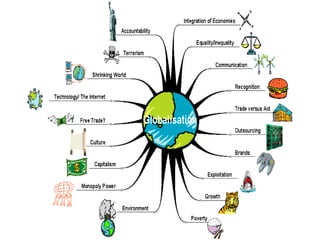
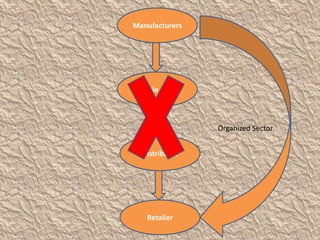
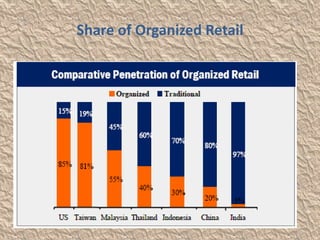
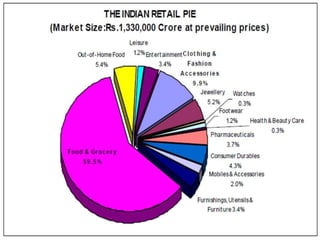
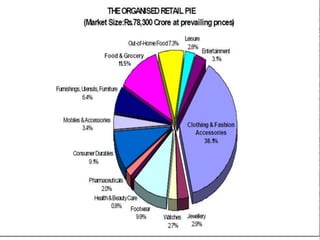
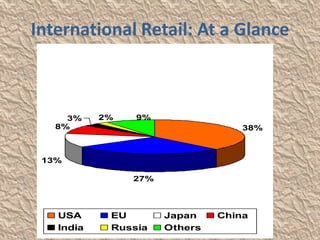
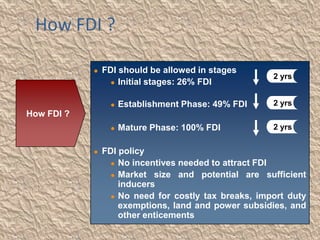
The document discusses globalization and its impact on the retail sector in India. It outlines the benefits and disadvantages of globalization. It then provides details on the organized and unorganized retail sectors in India, including the different types of retail stores. It also examines government policies around foreign direct investment and a SWOT analysis of the Indian retail industry.