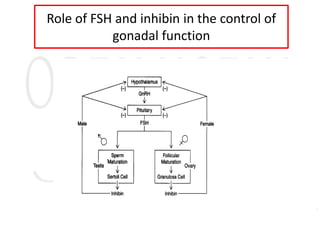
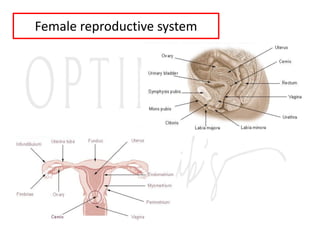
1. The document describes the reproductive systems of males and females including the testes, ovaries, hormones involved, and menstrual cycle.
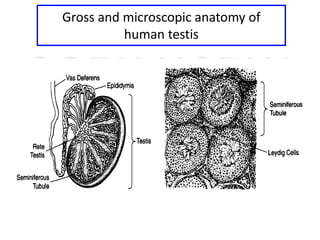
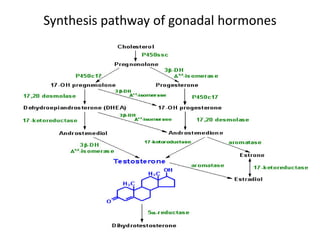
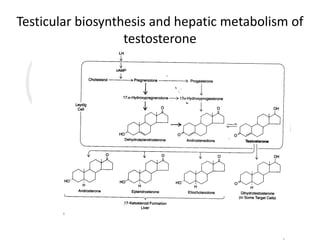
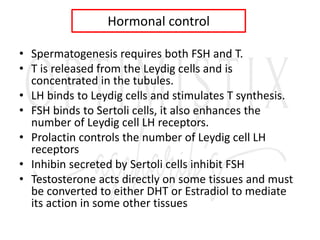
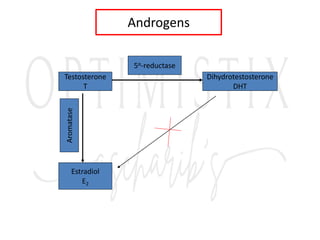
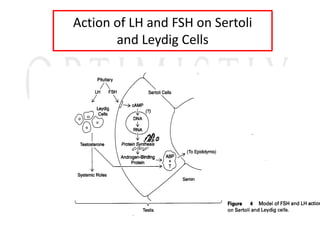
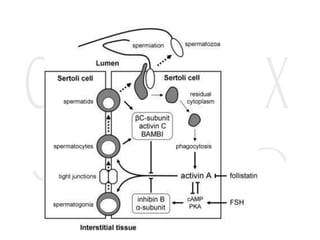
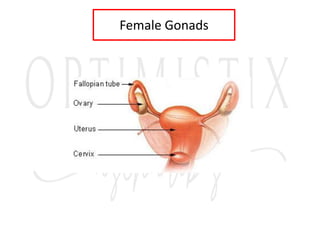
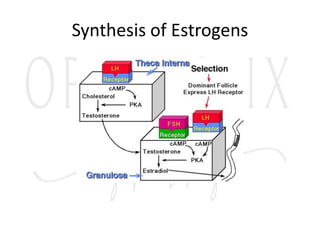
2. The testes produce sperm and testosterone while the ovaries produce eggs and estrogens and progesterone.
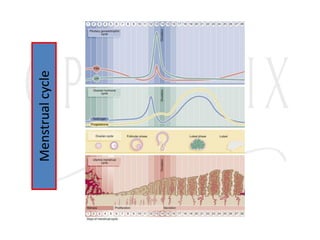
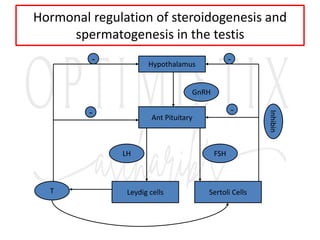
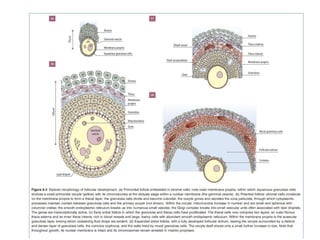
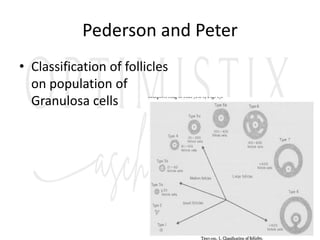
3. The menstrual cycle is regulated by hormones including FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone and consists of the follicular, ovulation, luteal, and menstrual phases.



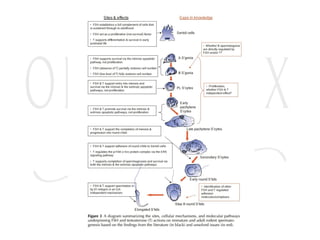

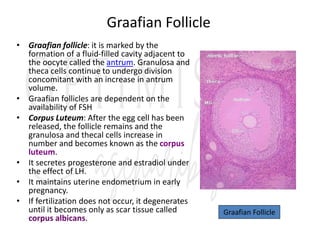
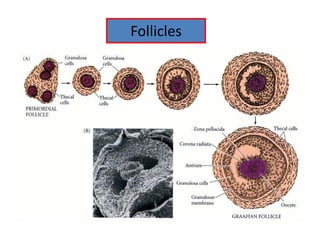

![Menstrual Cycle
• The control circuit of the hormonal cycle has two
essential control elements:
• The pulsatile liberation of GnRH, as well as FSH and
LH
• The long-loop feedback-effect of estrogen and
progesterone on the hypothalamic-hypophysial-
system (these two hormones are synthesized in the
[ready to rupture] follicle and so originate in the
ovary, thus the name "long loop").](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reproductiveendocrin-platform-240107121606-ee0e4e65/85/Reproductive-endocrin-Reproductive-physiology-24-320.jpg)