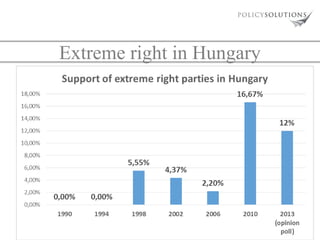
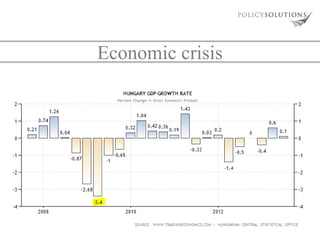
The document analyzes the rise of far-right extremism and populism in Hungary, as represented by the political party Jobbik. It identifies several key reasons for Jobbik's growth, including tensions between Roma and non-Roma populations, widespread disappointment in the political establishment, and an economic crisis since 2008 that increased poverty. The document also examines Jobbik's organizational strength, ideological stances, voter base, and influence on mainstream right-wing parties like Fidesz adopting some of its positions. It concludes by considering different strategies for countering the rise of extremism.