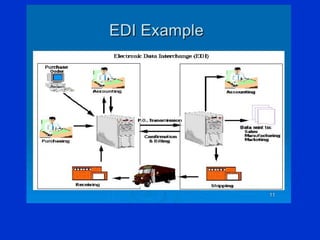
This document provides an overview of retailing and retail management. It discusses key topics such as the definition of retailing, characteristics of retailers, functions of retailers, factors influencing retail management, scope of retail management, retail formats (organized vs unorganized), multichannel retailing, e-tailing, applications of IT in retail like EDI, barcoding, RFID, EAS, ESL. It also covers foreign direct investment in retail, franchising, green retailing initiatives, and advantages of airport retailing.