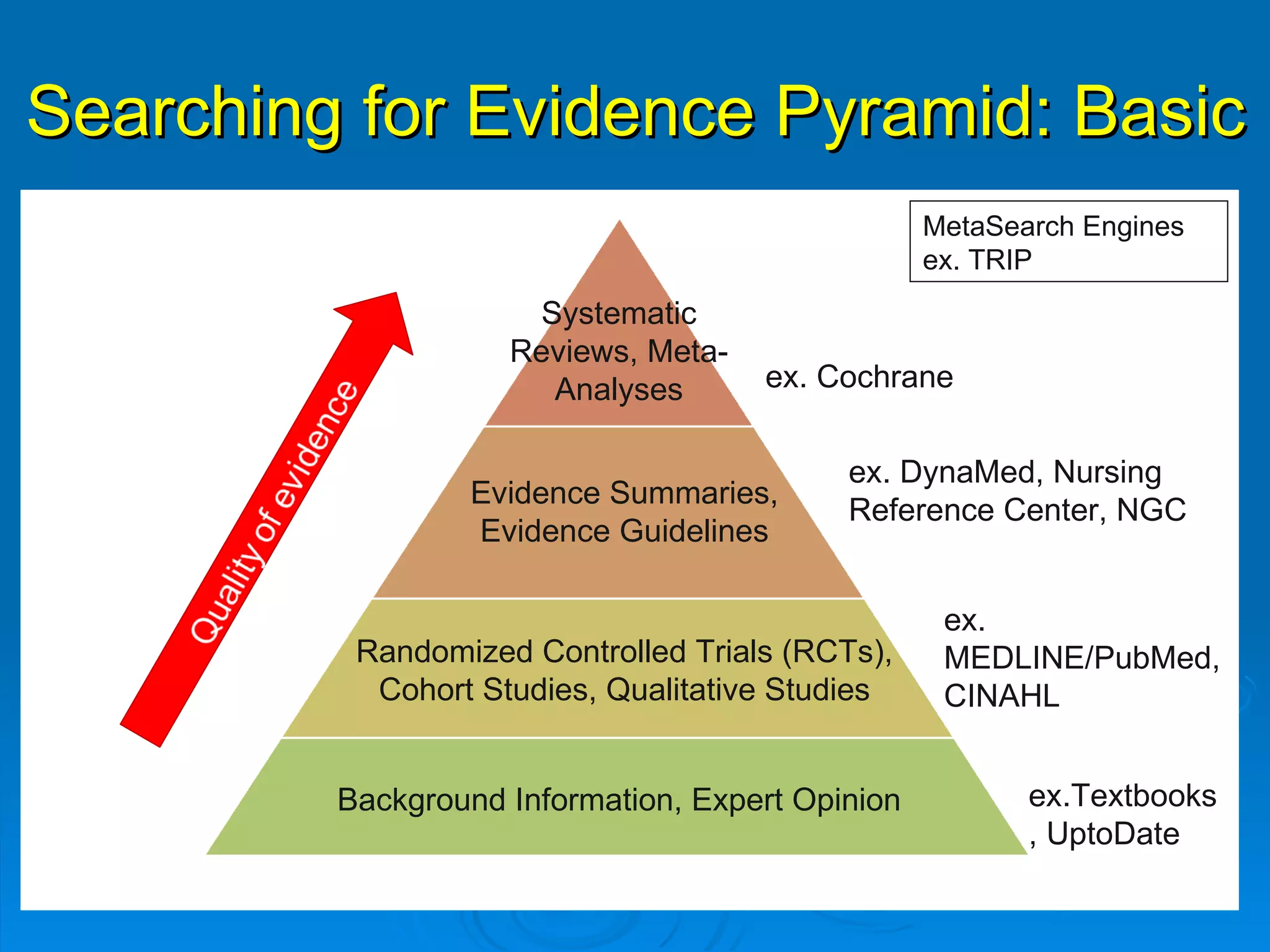
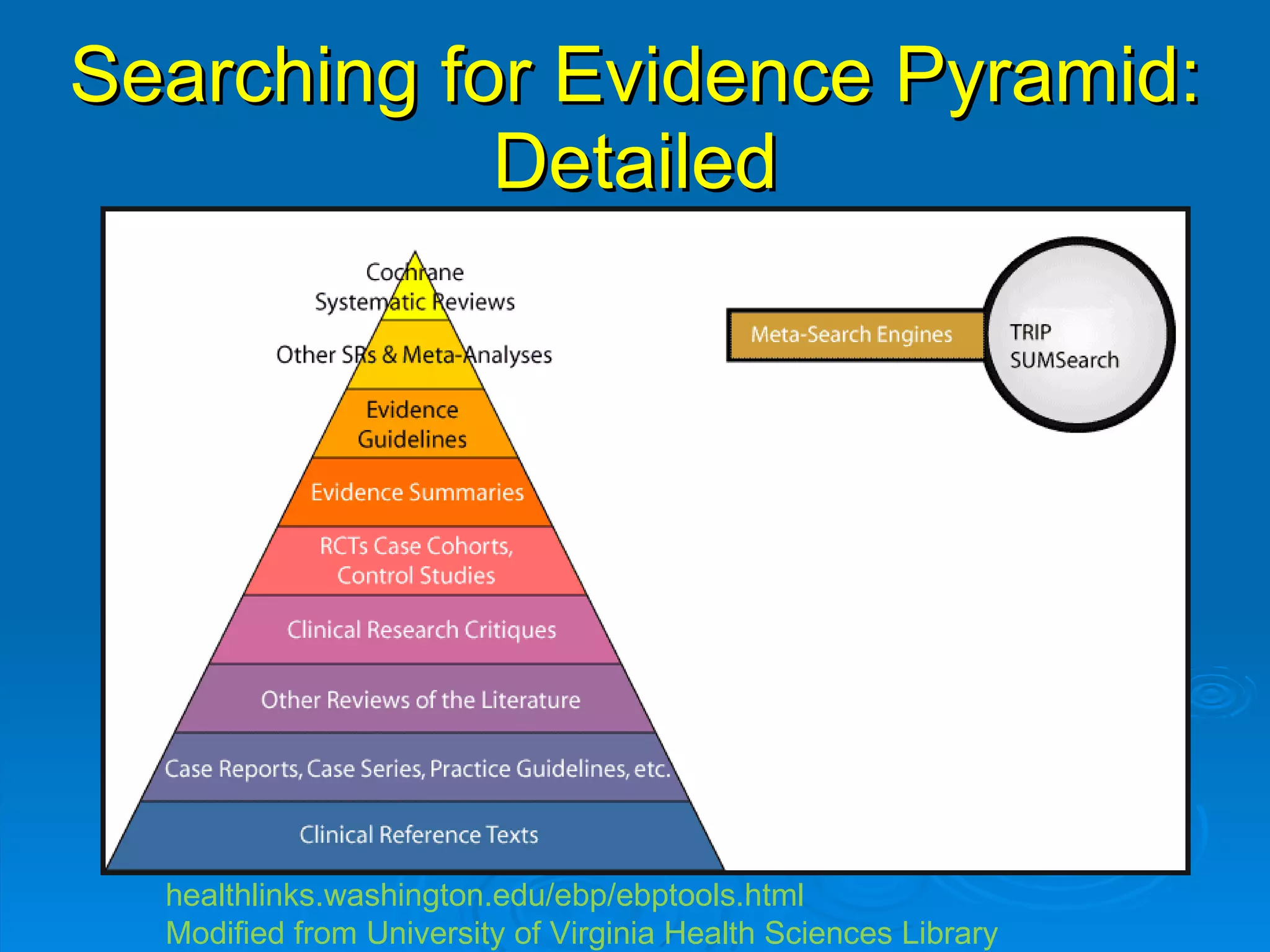
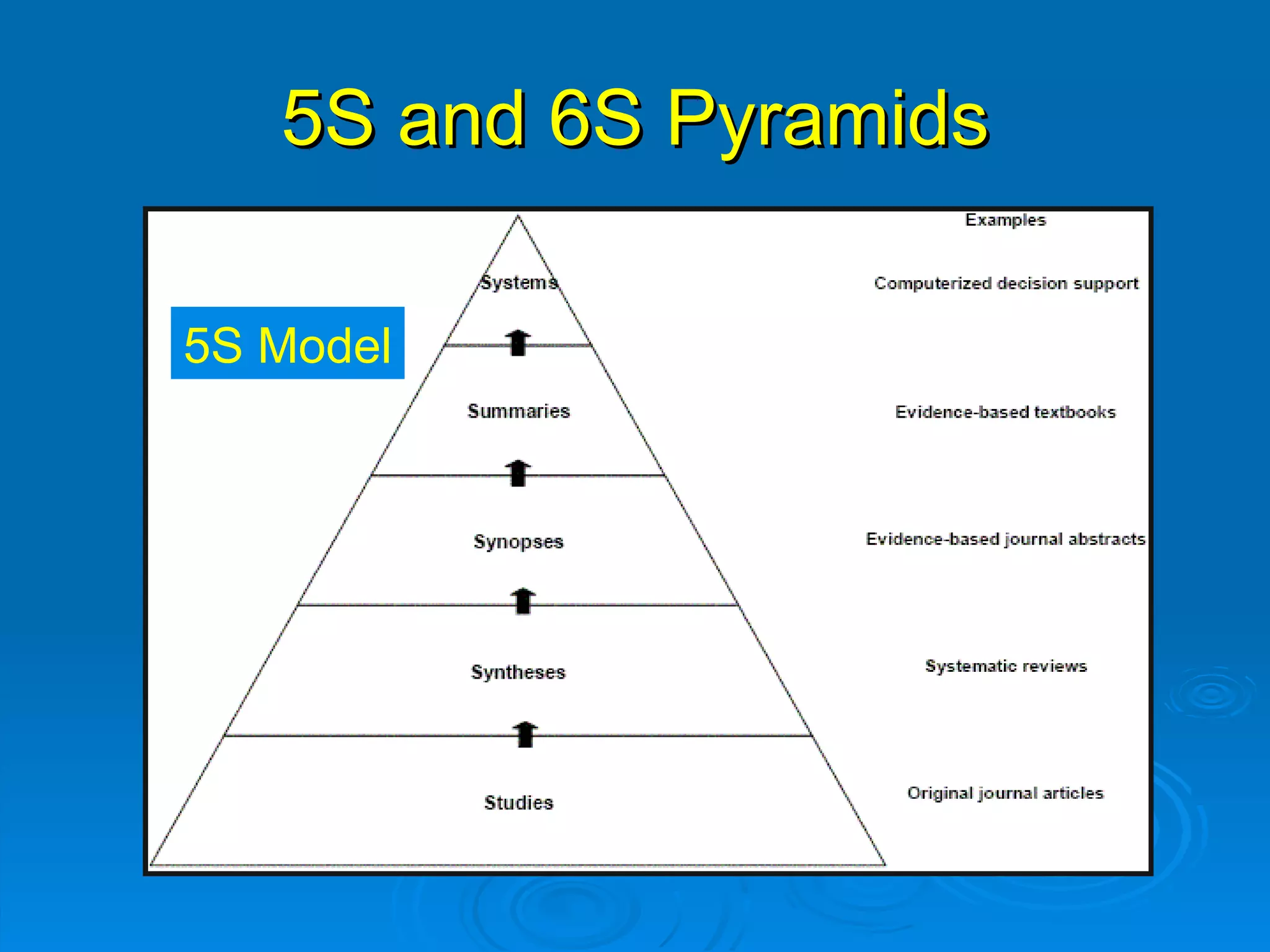
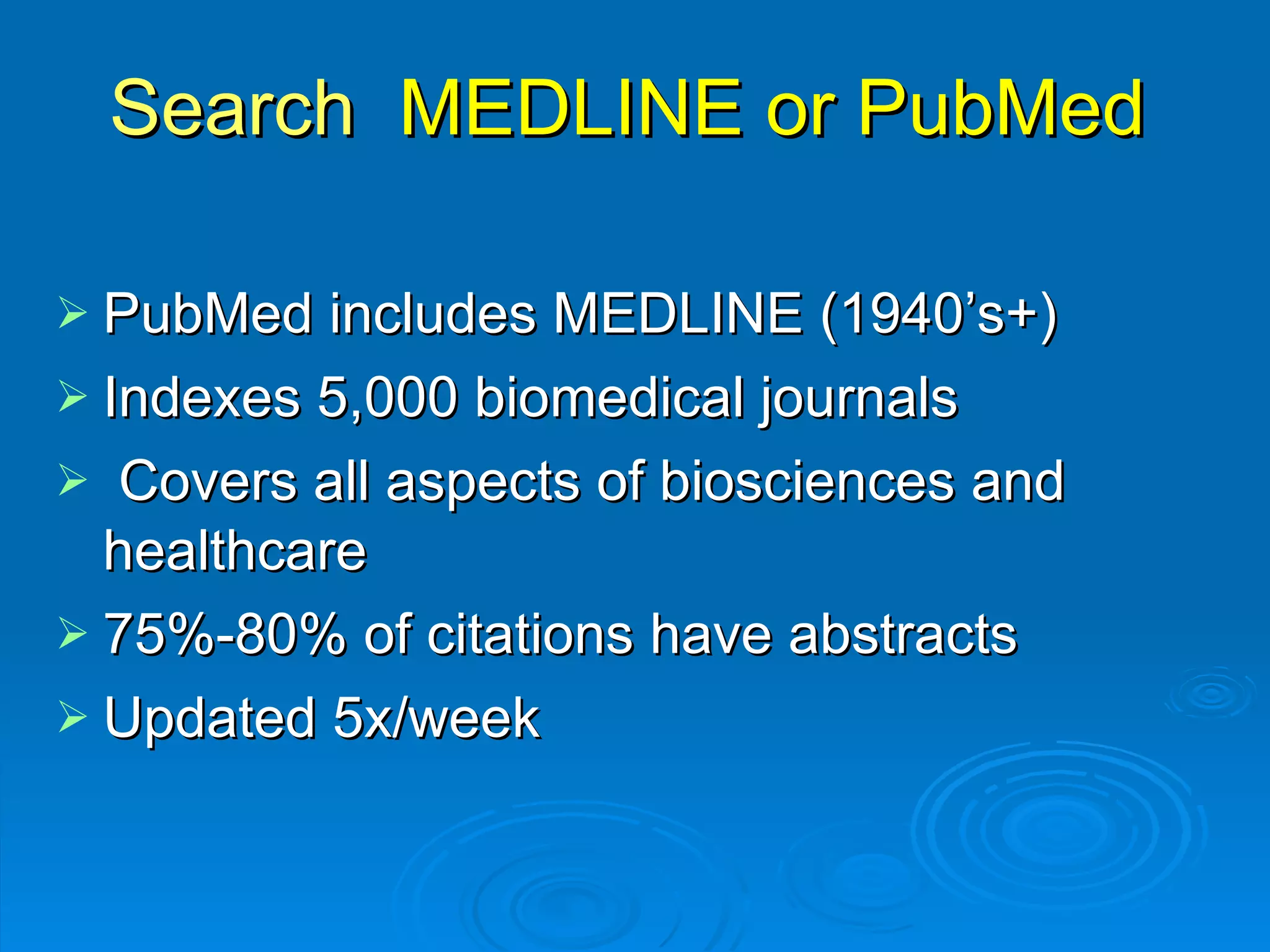
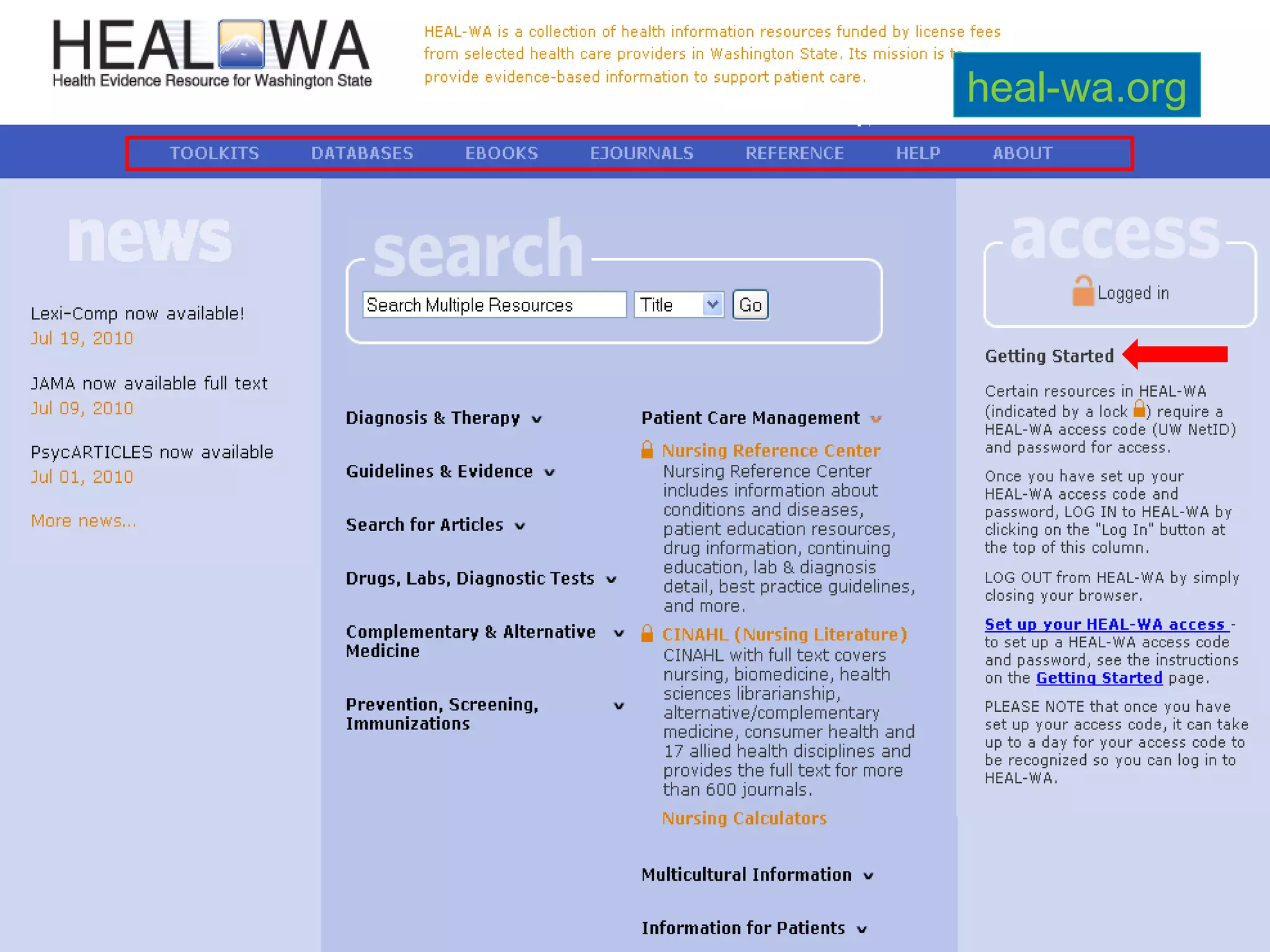
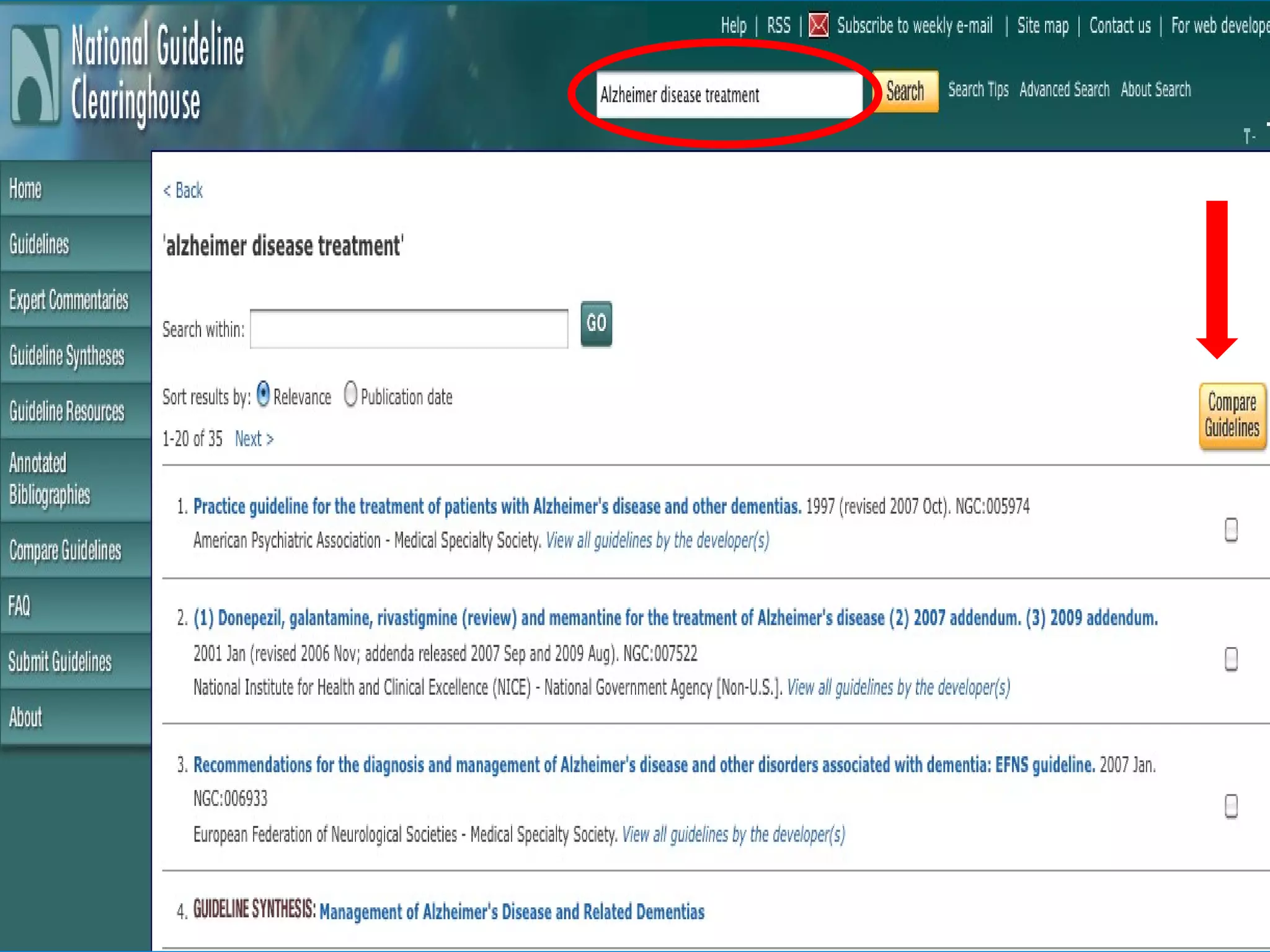
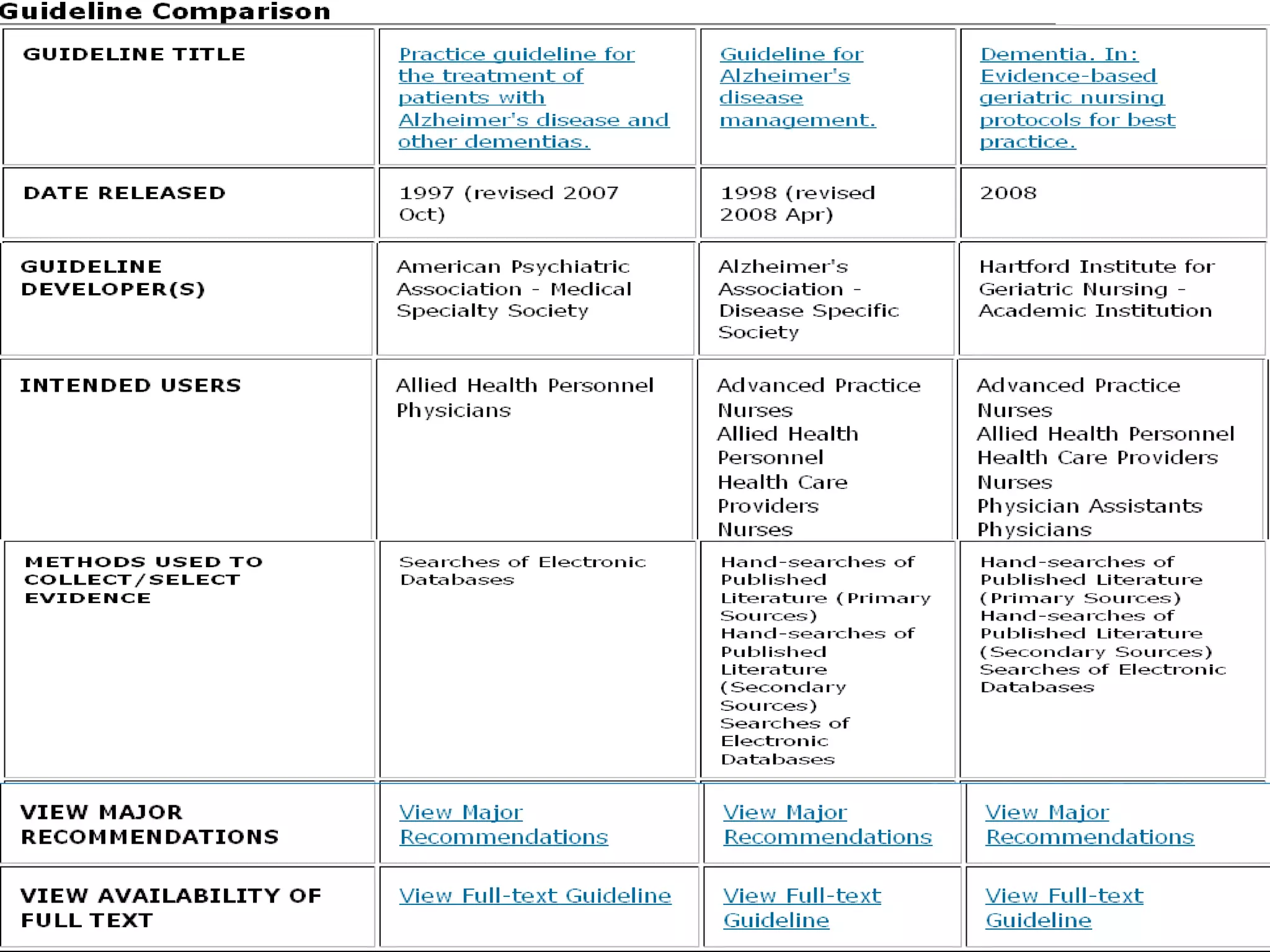
This document provides an overview of teaching evidence-based practice resources to nurses and nursing students. It defines evidence-based nursing practice and describes the importance of using evidence to improve patient care outcomes. Several strategies and resources for finding evidence on the web are highlighted, including searching databases like CINAHL and PubMed, as well as resources like DynaMed, Cochrane reviews, and clinical practice guidelines. Barriers to using evidence-based practice in nursing are also discussed.
