Embed presentation
Download to read offline
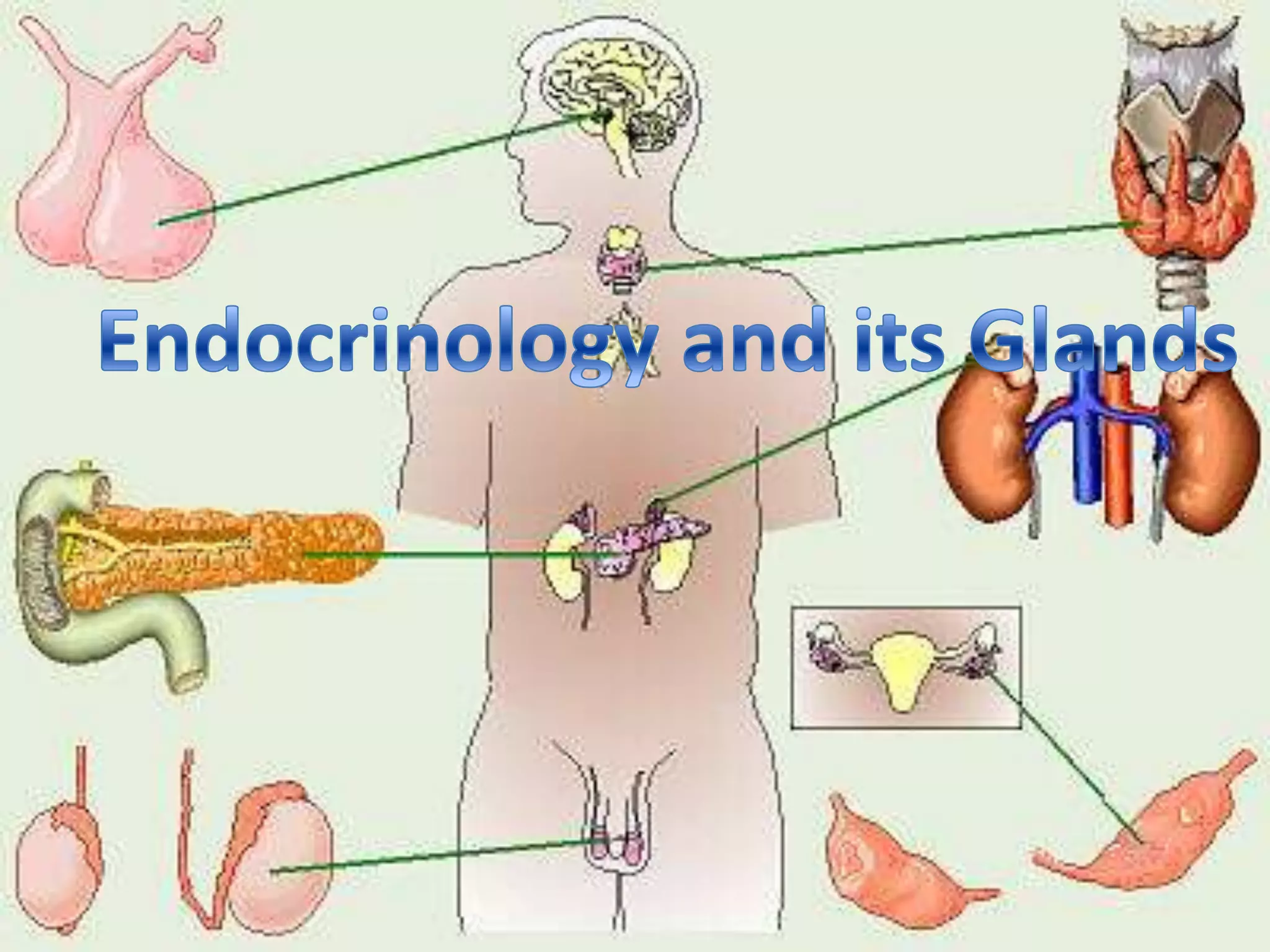
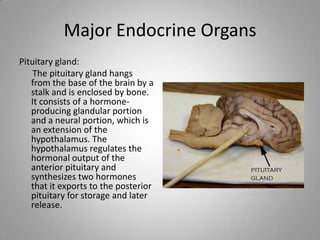
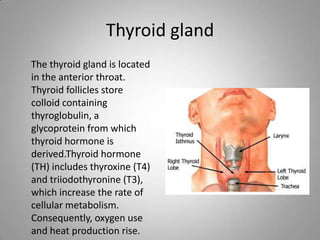
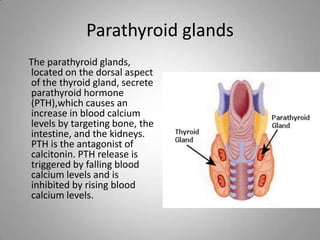
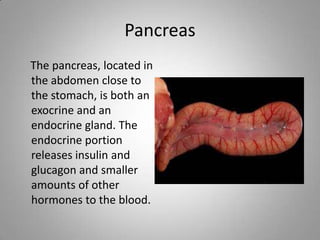

The document outlines key endocrine organs, highlighting the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and pancreas. The pituitary gland, controlled by the hypothalamus, regulates hormones, while the thyroid controls metabolism through thyroxine and triiodothyronine. The parathyroid glands manage calcium levels, and the pancreas regulates blood sugar through insulin and glucagon.




