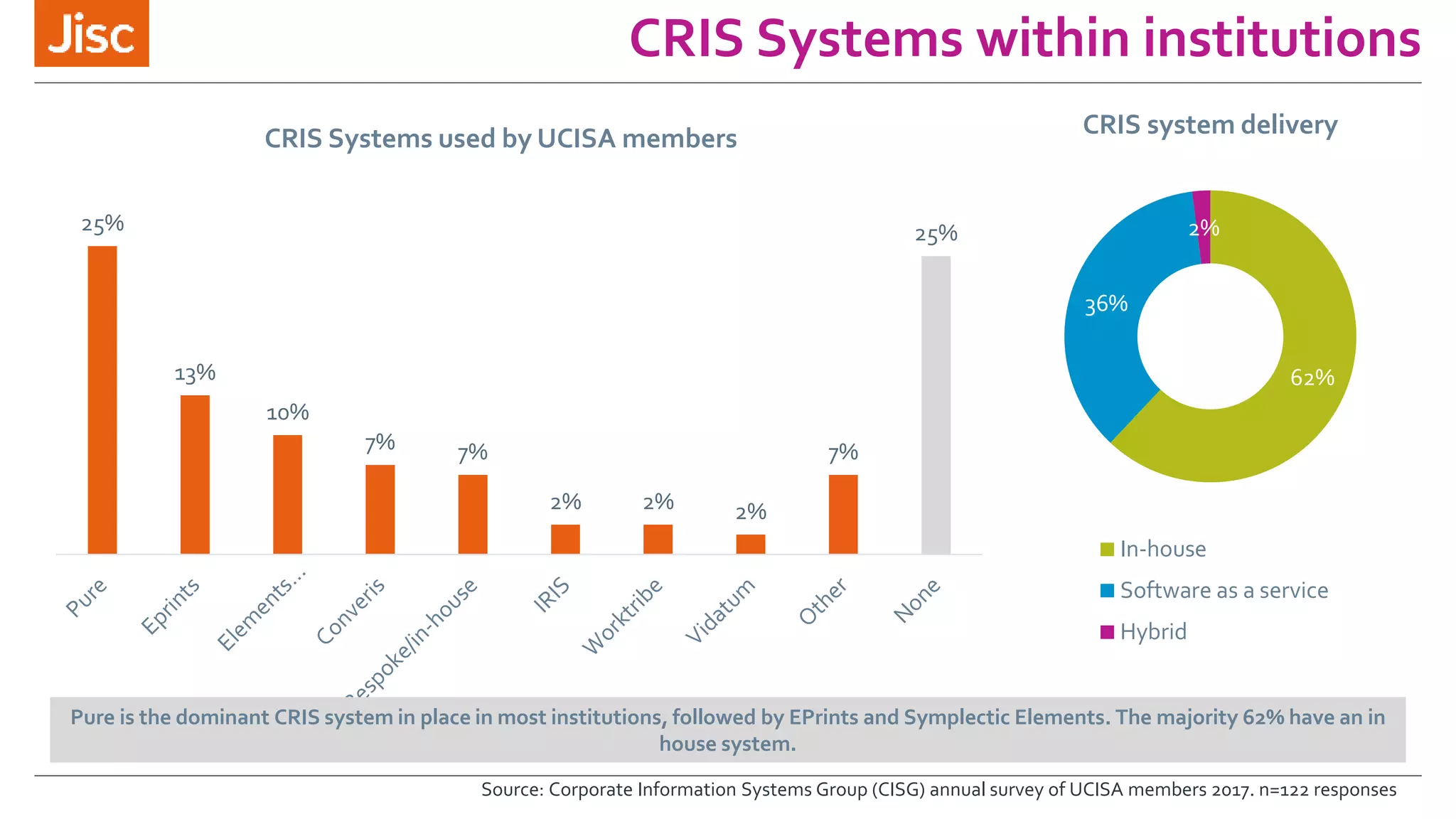
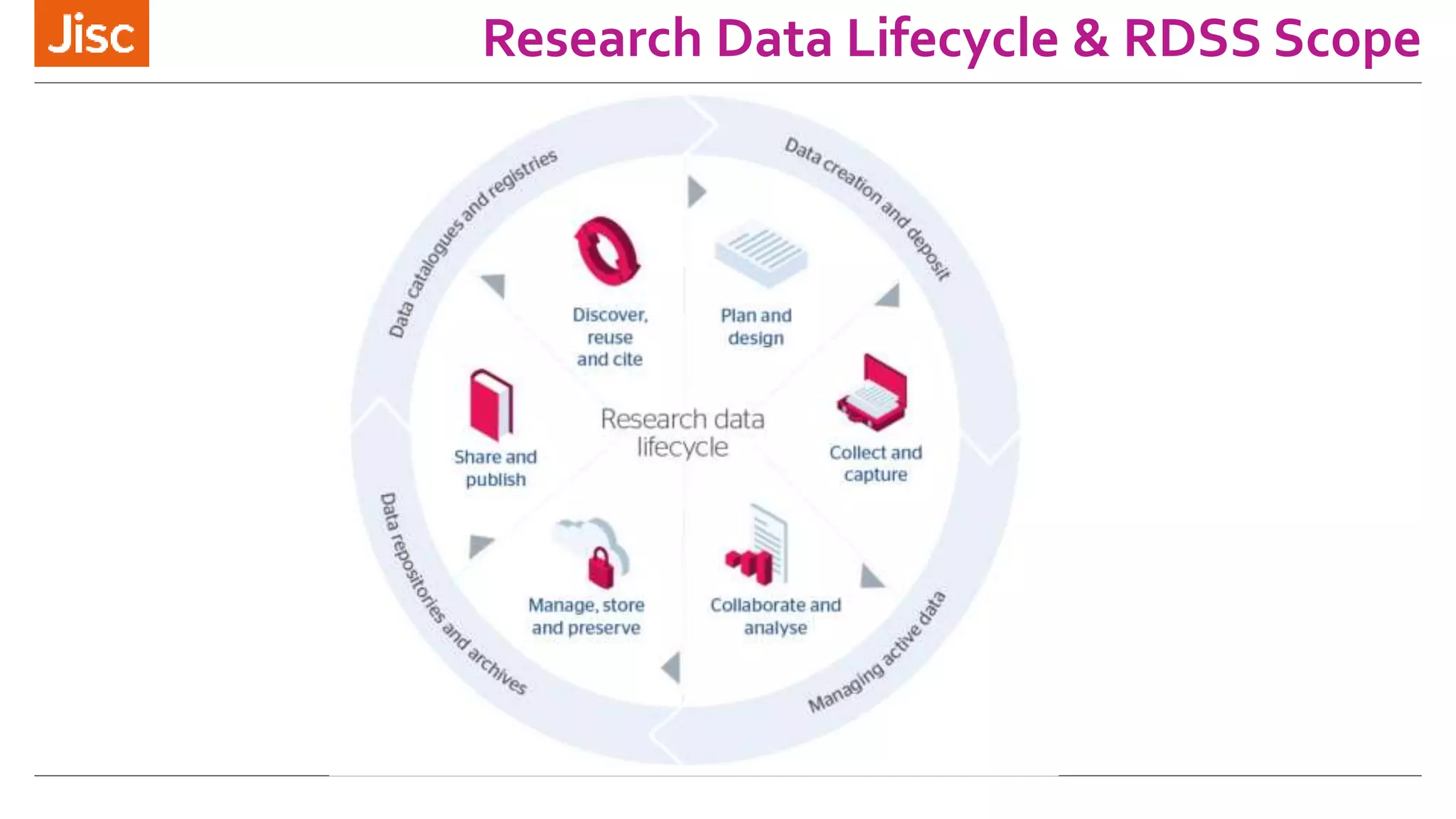
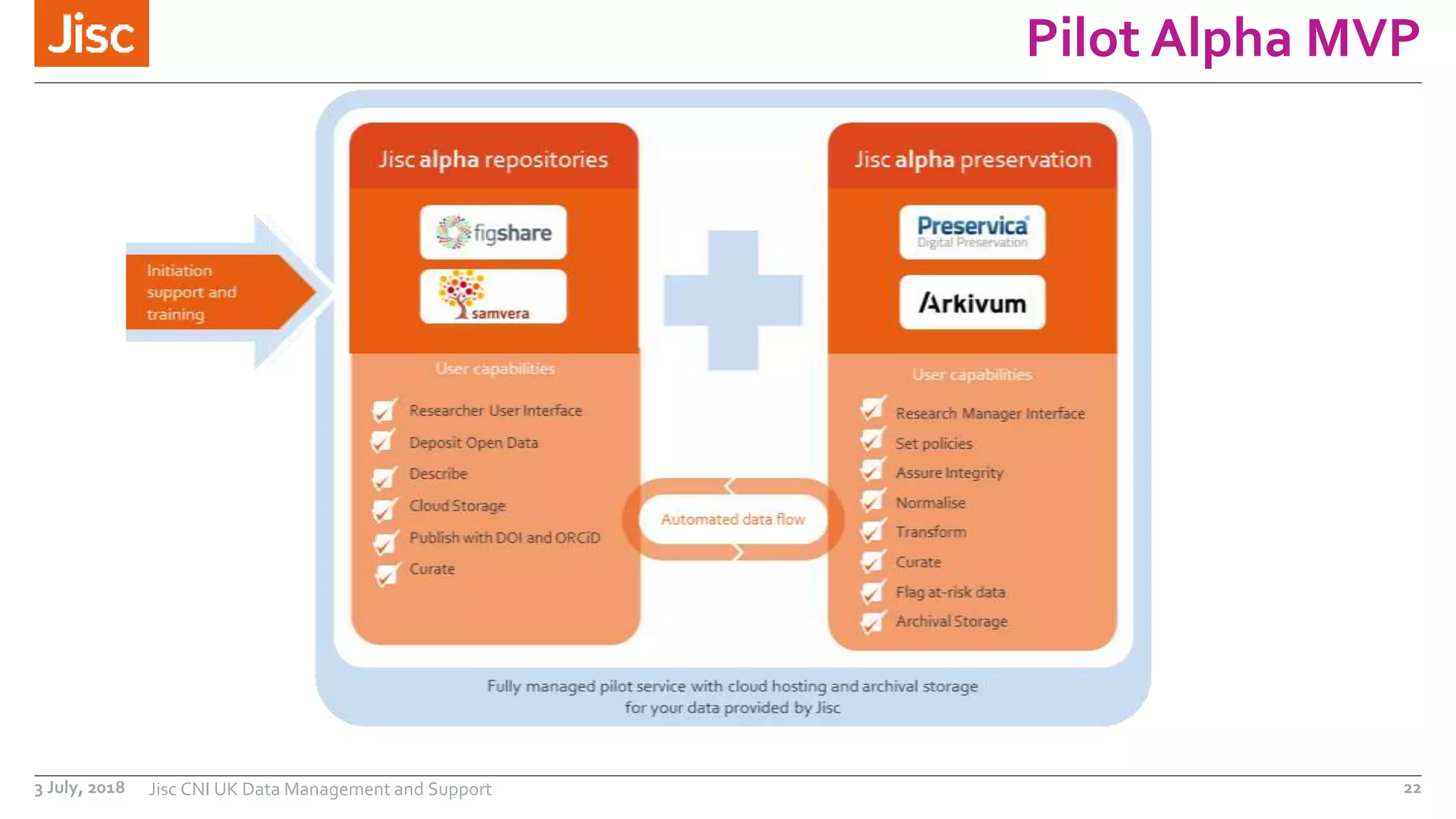
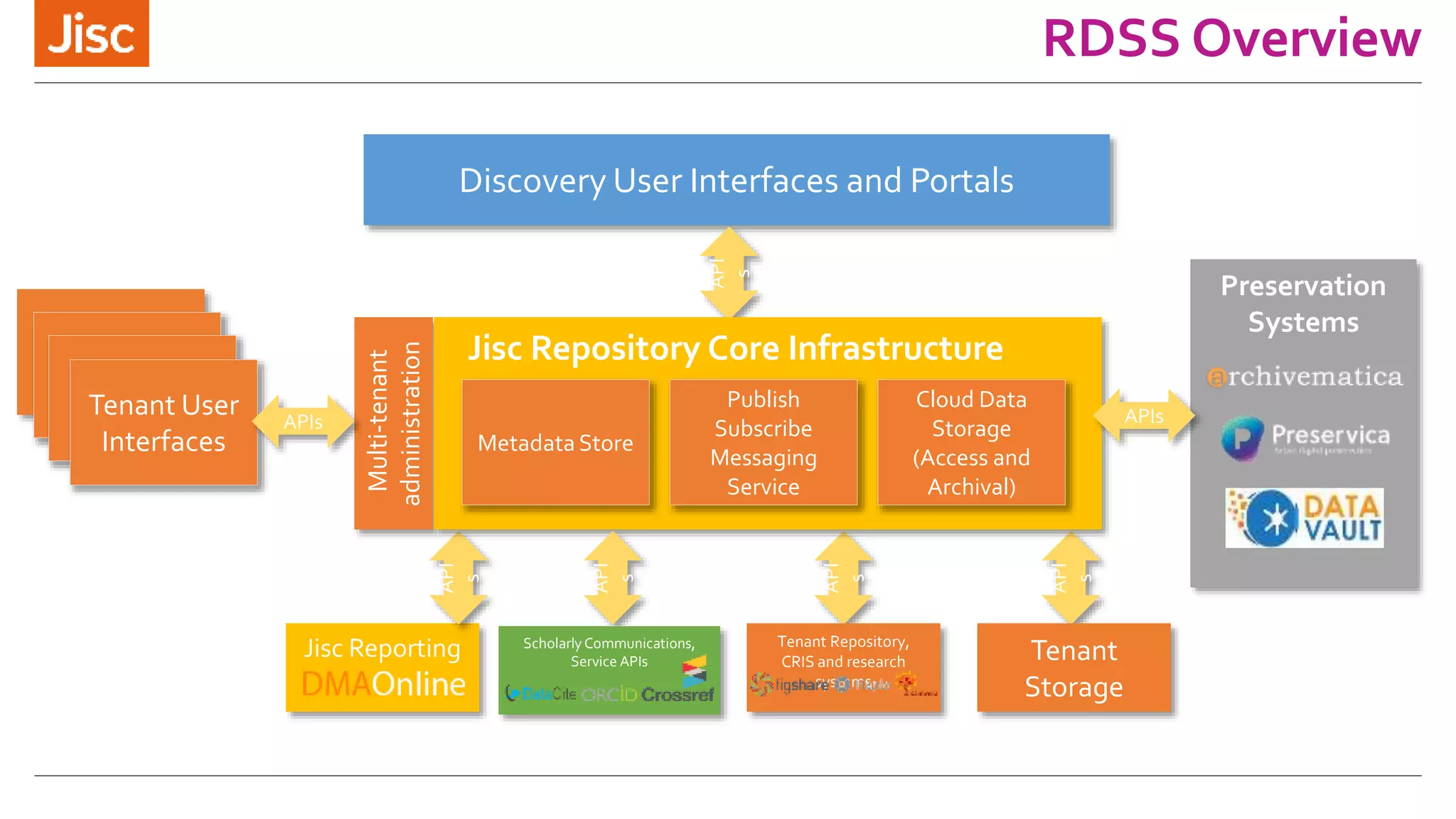