![Janet G Schnall, MS, AHIP Library Liaison to the UW School of Nursing Health Sciences Libraries Affiliate Instructor, UW School of Nursing University of Washington, Seattle, WA [email_address] Teaching Evidence-Based Practice Resources to Nurses and Nursing Students](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rendezvousebn-100923141512-phpapp01/75/RML-Rendezvous-Evidence-Based-Nursing-1-2048.jpg)











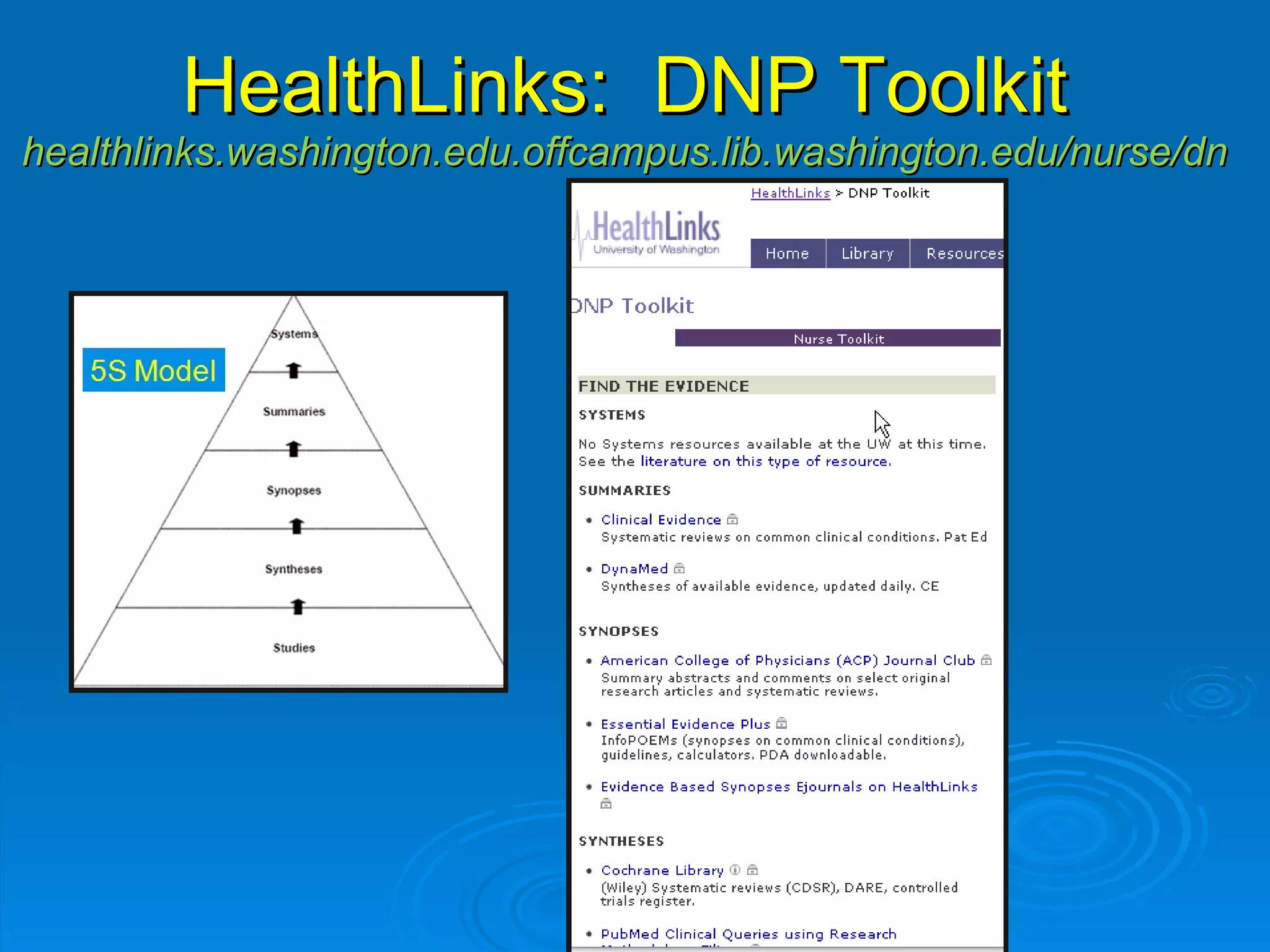
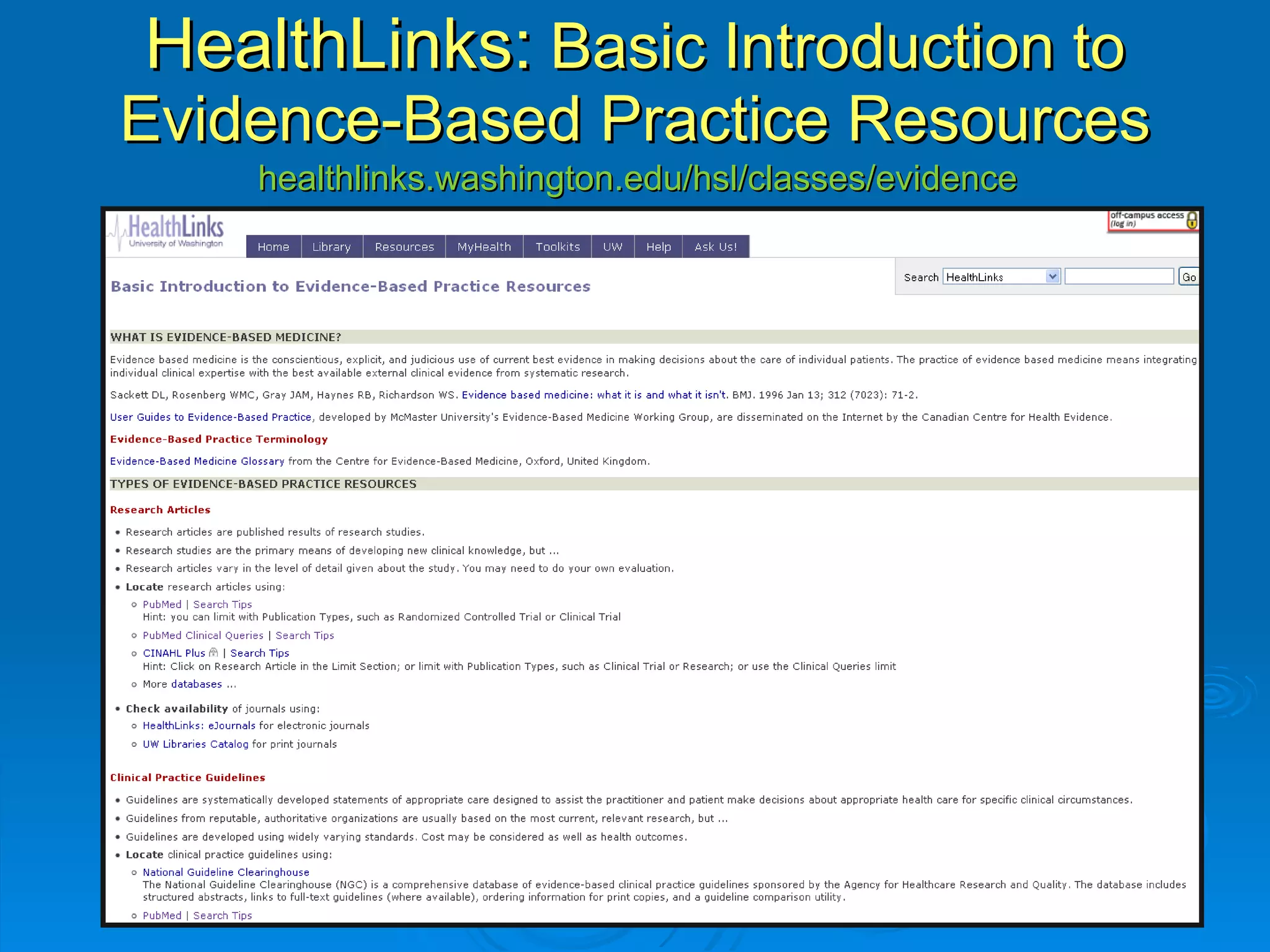
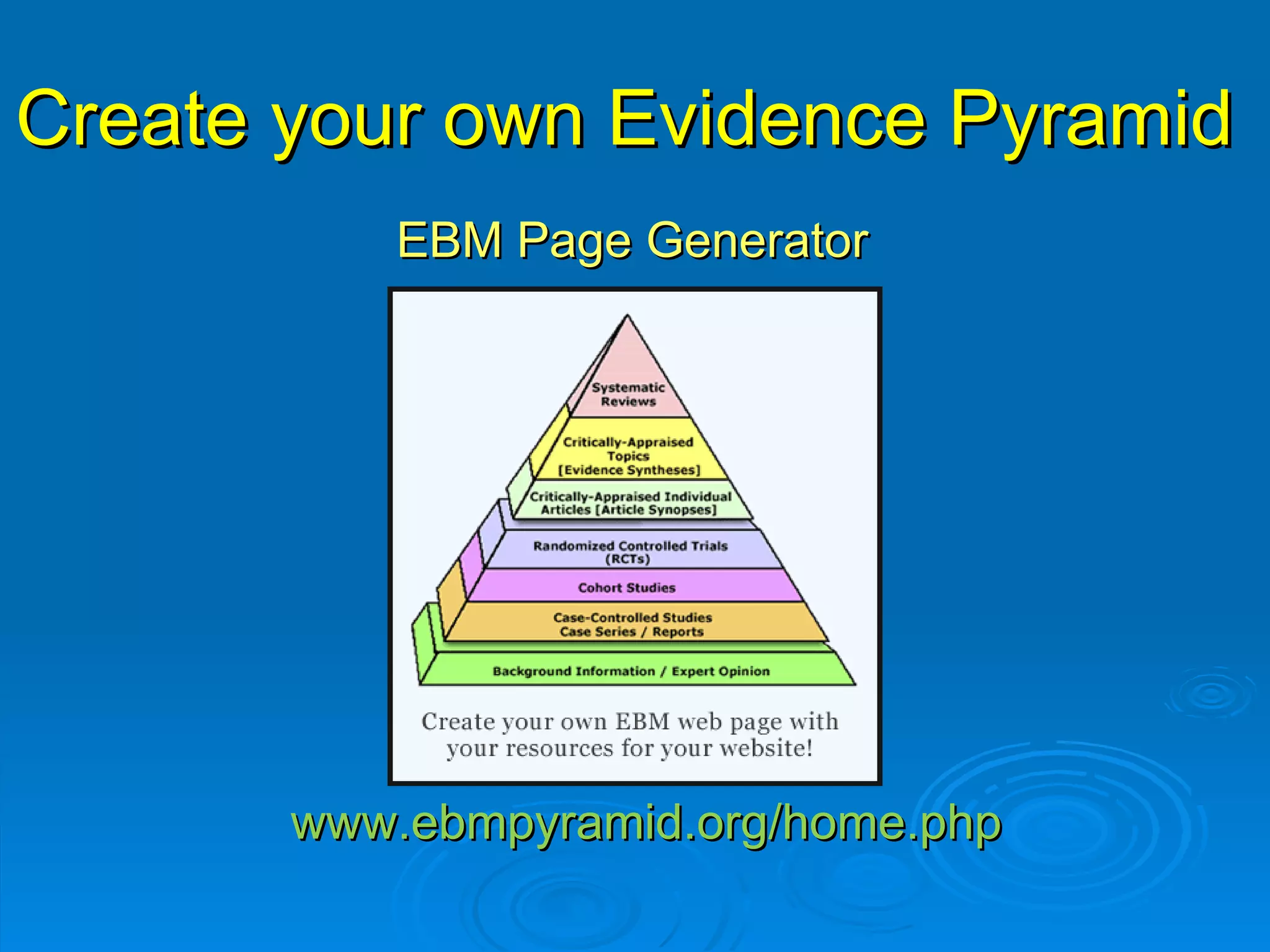
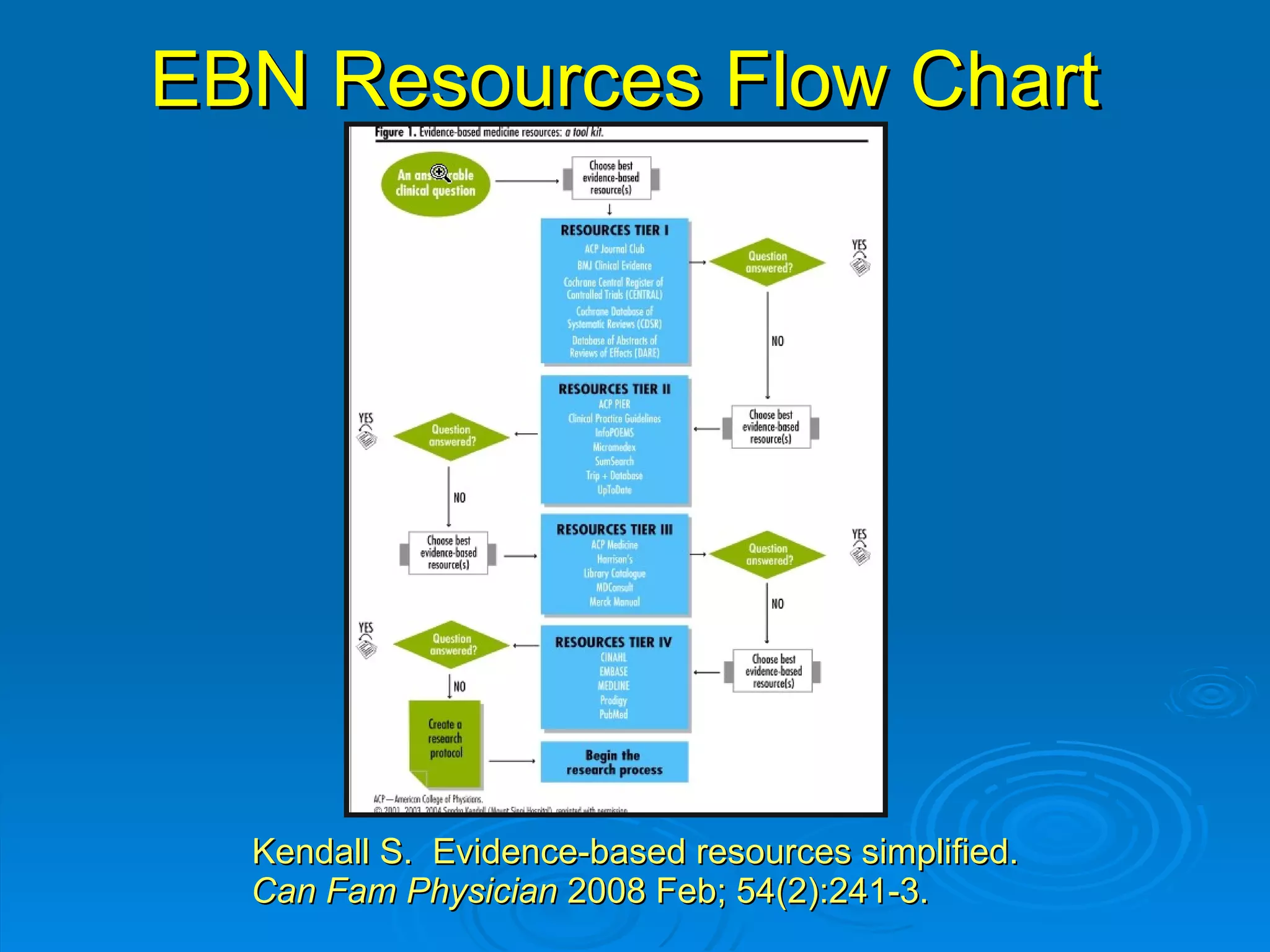


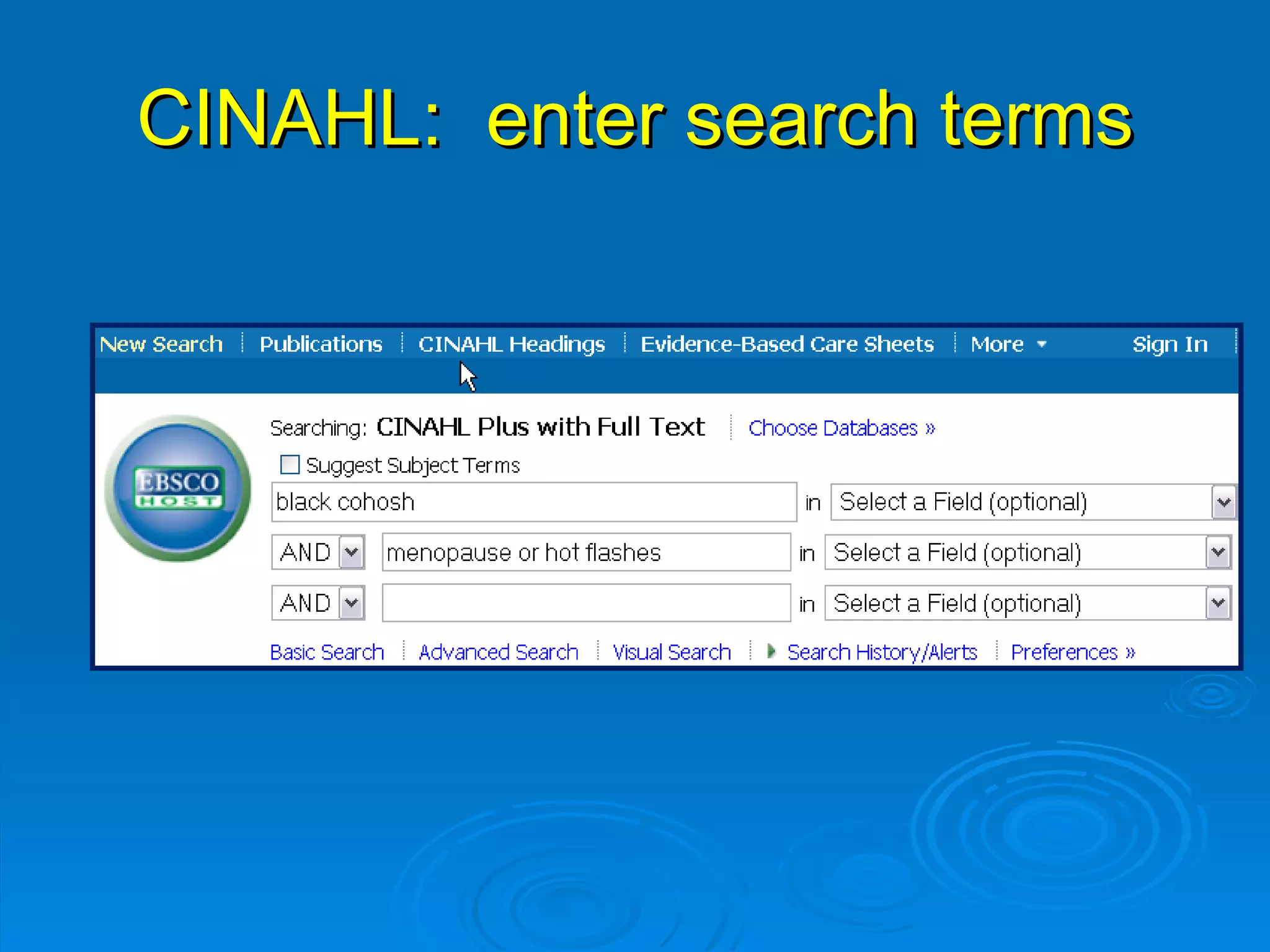
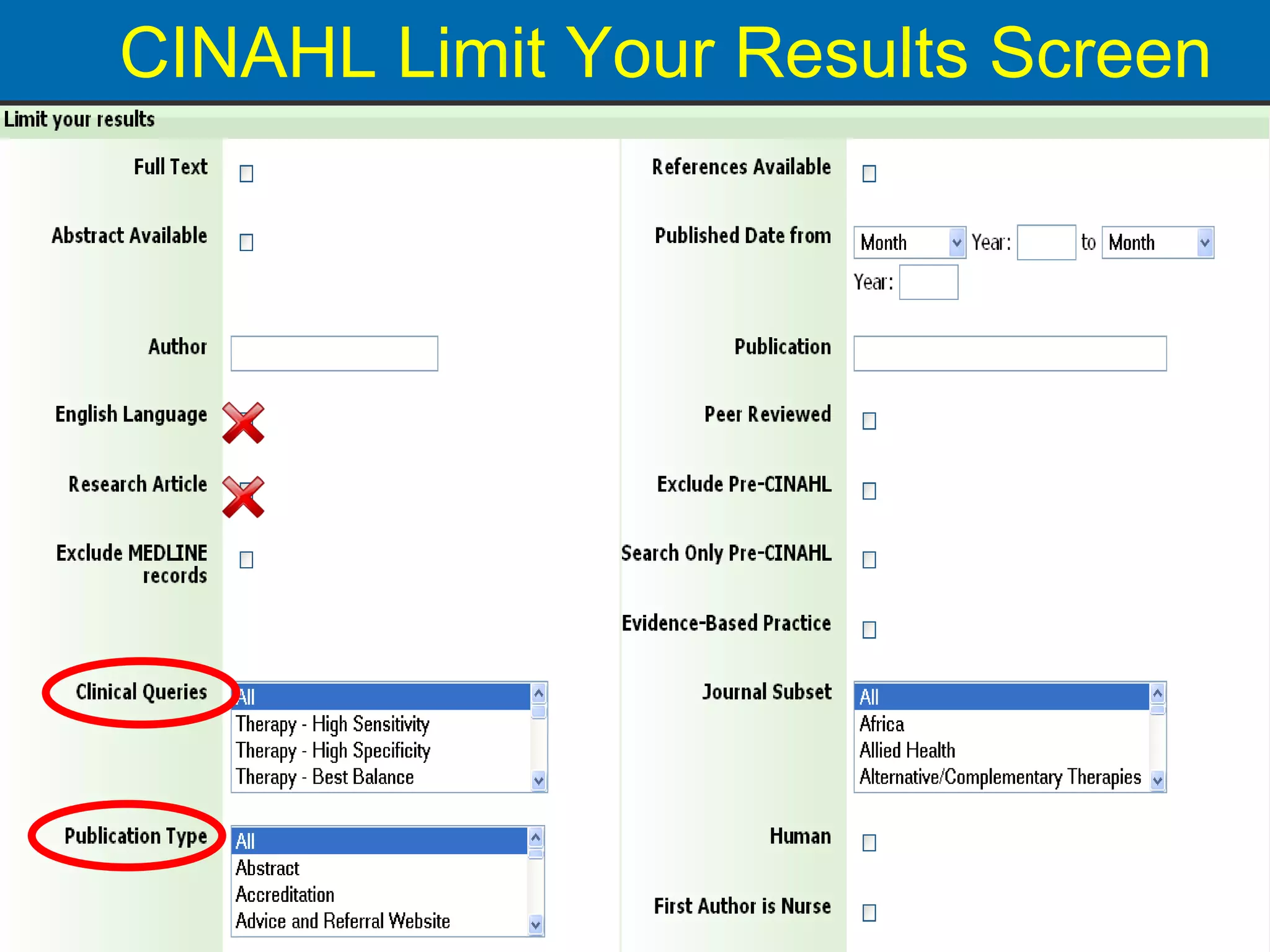
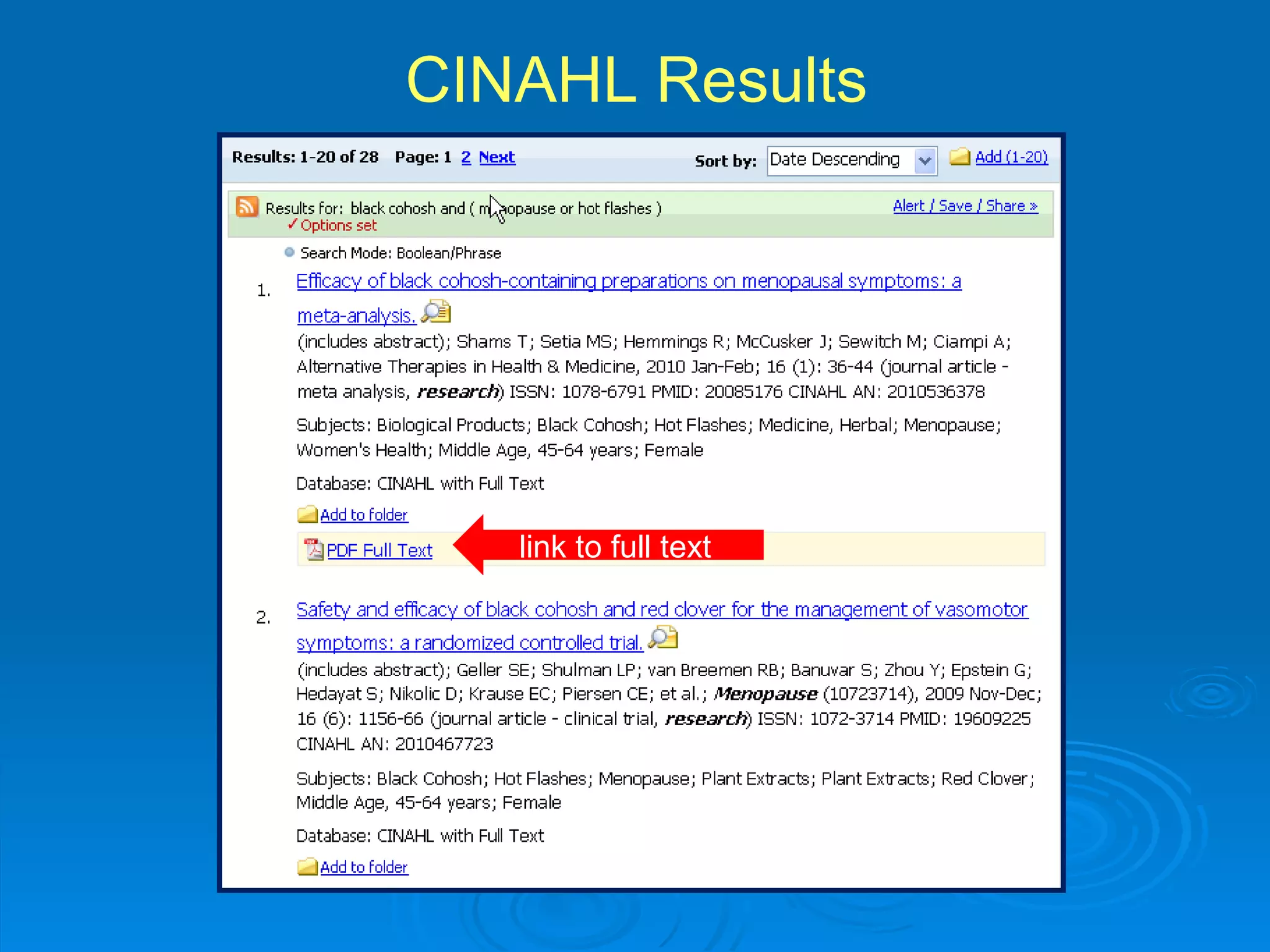
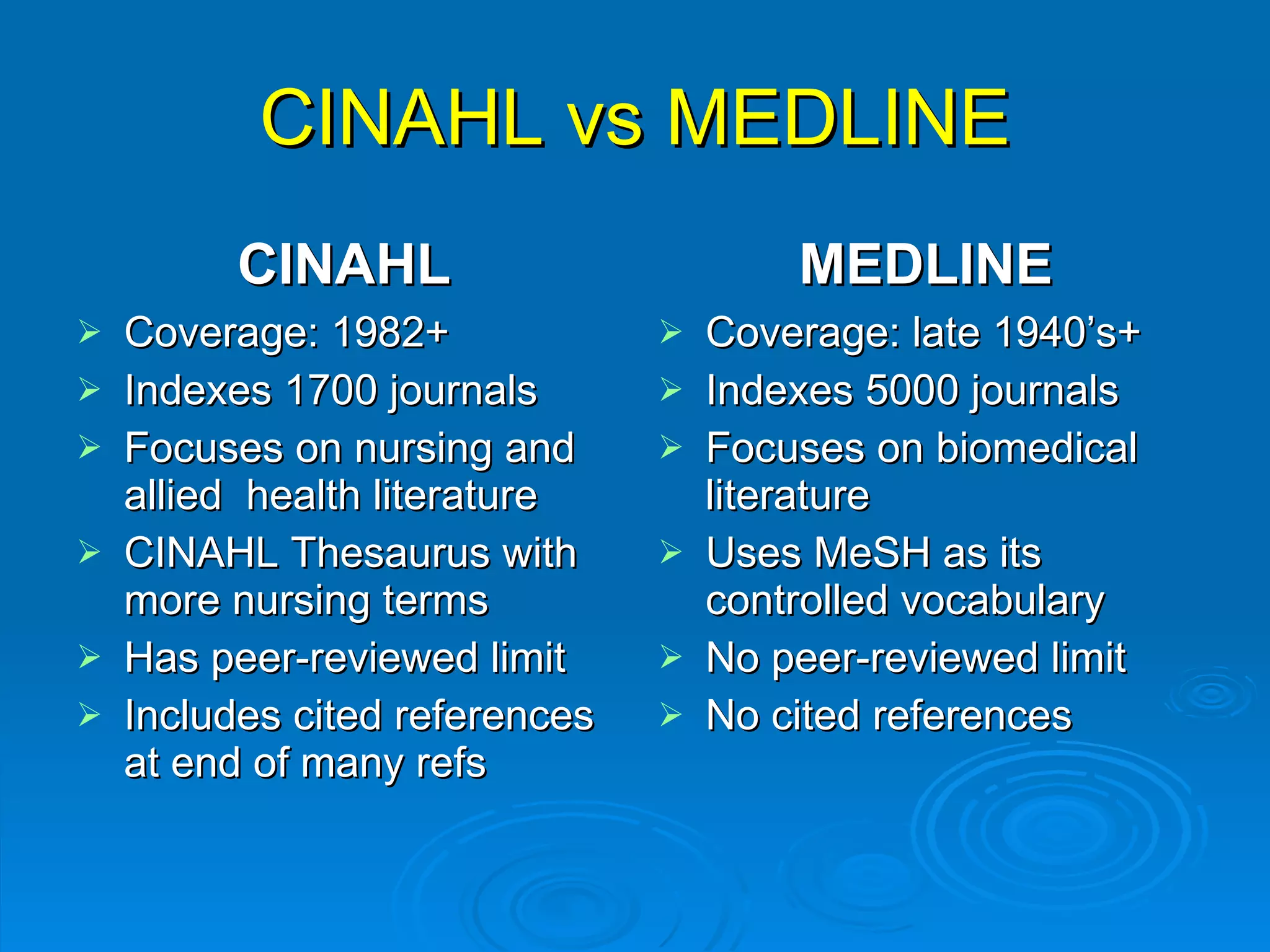
