Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times
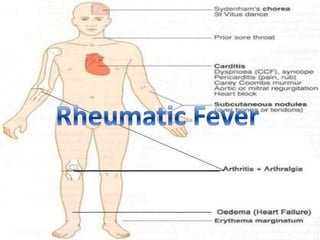
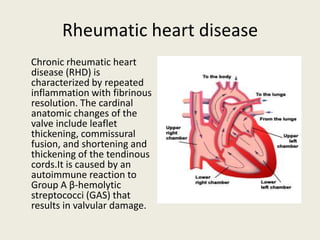

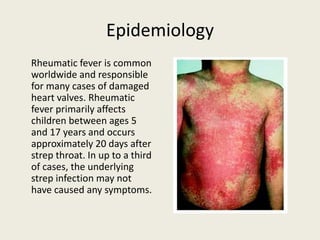

Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease following a streptococcus pyogenes infection, involving potential damage to the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Chronic rheumatic heart disease results from autoimmune reactions leading to valve damage, with specific treatment focused on anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics. This condition mainly affects children aged 5 to 17 and can occur even if the initial streptococcal infection was asymptomatic.