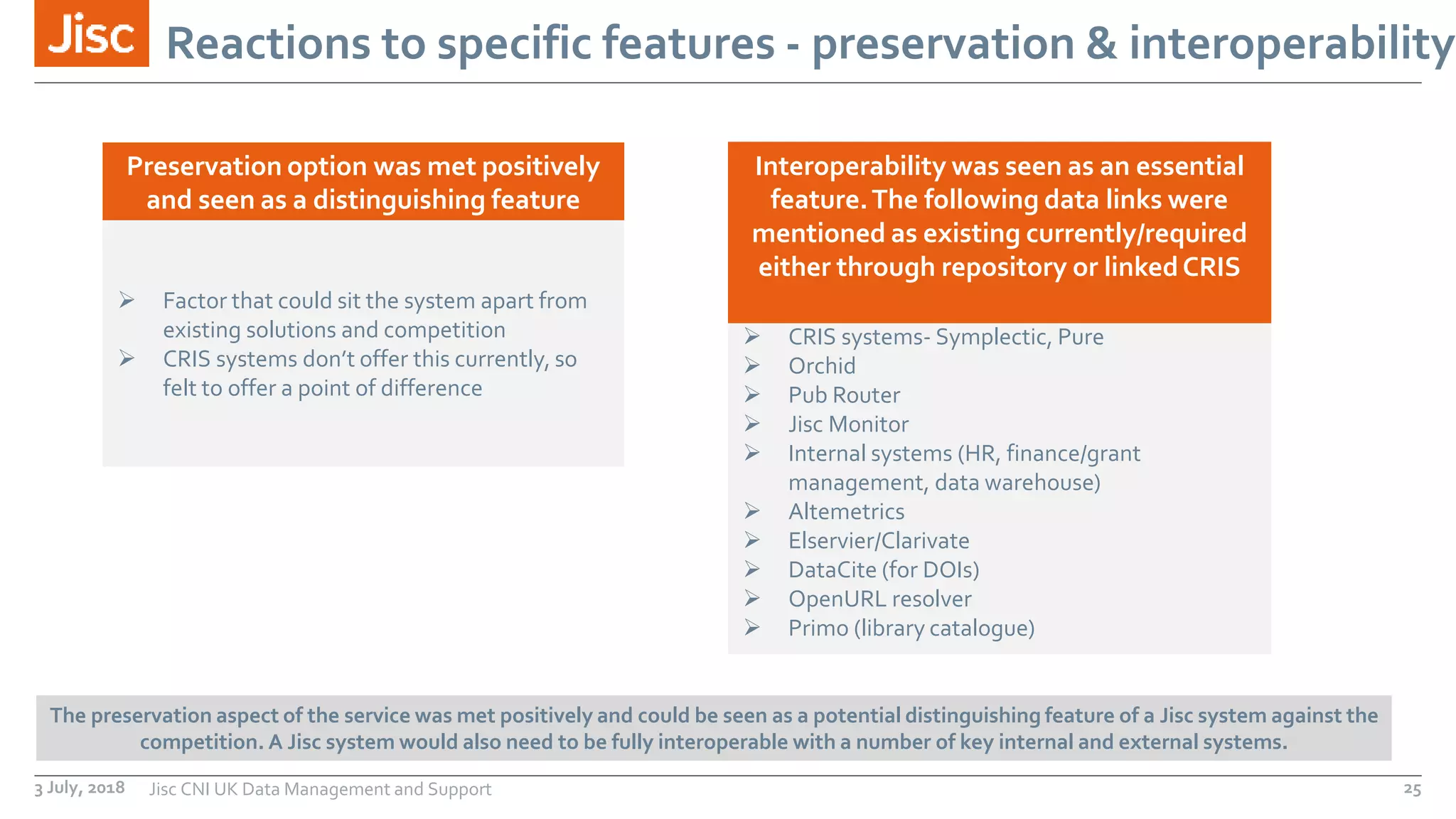
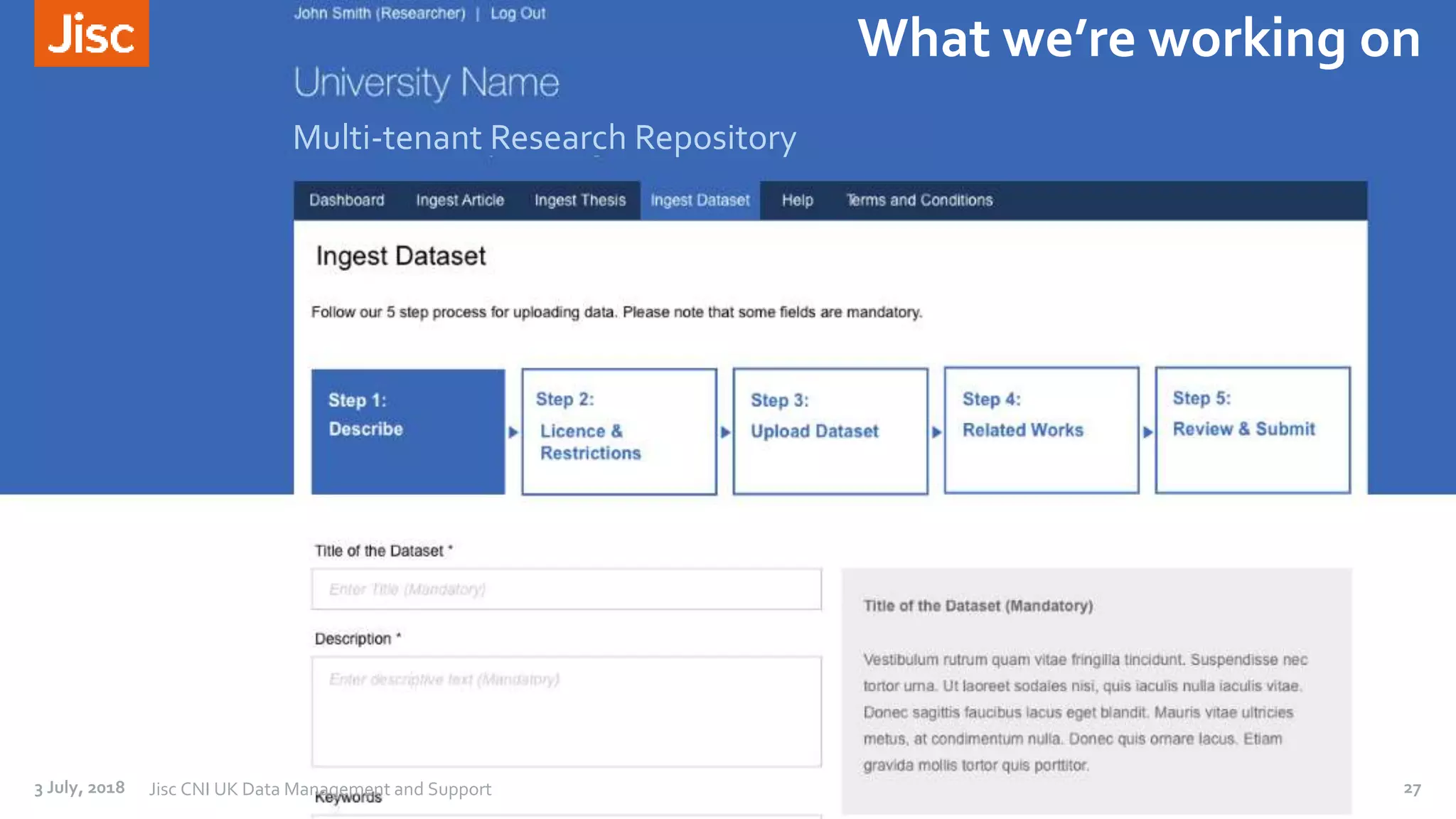
The document discusses a leaders conference on UK data management environments and support. It provides information on the current UK research data management policy environment, systems used, and challenges. It introduces Jisc's proposed Research Data Shared Service as a sector-wide approach to address these issues by providing a single, integrated solution for research data management across the UK. Key benefits identified include optimizing costs, growing the value of research data, and increasing compliance with funder requirements for data preservation and sharing. The development history and features of the proposed shared service are outlined.