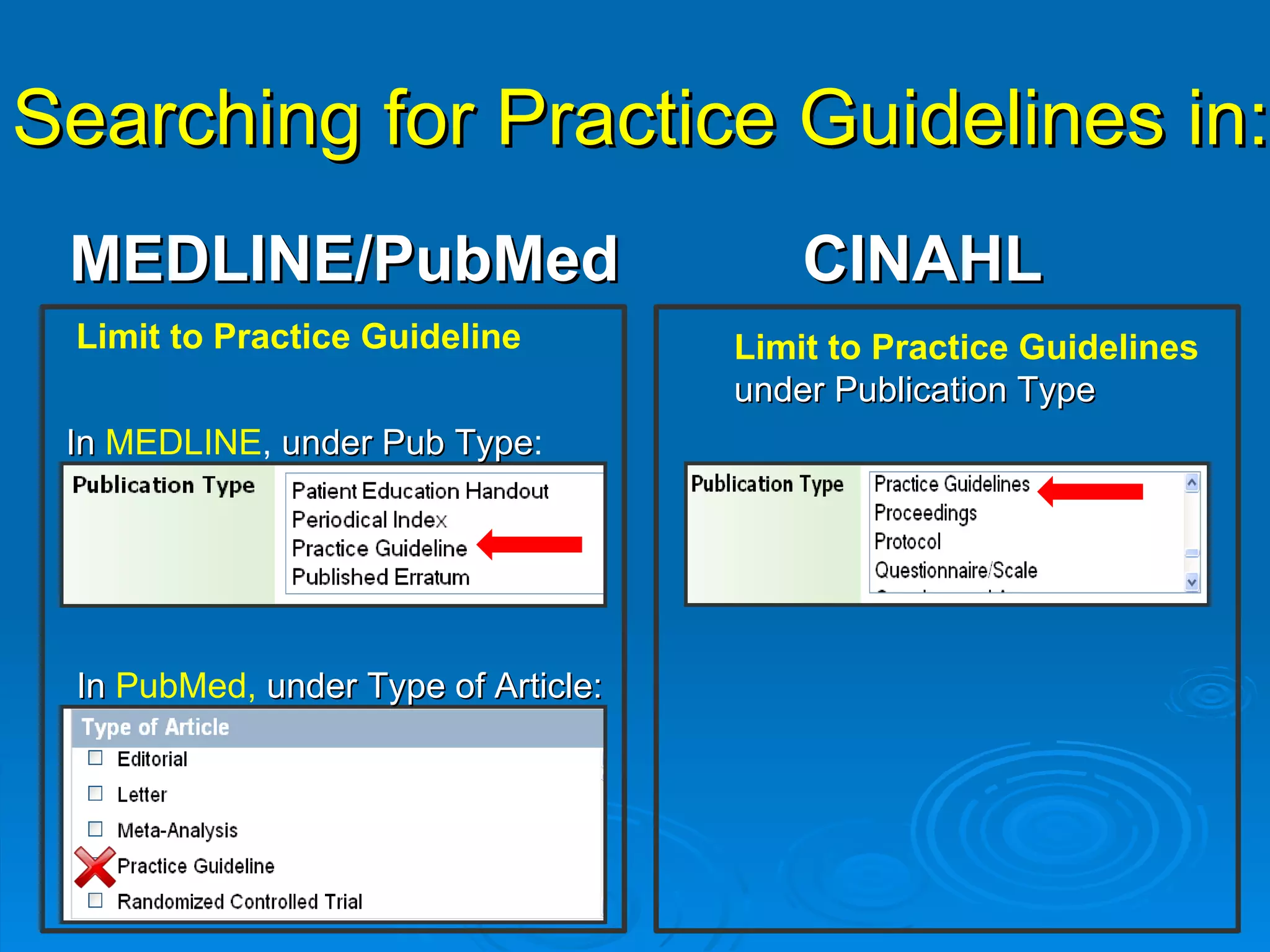
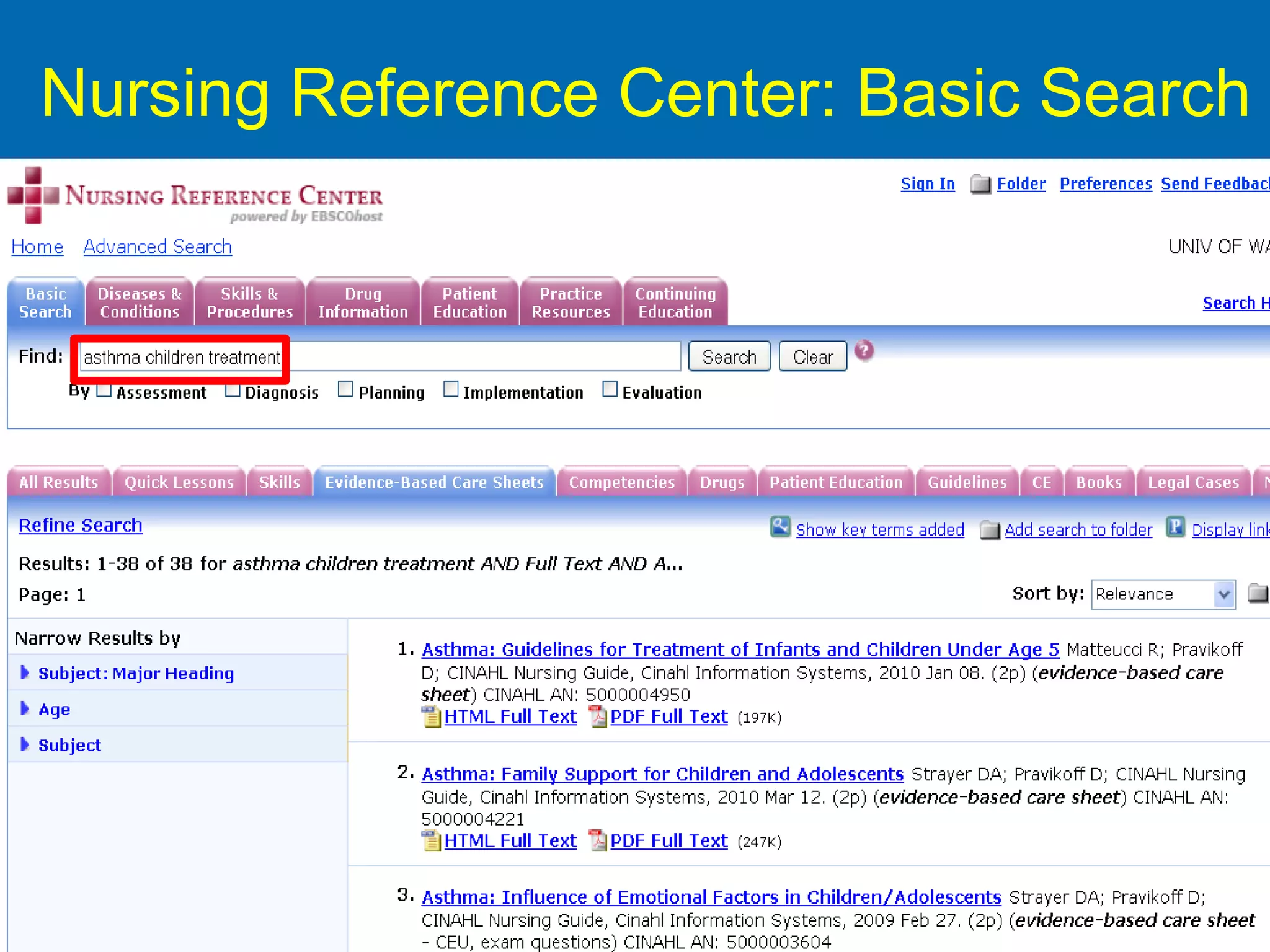
![CINAHL or [CINAHL Plus] cinahl.com Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature Provides coverage from 1982 [1937] to date, of nursing and 17 allied health disciplines literature 1700+ [3800+] journals indexed including virtually all English-language nursing journals Can easily search for Research