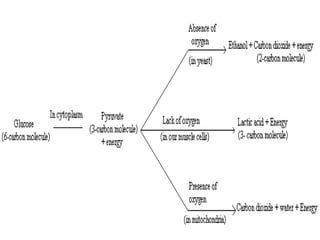
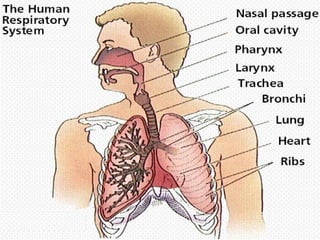
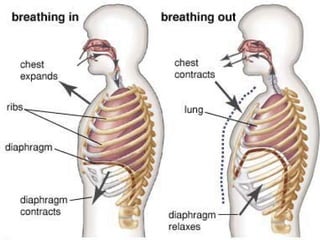
Respiration is the process by which organisms convert food into energy, using oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide and water. It occurs via two types of respiration - aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, producing more energy. Anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen, producing less energy and generating lactic acid or ethanol. In humans, respiration involves the respiratory system - nostrils, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and lungs - which work with the diaphragm and rib cage to inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide through breathing.