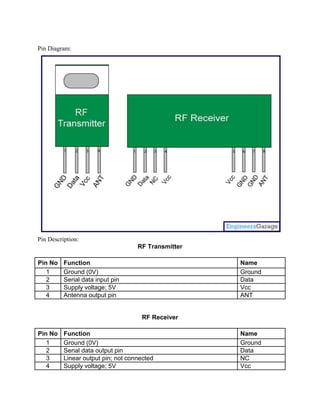
The document discusses an RFID reader module and its interface with a microcontroller. It explains that the RFID reader module uses MAX232 voltage converters to interface with the microcontroller as it operates at a different voltage level. Alternatively, the RFID reader can interface directly with the microcontroller by eliminating the MAX232 converters. It also provides the pin diagrams and explanations of the RFID reader module and an RF transmitter/receiver module.