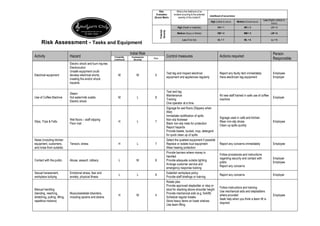
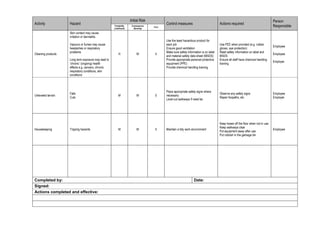
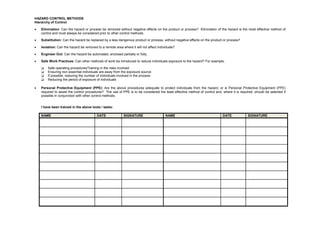
This document summarizes the risks and control measures for various tasks and equipment used at a café. It identifies hazards such as electrical equipment, use of coffee machines, slips and trips, noise, contact with customers, manual handling, cleaning products, uneven terrain, and general housekeeping. For each hazard, it rates the initial risk based on likelihood and severity of an incident occurring. It then lists control measures and actions required to minimize risks, and identifies the person responsible for implementing them. The overall goal is to eliminate hazards where possible, and implement engineering, administrative and personal protective equipment controls to reduce risks to acceptable levels.