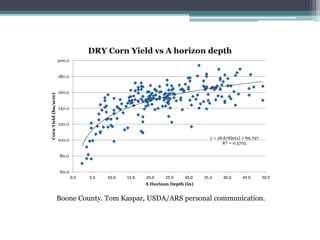
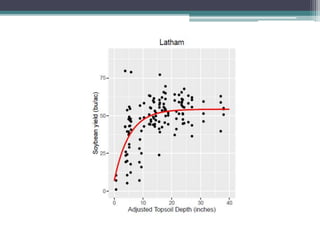
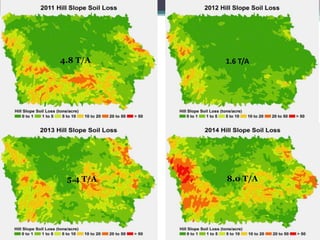
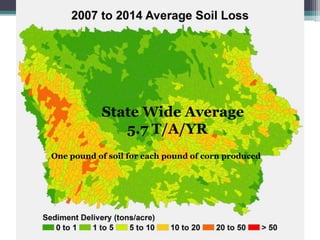
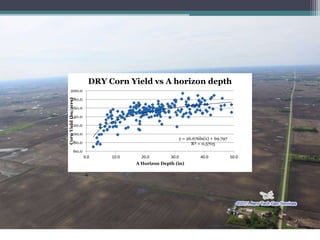
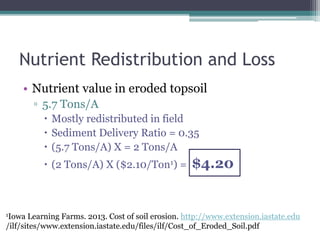
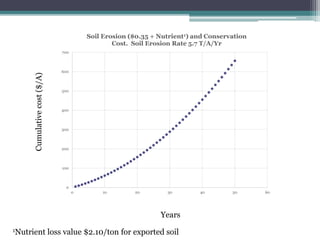
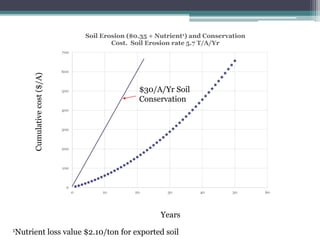
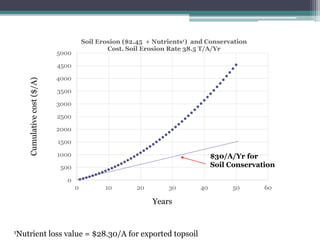
Soil erosion costs farmers money through lost productivity and nutrient loss, costing approximately $4.55 per acre annually. However, soil erosion also costs taxpayers and society through offsite impacts like water pollution, totaling around $25 per acre annually. Between 2005-2014, US taxpayers spent over $3 billion in Iowa alone to subsidize more sustainable farming practices at a rate of around $12.50 per acre annually. Unless erosion rates are high and a farmer owns land for a long time, soil conservation remains more expensive than soil erosion for individual farmers. Overall erosion costs to taxpayers and society exceed costs to individual farmers.