articles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rendezvousebn-100923141512-phpapp01/75/RML-Rendezvous-Evidence-Based-Nursing-23-2048.jpg)























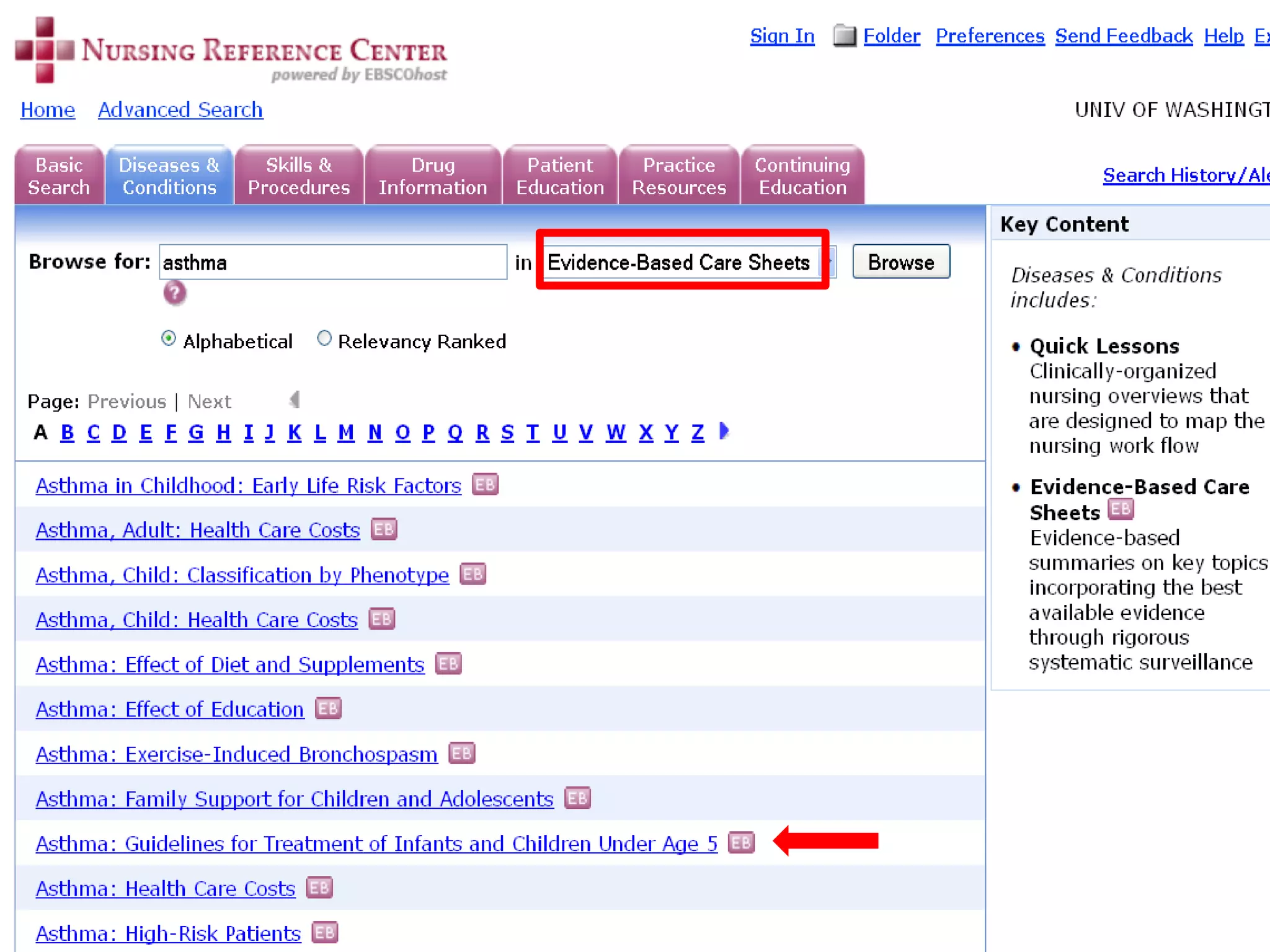
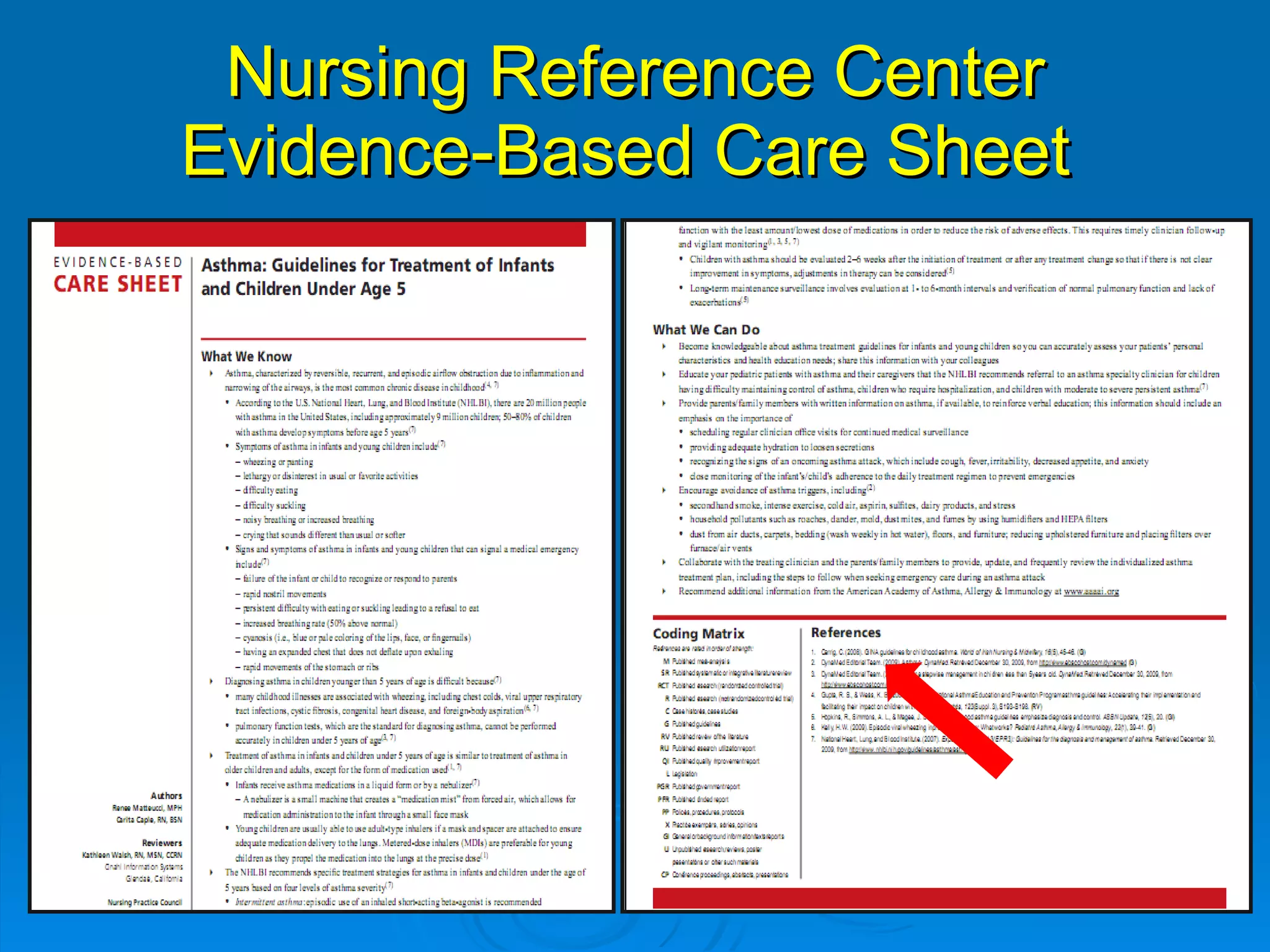



![Additional Point of Care Evidence-Based Resources for Nursing: [have some level of evidence-based information] Clini-eguide Nursing Advisor www.clineguide.com/nursing-standards-care-plan.aspx Lippincott’s Nursing Procedures & Skills www.healthstream.com/Lippincott/ Mosby’s Nursing Consult www.nursingconsult.com Mosby’s Nursing Skills mosbysnursingskills.com UptoDate uptodate.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rendezvousebn-100923141512-phpapp01/75/RML-Rendezvous-Evidence-Based-Nursing-68-2048.jpg)